(Press-News.org) Development of an exciting, ground-breaking plant and microbial science and innovation hub can go ahead with confirmation of funding announced today.
The transformational investment will fund new cutting-edge, world-class facilities for the John Innes Centre (JIC) and The Sainsbury Laboratory (TSL) at the heart of the Norwich Research Park. This will deliver a step change in our capability to translate scientific knowledge into bio-based solutions in response to some of society’s most pressing challenges.
As well as transforming the existing capabilities of the John Innes Centre and The Sainsbury Laboratory, both internationally recognised centres of excellence in plant and microbial science, the new hub also aims to become a net-zero carbon laboratory.
The JIC and TSL Next Generation Infrastructure programme is funded by the UKRI Infrastructure Fund, which invests in the facilities, equipment and resources that are essential for researchers and innovators to do ground-breaking work.
The programme will develop the site over the next seven years, with £54.7 million being invested over the first three years, and a total investment of £317.7 million from the Fund.
Professor Melanie Welham, Executive Chair of the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), part of UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), said: “Providing access to cutting-edge, sustainable research and innovation infrastructures is mission-critical to the competitiveness and long-term success of UK bioscience.
“UKRI's investment in the John Innes Centre and The Sainsbury Laboratory Next Generation Infrastructure provides an important opportunity to further improve our local connections with key partners at Norwich Research Park, the likes of which include Earlham Institute and Quadram Institute Bioscience.
“Beyond that, the investment also represents a real opportunity to establish a world-leading global interdisciplinary hub for plant and microbial sciences that will help deliver the bio-based solutions needed to address global challenges around sustainable agriculture, food, nutrition and health.”
With construction of the new hub expected to be completed in 2030, an ongoing fundraising campaign is underway to secure a further £30 million investment to support the full cost of the Next Generation Infrastructure programme.
Professor Graham Moore, Director of the John Innes Centre, said: “Securing this funding is a major step forward in realising our vision to improve collaborative working across the UK and overseas, helping us to provide a safer, healthier and more sustainable future through the power of plant and microbial science. As well as new laboratories, the investment includes a redevelopment of our plant growth facilities, which in conjunction with our existing field station, will improve our ability to study the effects of climate change.”
Professor Nick Talbot FRS, Executive Director of The Sainsbury Laboratory, said: “This transformational investment exemplifies the UK’s confidence in the future of our research institutes and their ability to transform global agriculture through innovation. It is imperative that agricultural production is transformed to become a net carbon zero activity that no longer relies on fossil fuels. The investment from UKRI will enable us to harness the collaborative environment on the Norwich Research Park, catalysing new research initiatives and creating a unique asset for UK science and innovation.”
Enabling an ambitious vision
The investments from the UKRI Infrastructure Fund and other key partners will enable the realisation of an ambitious longer-term vision. Healthy Plants, Healthy People, Healthy Planet (HP3) seeks to provide a safer, healthier and more sustainable future through the power of plant and microbial science.
This bold vision represents a revolution in plant and microbial sciences that strives to integrate advances in genetics, genomics, structural biology, live cell imaging and computational biology to reach new levels of understanding.
HP3, and the development of a global interdisciplinary hub for plant and microbial research has garnered generous contributions from the Gatsby Charitable Foundation, the University of East Anglia, the John Innes Foundation, the Wolfson Foundation and the Garfield Weston Foundation.
The new hub will play a pivotal role in reducing the impact of climate change, providing long term sustainable food solutions, improving human health and enhancing growth and economic prosperity across the UK and beyond.
ENDS
END
Essential investment in plant and microbial research in Norwich, UK, confirmed
2023-06-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
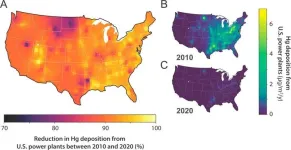
Despite major progress nationally, two mercury emissions hotspots remain
2023-06-07
Missing from partisan political debates over regulations affecting the energy sector is the stunning success of the federal government’s signature environmental laws. A prime example: the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s rules aimed at reducing the harmful effects of hazardous air pollutant (HAP) emissions from fossil fuel-fired power plants known as the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards, or MATS.
A new study from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) shows that in the decade since the standard was ...
What your likes, posts really say about you
2023-06-07
The myriad ways in which we use social media can be grouped into four broad categories, each of which is associated with a cluster of specific personality and behavioral traits, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
“Social media is here to stay, so clarifying how people use social media and raising awareness of these findings are crucial first steps toward ultimately helping people understand how they can avoid the negative aspects of social networking and engage in healthier social media usage,” said Alison B. Tuck, first author of the study and a PhD candidate in clinical psychology in Arts & Sciences.
