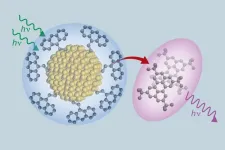
(Press-News.org) A group of scientists and engineers that includes researchers from The University of Texas at Austin have created a new class of materials that can absorb low energy light and transform it into higher energy light. The new material is composed of ultra-small silicon nanoparticles and organic molecules closely related to ones utilized in OLED TVs. This new composite efficiently moves electrons between its organic and inorganic components, with applications for more efficient solar panels, more accurate medical imaging and better night vision goggles.
The material is described in a new paper in Nature Chemistry.
“This process gives us a whole new way of designing materials,” said Sean Roberts, an associate professor of chemistry at UT Austin. “It allows us to take two extremely different substances, silicon and organic molecules, and bond them strongly enough to create not just a mixture, but an entirely new hybrid material with properties that are completely distinct from each of the two components.”
Composites are composed of two or more components that adopt unique properties when combined. For example, composites of carbon fibers and resins find use as lightweight materials for airplane wings, racing cars and many sporting products. In the paper co-authored by Roberts, the inorganic and organic components are combined to show unique interaction with light.
Among those properties are the ability to turn long-wavelength photons — the type found in red light, which tends to travel well though tissue, fog and liquids — into short-wavelength blue or ultraviolet photons, which are the type that usually make sensors work or produce a wide range of chemical reactions. This means the material could prove useful in new technologies as diverse as bioimaging, light-based 3D printing and light sensors that can be used to help self-driving cars travel through fog.
“This concept may be able to create systems that can see in near infrared,” Roberts said. “That can be useful for autonomous vehicles, sensors and night vision systems.”
Taking low energy light and making it higher energy also can potentially help to boost the efficiency of solar cells by allowing them to capture near-infrared light that would normally pass through them. When the technology is optimized, capturing low energy light could reduce the size of solar panels by 30%.
Members of the research team, which includes scientists from the University of California Riverside, University of Colorado Boulder and University of Utah, have been working on light conversion of this type for several years. In a previous paper, they described successfully connecting anthracene, an organic molecule that can emit blue light, with silicon, a material used in solar panels and in many semiconductors. Seeking to amplify the interaction between these materials, the team developed a new method for forging electrically conductive bridges between anthracene and silicon nanocrystals. The resulting strong chemical bond increases the speed with which the two molecules can exchange energy, almost doubling the efficiency in converting lower energy light to higher energy light, compared with the team’s previous breakthrough.
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation, The Welch Foundation, the W.M. Keck Foundation, and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
Kefu Wang and Ming Lee Tang of University of Utah, R. Peyton Cline and Joel D. Eaves of University of Colorado Boulder, Joseph Schwan and Lorenzo Mangolini of University of California Riverside and Jacob M. Strain of UT Austin also contributed extensively to the research.
END
New material transforms light, creating new possibilities for sensors
2023-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The latest weapon against cancer is … a keto diet?
2023-06-12
Dietitians say a keto diet could help you lose up to 10% of your body weight. These high-fat, low-carb meal plans trick the body into burning its own fat. They could also help fight a variety of cancers by starving tumors of the glucose they need to grow. On the surface, this seems ideal. But research suggests these diets may have a deadly, unintended side effect for cancer patients.
In mice with pancreatic and colorectal cancer, keto accelerates a lethal wasting disease called cachexia. Patients and mice with cachexia experience loss of appetite, extreme weight loss, fatigue, and immune suppression. The disease has no effective treatment and contributes to about 2 million ...
Which came first: the reptile or the egg?
2023-06-12
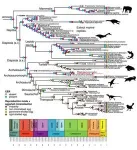
The earliest reptiles, birds and mammals may have borne live young, researchers from Nanjing University and University of Bristol have revealed.
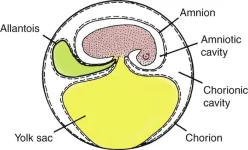
Until now, the hard-shelled egg was thought to be the key to the success of the amniotes - a group of vertebrates that undergo embryonic or foetal development within an amnion, a protective membrane inside the egg.
However, a fresh study of 51 fossil species and 29 living species which could be categorised as oviparous (laying hard or soft-shelled eggs) or viviparous (giving birth to live young) suggests otherwise.
The findings, published today in Nature Ecology & Evolution, show that all the great evolutionary branches ...
