(Press-News.org) Many neurological conditions that involve involuntary muscle contractions have long been considered as diseases of the brain. However, both the brain and the spinal cord contain many nerve cells associated with movement.
The research, published in Science Translational Medicine, used state-of-the-art mouse genetics to distinguish whether the brain or spinal cord was responsible for the disorganisation of movement experienced by dystonia patients.
Focusing on the most common inherited form of dystonia called DYT1, UCL scientists confined a genetic mutation to the spinal cord of the mice, while sparing nerve cells in the brain. They discovered that the mice consequently developed signs of dystonia that were remarkably similar to those seen in people with the condition.
The researchers also observed how specific nerve cells in the spinal cord were affected through the course of the disease.
The team hope that their findings will help towards the development of new treatments.
Corresponding author, Professor Rob Brownstone (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology), said: “We take our ability to move for granted. However, some conditions – such as dystonia – can affect both movement and quality of life.
“Until now, research on how neurological diseases impact nerve cells in the spinal cord has been scant. But it is crucial to understand the origins of disease in order to be able to treat them correctly.
“We hope that our findings will provide a key first step towards the development of new treatments for dystonia.”
Dystonia is a potentially disabling condition that can impact both physical and emotional wellbeing. It can affect various parts of the body, including the vocal cords, neck muscles and fingers and is considered the third most common movement disorder behind essential tremor and Parkinson’s disease, affecting at least 100,000 people in the UK alone.
While the exact incidence rate remains unknown as many cases go undiagnosed, DYT1 dystonia is estimated to affect about 25 in 100,000 people.
Lead author, Dr Amanda Pocratsky (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology) said: “There is no cure for dystonia, and progress towards finding one has been prevented by a lack of preclinical models that develop the movement disorder. By focusing on the nervous system’s final common pathway for producing movement – spinal motor circuits – we have developed a preclinical model that imitates the human condition. From this work, we have a newfound entry point into investigating the complex changes in the body that cause the disease and a potential target for developing new therapeutic interventions.
“Spinal circuit dysfunction is rarely considered in movement disorder research, but the symptoms of these conditions are largely produced by neurons resident within the spinal cord. To this end, while DYT1 dystonia is a relatively rare condition, our findings could also be important not only for the dystonia community but for forming new treatment strategies for other neurological disorders that similarly affect the movement of limbs.”
This research was directly supported by Wellcome, the Medical Research Council, and the European Molecular Biology Organisation.
END
Movement symptoms in dystonia are caused by spinal cord dysfunction
Peer reviewed | Experimental study | Animals
2023-06-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Why are dog breeds with innate diseases popular?
2023-06-06
Flat-faced dogs, such as French and English Bulldogs, are extremely popular despite suffering from severe innate diseases. Hungarian researchers have attempted to uncover the explanation for this paradox. In the end, they concluded that although enthusiasts of flat-faced dogs are aware of the health issues and strive to provide the best for their dogs, they are likely to normalize health problems.
The French and English Bulldogs are among the most popular breeds in both the United States and Europe, but Pugs ...
Nursing home dementia residents’ care linked to majority presence, UC Irvine-led study finds
2023-06-06
Irvine, Calif., June 6, 2023 — The quality of care for nursing home residents with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias is best when they are in the majority, but most facilities also accommodate a heterogeneous population, where specialized staff training is limited, according to a study led by the University of California, Irvine.
“Recognizing and managing the complex medical conditions and behavioral symptoms of residents with ADRD require enhanced knowledge among staff. These findings raise significant concerns regarding the level of care and quality of life for the majority of these people, highlighting ...
SRF operations earns certification to ensure customer satisfaction
2023-06-06
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – An important certificate now hangs on the wall of the Superconducting Radiofrequency Operations group at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility.
SRF Operations builds cryomodules and other particle accelerator parts for the lab’s very own Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility (CEBAF), a DOE Office of Science user facility. The group also supports user facilities at other DOE labs, including SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Oak Ridge National Laboratory. This piece of paper represents the department’s dedication to supplying ...