The study, published online ...
Scientists develop inorganic resins for generating and purifying radium and actinium
2023-06-07
The Science
Targeted alpha therapy can destroy cancerous cells without harming healthy cells. It’s especially useful for treating metastasized cancers. The Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science’s Isotope Program is developing and marketing novel radioactive isotopes for targeted alpha therapy. One method of making one isotope, actinium-225, involves bombarding radium targets with neutrons. This method poses a challenge: how to chemically separate the radium from the actinium. This can destroy typical separation equipment due to a radioactive process called alpha decay. Now, researchers ...
New research: Maybe crying in baseball is a good thing?
2023-06-07
ITHACA, N.Y. – Venturing out of one’s comfort zone to perform a task – and then performing poorly in that task, such as a baseball pitcher trying to hit – can lead to better performance when returning to one’s specialty, according to new research.
Brittany Bond, an assistant professor of organizational behavior in the Cornell School of Industrial and Labor Relations, and Ethan J. Poskanzer of the University of Colorado argue that this phenomenon occurs through a process they call “forced task inferiority,” in which underperformance in tasks outside their specialty frustrates ...
Electronic health records can contain bias, potentially impacting clinical trials
2023-06-07
Results of clinical trials are only as good as the data upon which they rest. This is especially true in terms of diversity — if most people in a trial are from a certain race or socioeconomic group, then the results may not be broadly applicable.
This form of potential bias is not a novel concept. But a group of researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago and colleagues have identified a potential hidden source of bias: electronic health records.
In a recent Contemporary Clinical ...
Yale-led study shows ‘significant overall survival benefit’ when lung-cancer drug is taken after surgery
2023-06-07
New Haven, Conn. — A clinical trial led by Yale Cancer Center shows that the drug osimertinib, a targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer, improved rates of survival and reduced risk of recurrence in patients after surgery.
The results, published June 4 in the New England Journal of Medicine, were presented this week by Dr. Roy Herbst, deputy director of Yale Cancer Center and principal investigator of the ADAURA Phase III clinical trial, during the 2023 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Herbst is also assistant dean for translational research, ensign professor of medicine (medical oncology), ...
Temptation at the checkout: 70% of food, drinks within arm’s reach are unhealthy
2023-06-07
We’ve all been there: waiting in line at a store checkout, surrounded by tempting snacks and drinks. Navigating the checkout lane in search of healthy options could be a challenge, according to researchers at the University of California, Davis, who found that 70% of foods and beverages at checkout are unhealthy.
For snack-sized options, an even higher proportion were unhealthy — 89%.
A study published this month in the journal Current Developments in Nutrition suggests most food and beverage options at checkout consist of candy (31%), sugar-sweetened beverages (11%), salty snacks (9%) and sweets (6%).
Healthy ...
Devastating heart condition can be reversed, study shows for the first time
2023-06-07
Three men who had heart failure caused by the build-up of sticky, toxic proteins are now free of symptoms after their condition spontaneously reversed in an unprecedented case described by a team at UCL (University College London) and the Royal Free Hospital.
The condition, a form of amyloidosis affecting the heart, is progressive and has until now been seen as irreversible, with half of patients dying within four years of diagnosis.
The new study, published as a letter in The New England Journal of Medicine, reports ...
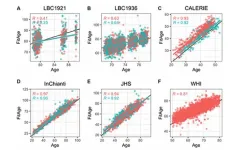
DNAmFitAge: Biological age indicator incorporating physical fitness
2023-06-07
“We expect DNAmFitAge will be a useful biomarker for quantifying fitness benefits at an epigenetic level and can be used to evaluate exercise-based interventions.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 7, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 10, entitled, “DNAmFitAge: biological age indicator incorporating physical fitness.”
Physical fitness is a well-known correlate of health and the aging ...
Now is already too late – The European and international endocrine community calls for immediate action on chemicals legislation is the only way forward to address Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals
2023-06-07
Brussels, Belgium 7 June 2023 – The call for action reverberated across the halls of the European Parliament as a diverse group of scientists, policy makers and interest organisations gathered in a packed room, to discuss how to address the gaps between science and legislation and "Shape an ambitious legislative framework for endocrine disruptors."
“Through such meetings with experts, we as policy makers can obtain valuable insight into the latest available science and benefit from it in our legislative ...