Determining how a sugar molecule can affect cancer cell response to chemoradiotherapy
2023-06-12
WASHINGTON --- Researchers at Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center and colleagues who have been exploring the complexities of biochemical pathways involved in cancer development have found that a form of glucose, a type of sugar, is intricately linked to a pathway used to build DNA molecules. When this pathway is overactive, it can lead to cancer and resistance to chemoradiotherapy.
The findings appear June 12, 2023, in Nature Chemical Biology.
“For a good while, my lab has been exploring cell signaling and DNA transcription mechanisms by which cellular metabolism changes in response to environmental and genetic cues, with the goal of designing ...
Unhealthy neighborhood food environments are linked to poor birth weight outcomes in New York
2023-06-12
Higher neighborhood density of unhealthy retail food establishments was associated with a higher risk of delivering a baby that was large-for-gestational age, according to a new study at Columbia Mailman School of Public Health, while neighborhoods with a high density of healthy food retail establishments was linked with a lower risk of giving birth to a baby that was small-for-gestational age. Babies born either small- or large-for-gestational age, a measure of birth weight adjusted for length of pregnancy, are at greater risk for long term health complications, but until now little was known about how neighborhood characteristics including walkability and the ...
Astronomers discover supernova explosion through rare ‘cosmic magnifying glasses’
2023-06-12
According to Einstein’s general theory of relativity, time and space are fused together in a quantity known as spacetime. The theory suggests that massive objects, like a galaxy or galaxy clusters, can cause spacetime to curve. Gravitational lensing is a rare yet observable example of Einstein’s theory in action; the mass of a large celestial body can significantly bend light as it travels through spacetime, much like a magnifying lens. When light from a more distant light source passes by this lens, scientists can use the resulting visual distortions to view objects that would otherwise be too far away and too faint to be seen.
An ...
Study brings new understanding of multiple myeloma evolution
2023-06-12
HOUSTON – A new study by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center highlights novel insights into the evolution of multiple myeloma from precursor disease, which may help better identify patients likely to progress and develop new interventions.
Published today in Cancer Cell, the study integrates paired single-cell RNA sequencing and B cell receptor sequencing from 64 patients with multiple myeloma or precursor disease. The study achieved several notable milestones in the effort to better understand ...
Previously unknown material could revolutionize cancer treatment
2023-06-12
A new material, created at the little-explored intersection of organic and inorganic chemistry, could not only enable more powerful solar panels, but it could also usher in the next generation of cancer treatments.
Described in a Nature Chemistry journal paper published today, the composite is made of ultra-tiny silicon nanoparticles, and an organic element closely related to those used in OLED televisions. It is capable of increasing the speed with which two molecules can exchange energy, and of converting lower-energy light into higher-energy light.
Only a handful of laboratories ...
19-hour days for a billion years of Earth’s history: Study
2023-06-12
It's tough accomplishing everything we want to get done in a day. But it would have been even more difficult had we lived earlier in Earth's history.
Although we take the 24-hour day for granted, in Earth's deep past, days were even shorter.
Day length was shorter because the Moon was closer. "Over time, the Moon has stolen Earth's rotational energy to boost it into a higher orbit farther from Earth," said Ross Mitchell, geophysicist at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and lead author of a new study published in Nature Geoscience.
"Most models of Earth's rotation predict that day length was consistently shorter ...
New method enables study of nano-sized particles
2023-06-12
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have created a new method of studying the smallest bioparticles in the body. The study, which is published in Nature Biotechnology, has considerable scientific potential, such as in the development of more effective vaccines.
Circulating around the body are nanoparticles that affect it in one way or another. For example, there are lipoproteins that maintain cell metabolism, pathogenic viruses that cause many diseases and lipid nanoparticles that are used to carry drugs, like recent lipid nanoparticle-based mRNA vaccines.
However, ...
Unveiling quantum gravity: New results from IceCube and Fermi data
2023-06-12
In a study published in Nature Astronomy today, a team of researchers from the University of Naples “Federico II”, the University of Wroclaw, and the University of Bergen examined a quantum-gravity model of particle propagation in which the speed of ultrarelativistic particles decreases with rising energy. This effect is expected to be extremely small, proportional to the ratio between particle energy and the Planck scale, but when observing very distant astrophysical sources, it can accumulate to observable levels. The ...