(Press-News.org) Two major ridesharing companies have promised all-electric fleets by 2030 in an effort to reduce their carbon footprint. To understand additional impacts of this transition, researchers reporting in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology conducted life-cycle comparisons of battery-powered electric vehicle fleets to a gas-powered one, using real-world rideshare data. They found up to a 45% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from full electrification; however, traffic problems and air pollution could increase.
Ridesharing apps are an increasingly popular way to travel around urban areas, especially for people without their own vehicles. But the cars and SUVs used in these situations drive more miles each year than a typical personal vehicle, contributing a higher proportion of greenhouse gases to the environment. Previously, researchers calculated that rideshare companies’ carbon footprints could significantly decrease by fully electrifying their fleets. However, few studies have used real-world rideshare trip data in their estimates, or included additional assessments of air pollution and traffic impacts, from the switch. So, Aniruddh Mohan and colleagues wanted to develop a method that evaluated the life-cycle costs and benefits for two battery-powered ridesource fleets and a gasoline-powered one.
The researchers collected real-world rideshare trip data for Chicago and used it to simulate rides provided by three fleets: gasoline-powered, and electric-powered with either 40 kWh or 60 kWh battery packs. Then, they did a comprehensive estimate of the use-phase and life-cycle impacts of the trips made in the simulations. Combining these data, they assigned a monetary value to each trip, based on the assumed damage done by carbon emissions, negative health impacts and traffic-related issues.
The analysis indicated that electrified fleets had 40-45% lower greenhouse gas costs per trip compared to the gasoline-powered version. But the battery-powered electric vehicles were responsible for slightly higher air pollution from increased demand at local power plants for recharging purposes, as well as more ground-level particulates from tire and brake dust. They also were involved in more traffic problems, including crashes, congestion and noise, than the internal combustion option. In the simulations, battery-powered vehicles, particularly the 40 kWh ones, needed more frequent and longer trips without passengers to get to recharging stations. Overall, a conversion to battery-powered electric rideshare fleets could reduce the costs to society by 3-11% per trip, depending on the cost assigned to greenhouse gas emissions, the researchers say. They conclude that these results are specific to Chicago, and cities with different power grids and street layouts could have different assessments from full electrification.
The authors acknowledge funding from Carnegie Mellon University’s Wilton E. Scott Institute for Energy Innovation.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
All-electric rideshare fleet could reduce carbon emissions, increase traffic issues
2023-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Taking biofabrication to the next level: innovations in volumetric bioprinting
2023-06-12
Taking biofabrication to the next level: innovations in volumetric bioprinting
UMC Utrecht researchers propose solutions for bioprinting living tissue
Bioprinting is the printing of living cells and tissues. It's a promising technique that hopefully, one day, can solve the organ donor shortage by growing organs from patients' own cells. However, printing living tissues and cells is extremely complicated, and many hurdles need to be overcome to be able to get there. In this article, three recent innovations ...
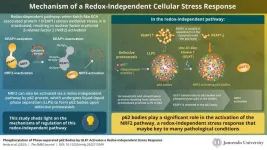
Insights into redox-independent cellular stress response
2023-06-12
Cellular stress, or oxidative stress, occurs when there is a buildup of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which interferes with cellular mechanisms and can even cause damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA. Owing to their destructive nature, all cells have robust mechanisms in place to remove ROS and reduce oxidative stress. One such mechanism is the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2)-mediated stress response, where NRF2 is a master transcription factor that aids in reducing oxidative stress.
Much is known about the redox-dependent activation of NRF2 and its subsequent role in stress response. In this pathway, ...
Chronic exposure to lead, cadmium and arsenic increases risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-06-12
Statement Highlights:
Around the world, most people are regularly exposed to low or moderate levels of lead, cadmium and arsenic in the environment, increasing risk of coronary artery disease, stroke and peripheral artery disease, according to a new American Heart Association statement.
