(Press-News.org) A research team led by Prof. ZHANG Haijiang from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Prof. HOU Zengqian from Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, revealed the seismically imaged lithospheric delamination and its controls on the Mesozoic Magmatic Province in South China by using a new joint seismic inversion algorithm. The study was published in Nature Communications.
Based on the latest developed seismic joint inversion algorithm, the researchers made use of the seismic body wave travel time, surface wave dispersion data and receiver function to determine the high-resolution shear wave velocity model of the South China lithosphere. They found that there were high-velocity anomalies in the asthenosphere at a depth of less than 90 kilometers.
These high-velocity anomalies could be interpreted as lithosphere blocks that began to delaminate at 180-170Ma, which was later heated by the deep mantle and floated back to its previous position. Large-scale delamination led to lithosphere transformation, triggering thinning of lithosphere and adiabatic upwelling of asthenosphere. Subsequently, lithosphere extended and overlaying crust melted, forming magmatic province in South China.
As further revealed by geochemical analysis, large amounts of water and heat from the convective mantle was required to trigger delamination. As a result, abundant granitoid and mafic rocks were formed, which explained the formation magmatic rocks and metal deposits.
This study proposed a new understanding of the formation mechanism of Mesozoic magma Province in South China, which help to deeply understand the kinetics of the Paleo-Pacific plate and that of the large-scale mineralization during late Mesozoic in South China. It also provides new ideas for the establishment of the deep process of the lithosphere and the connection between shallow magma and mineralization.
END
Seismic Waves tell lithospheric delamination mechanism in south China
2023-06-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Program for underrepresented undergraduate students in STEM receives NIH funding
2023-06-09
Alexandra Hanlon, director of the Virginia Tech Center for Biostatistics and Health Data Science, was recently awarded a $1.25 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) for a summer program aimed at promoting and diversifying the field of collaborative biostatistics.
The Collaborative Undergraduate Biostatistics Experience (CUBE), an eight-week summer program geared toward underrepresented undergraduate students, will receive $250,000 per year over the next five years through the NIH Research Education Program.
This R25 award, which is funded in a joint effort ...
USTC enhances fluorescence brightness of single silicon carbide spin color centers
2023-06-09
In a study published online in Nano Letters, the team led by Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Dr. XU Jinshi from the University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences made progress in enhancing the fluorescence of single silicon carbide spin defects. The researchers leveraged surface plasmons to markedly boost the fluorescence brightness of single silicon carbide double vacancy PL6 color centers, leading to an improvement in the efficiency of spin control using the properties of co-planar waveguides. This low-cost method neither calls for complex micro-nano processing ...
Researchers determine quantitative composition of ultrahigh-pressure fluid in deep subduction zones
2023-06-09
In a study published in PNAS, Prof. XIAO Yilin’s group from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) quantitatively determined, for the first time, the chemical composition of supercritical fluids in deep subduction zones, through 3D imaging modelling of ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) multiphase fluid inclusions, and revealed the important role of supercritical fluids in the cycling of carbon and sulfur in subduction zones, which is of great importance ...
USTC reveals reconfiguration process of solar eruptions
2023-06-09
Recently, a research team led by Prof. GOU Yanyu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found that the solar outburst structure undergoes a complex reconfiguration evolution during the early outbursts, thus making important advances in the study of solar outburst activity. This study was published in Nature Astronomy.
In classical images, the core structure of a solar eruption is a magnetic rope consisted of spirally wound magnetic lines. When the eruption begins, the magnetic ropes around the core are transformed by magnetic reconnection ...
DNA facilitates escape from metastability
2023-06-09
Prof. LIANG Haojun from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a new method to escape from metastability for self-assembly in a far-from-equilibrium system. The study was published in PNAS.
Self-assembly refers to the process in which assembled primitive elements (molecules, nanoparticles, etc.) spontaneously form ordered structures through non-covalent interactions. Its excellent capacity to create new materials has drawn attention. In an ...
Single quantum bit achieves complex systems modeling
2023-06-09
A team led by Academician GUO Guangcan from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), with collaborative efforts from the University of Manchester, and Nanyang Technological University, has achieved new progress in applying quantum technologies in complex systems modeling. The results were published in Nature Communications on May 6.
Stochastic modeling can help us to predict the future behavior of complex processes, which are non-Markovian. In order to simulate a non-Markovian process, a memory is of necessity to store a large amount of observed information about the past of the system. However, ...
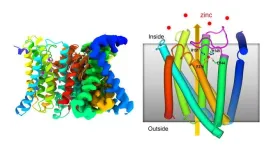
Zinc transporter has built-in self-regulating sensor
2023-06-09
UPTON, NY — Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have determined the atomic-level structure of a zinc-transporter protein, a molecular machine that regulates levels of this crucial trace metal micronutrient inside cells. As described in a paper just published in Nature Communications, the structure reveals how the cellular membrane protein shifts its shape to move zinc from the environment into a cell, and temporarily blocks this action automatically when zinc levels inside the cell get too high.
“Zinc is important for many biological ...
New model offers a way to speed up drug discovery
2023-06-09
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Huge libraries of drug compounds may hold potential treatments for a variety of diseases, such as cancer or heart disease. Ideally, scientists would like to experimentally test each of these compounds against all possible targets, but doing that kind of screen is prohibitively time-consuming.
In recent years, researchers have begun using computational methods to screen those libraries in hopes of speeding up drug discovery. However, many of those methods also take a long time, as most of them calculate each target protein’s ...
Black, Hispanic survivors of breast cancer have higher death rates from second cancers
2023-06-09
Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black female survivors of breast cancer experience higher death rates after being diagnosed with a second primary cancer than members of other ethnic and racial groups, according to recent research from investigators at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
In a study of nearly 40,000 adult survivors of breast cancer, the risk of death from a second cancer was 12% higher among non-Hispanic Black survivors and 8% higher among Hispanic survivors compared with non-Hispanic white survivors. Survivors in racial and ethnic minorities were diagnosed with second cancers ...
Mouse models of adolescent binge drinking reveal key long-lasting brain changes
2023-06-09
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa — Heavy alcohol consumption may cause permanent dysregulation of neurons, or brain cells, in adolescents, according to a new study in mice. The findings suggest that exposure to binge-levels of alcohol during adolescence, when the brain is still developing, lead to long-lasting changes in the brain’s ability to signal and communicate — potentially setting the stage for long-term behavioral changes and hinting towards the mechanisms of alcohol-induced cognitive changes in humans.
“What we’re seeing here,” said Nikki Crowley, assistant professor in biology and biomedical engineering ...