Two new studies identify promising pathways to treat chronic COVID-19
2023-06-06
Philadelphia, June 6, 2023 – Early studies of COVID-19 focused on the acute phase of the disease. However, attention has now turned to the long-term consequences of the disease, which are also significant causes of morbidity and mortality. Two studies reported in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, seek to understand the drivers of the chronic and sometimes progressive phase of the disease and identify possible pathways for drug treatment.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted ...
How the gut microbiome responds to antibiotics
2023-06-06
Each person's gut microbiome contains a specific community of microorganisms that normally remains stable for years. However, it can be thrown off balance by factors such as dietary changes, infections or medications. Antibiotics in particular have a strong influence on the microbiome. In response, microorganisms employ various resistance mechanisms, with individual bacterial populations evolving through selection of antibiotic-resistant variants. Yet, the extent and mechanisms of these processes and their impact on the ecology of the microbial community are ...
New study finds that women and underrepresented groups experience higher rates of sexual harassment, cyber incivility and negative workplace climate in academic medicine
2023-06-06
(Atlanta – June 6, 2023) – A new study led by Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University researcher Reshma Jagsi, MD, DPhil, has found that women, racial and ethnic minorities and individuals identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer are disproportionately affected by workplace mistreatment in academic medicine, and this mistreatment negatively impacts their mental health.
The study, which was published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association, looked specifically at three aspects of workplace mistreatment in academic medicine – sexual harassment, cyber incivility and negative workplace climate – and whether they differ by ...
Researchers target proteins, pathways behind congenital heart disease
2023-06-06
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Researchers at the UNC School of Medicine, UNC McAllister Heart Institute, and the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center characterized the expression of thousands of cardiac proteins during eight critical stages of embryonic heart development.
This research, published in Development Cell, will provide scientists with much-needed information to identify biological causes for congenital heart disease, or CHD.
“We now have a foundational data set that shows how protein dynamics change in normal heart development,” said first ...
New push will digitize records of African plants held in herbaria and museums across the US
2023-06-06
LAWRENCE — Over the past few decades, herbaria and museums worldwide have created digital data records documenting millions of specimens in their holdings. The benefits of digitizing the contents of natural history museums and research institutions flow to the public and researchers worldwide.
Now, through a group of related grants from the National Science Foundation, researchers are systemically digitizing more than a million specimens of plants from across tropical Africa held at 20 institutions throughout the United States. The tropical African plant specimens — documenting some of ...
Turning up the heat
2023-06-06
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists found that a small tweak created big performance improvements in a type of solid-state battery, a technology considered vital to broader electric vehicle adoption.
These batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a potentially flammable liquid. When the battery charges or operates, ions move between electrodes through the electrolyte between them. A new method for pressing the solid electrolyte practically eliminates tiny air pockets that block ion flow, so the battery charges twice as fast.
ORNL lead researcher Marm Dixit said the approach involved heating the press after spreading ...
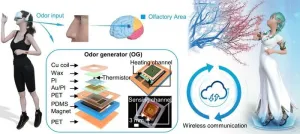
CityU invents wireless olfactory feedback system to let users smell in the VR world
2023-06-06
A research team co-led by researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently invented a novel, wireless, skin-interfaced olfactory feedback system that can release various odours with miniaturised odour generators (OGs). The new technology integrates odours into virtual reality (VR)/augmented reality (AR) to provide a more immersive experience, with broad applications ranging from 4D movie watching and medical treatment to online teaching.
“Recent human machine interfaces highlight the importance of human sensation feedback, including vision, audio and haptics, associated with wide applications in entertainment, medical treatment and VR/AR. Olfaction also plays a significant ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Movement symptoms in dystonia are caused by spinal cord dysfunctionPeer reviewed | Experimental study | Animals