These metals, considered contaminant metals, have no function in the human body. They are found in groundwater, water pipes, paint, tobacco products, fertilizer, plastic, electronics, gasoline, batteries, some foods and other commonly used items.
Lead, ...
Which women should receive more than mammograms to screen for breast cancer?
2023-06-12
Study’s findings point to the importance of considering other risk factors beyond breast density.
Dense breast tissue, which contains a higher proportion of fibrous tissue than fat, is a risk factor for breast cancer and also makes it more difficult to identify cancer on a mammogram. Many states have enacted laws that require women with dense breasts to be notified after a mammogram, so that they can choose to undergo supplemental ultrasound screening to improve cancer detection. A recent study published ...
Twenty species of sea lettuce found along the Baltic and Scandinavian coasts
2023-06-12
The number of species of the green alga sea lettuce in the Baltic Sea region and Skagerak and is much larger than what was previously known. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have surveyed 10,000 kilometres of coast and found twenty species of sea lettuce.
Green macroalgae of the genus Ulva, also known as sea lettuce, are almost ubiquitous in the wider Baltic Sea region and and can be found from the Atlantic waters all the way up to the Bay of Bothnia in the Baltic Sea. Sea lettuce reproduce easily and grow ...
Cancer diagnoses dropped sharply in Alberta during COVID-19 response
2023-06-12
Pandemic restrictions corresponded with a significant drop in diagnoses of breast, colorectal and prostate cancers as well as melanoma, according to a new Alberta study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221512.
"The sweeping and unprecedented measures enacted at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in Alberta had an inevitable impact on cancer care," writes Dr. Darren Brenner, an epidemiologist in Calgary, Alberta, and associate professor at the University of Calgary's Cumming School of Medicine, with coauthors. "Even though treatment and urgent surgeries for cancers were prioritized ...
Canada’s carbon pricing poses a $256 billion financial risk for borrowers and banks
2023-06-12
By putting a price on the cost of carbon, the Government of Canada aims to curtail greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, but it comes with an increased risk for financial lenders and borrowers with high carbon emissions.
In a first-of-its-kind study, University of Waterloo researchers analyzed the effects of Canada’s carbon price regime on the economy. The results indicate that as carbon costs rise, high-emitting carbon industries such as mining and energy are at the greatest risk of default, with total assets of $256 billion at risk of being lost and almost a quarter ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers uncover new insights into why individuals are affected differently by COVID-19 infection
2023-06-12
Abu Dhabi, UAE (June 12): A team of researchers at NYU Abu Dhabi, led by Associate Professor of Biology Youssef Idaghdour and working in collaboration with clinicians at several Abu Dhabi hospitals, investigated the association between microRNAs, a class of small RNA molecules that regulate genes, and COVID-19 severity among 259 unvaccinated COVID-19 patients living in Abu Dhabi. The team identified microRNAs that are associated with a weakened immune response and admission to ICU.
During this process, ...
Vaccine against deadly chytrid fungus primes frog microbiome for future exposure
2023-06-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A human or animal’s microbiome — the collection of often beneficial microorganisms, including as bacteria and fungi, that live on or within a host organism — can play an important role in the host’s overall immune response, but it is unclear how vaccines against harmful pathogens impact the microbiome. A new study led by researchers at Penn State found that a new vaccine against the deadly chytrid fungus in frogs can shift the composition of the microbiome, making frogs more resilient to future exposure to the ...
Should robots be given a human conscience?
2023-06-12
Modern-day society relies intrinsically on automated systems and artificial intelligence. It is embedded into our daily routines and shows no signs of slowing, in fact use of robotic and automated assistance is ever-increasing.
Such pervasive use of AI presents technologists and developers with two ethical dilemmas – how do we build robots that behave in line with our values and how to we stop them going rogue?
One author suggests that one option which is not explored enough is to code more humanity into robots, gifting robots with traits such as empathy and compassion.
Is ...