(Press-News.org) LOGAN, UTAH, USA -- Genetic variation is the ultimate fuel for evolution, says Utah State University evolutionary geneticist Zachariah Gompert. But, over centuries, that fuel reservoir gets depleted in the course of natural selection and random genetic drift.
Whether, or how, genetic variation can persist over the long haul remains a big question for scientists. Gompert and colleagues from the University of Montpellier in France, the United Kingdom’s John Innes Centre, the National Autonomous University of México, Querétaro; the University of Nevada, Reno; and the University of Notre Dame, publish their investigation of this question in the June 12, 2023, online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The research was supported by a National Science Foundation CAREER Award Gompert received in 2019, along with funds from the European Research Council.
“We examined how you maintain genetic variation in a species, and how such variation impacts adaptation,” says Gompert, associate professor in USU’s Department of Biology and the USU Ecology Center.
For the study, the team investigated stick insects (genus Timema), which feed on a wide variety of plants.
“There are more than a dozen species of Timema in western North America and they’re generalists that can eat many types of plants,” Gompert says. “But one species, Timema knulli, feeds and thrives on Redwood trees, which one of the only plants that other Timema species can’t thrive on as well or at all.”
It appears T. knulli has this ability because of a chromosomal inversion – that is, a change in the structure of its genome. Unlike a gene mutation, which is a change in the DNA sequence, a chromosomal inversion occurs, Gompert says, when two breaks in the chromosome are followed by a 180-degree turn of the segment and reinsertion at the original breakpoints.
“With an inversion, big chunks – in this case, 30 million DNA bases – of the chromosome get flipped backwards,” he says.
And this inversion in T. knulli, the team determined, is ancient.
“We think it occurred about 7.5 million years ago,” Gompert says. “And the cool thing is, T. Knulli populations still carry both versions of the alleles – the one for feeding and thriving on Redwoods as a host plant, and the original one that increases survival on the ancestral host plant – a flowering plant – and may be especially favorable in the heterozygous form.”
Environmental heterogeneity and gene exchange among migrating populations of stick insects contribute to the persistence of the new and ancestral chromosomal variants or polymorphism, he says, which may give the organisms a leg up in a changing world by allowing for ongoing evolution and adaptation.
“Rather than being a detriment, the complexity of evolutionary processes affecting this inversion provides resilience against the loss of genetic variation, and may foster long-term survival,” Gompert says.
END
Evolutionary fuel: Researchers study maintenance of an ancient chromosomal inversion
The complexity of evolutionary processes affecting an inversion in stick insects provides resilience against loss of genetic variation, and may foster long-term survival
2023-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Jefferson Lab Virtual Series serves up science brain teasers
2023-06-12
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Here’s a question for you… Is it possible to learn key science concepts in three minutes or less? The answer: We sure hope so. The U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility is now offering a new playlist called “Here’s a Question” as part of its long-running Frostbite Theater video series. In the “Here’s a Question” videos, longtime Frostbite Theater hosts Steve Gagnon and Joanna Griffin help viewers understand the scientific concepts underlying iron oxidation, magnetism and thermodynamics - and many more!
The series is the newest featured playlist ...
Experiment in Brazil identifies flood-prone areas of cities
2023-06-12
Scientists affiliated with the National Space Research Institute (INPE) in Brazil have combined models that predict urban expansion and land-use changes with hydrodynamic models to create a methodology capable of supplying geographical information that identifies flood-prone areas of cities, especially those vulnerable to the impact of extremely heavy rainfall.
The groundbreaking study was based on data for São Caetano do Sul, a city in metropolitan São Paulo, but the methodology can be used by other cities to devise public policies and make ...
Updating cars as fast as a smart phone
2023-06-12
Cyber-physical systems, such as vehicles, trains, airplanes, smart homes, or production facilities, combine electronic and mechanical elements with software. Development of these systems is highly complex due to the large number of dependencies among the components. “When a car’s wire harness is modified, the diameter of the cable duct also has to be changed,” says Professor Ralf Reussner, Spokesman of the CRC at KIT. This must be agreed upon by electrical engineers, software engineers and mechanical engineers. ...
Excessive alcohol consumption may accelerate Alzheimer’s disease progression
2023-06-12
LA JOLLA, CA—Alcohol use disorder (AUD) quickens the pace of Alzheimer’s disease progression when paired with genetic susceptibility. Scripps Research and University of Bologna scientists reported in the journal eNeuro on June 12, 2023, that repeated alcohol intoxication is associated with changes to gene expression indicative of disease progression in the brains of mice that are genetically predisposed to Alzheimer’s. When repeatedly exposed to intoxicating amounts of alcohol, ...
A step toward safe and reliable autopilots for flying
2023-06-12
In the film “Top Gun: Maverick,” Maverick, played by Tom Cruise, is charged with training young pilots to complete a seemingly impossible mission — to fly their jets deep into a rocky canyon, staying so low to the ground they cannot be detected by radar, then rapidly climb out of the canyon at an extreme angle, avoiding the rock walls. Spoiler alert: With Maverick’s help, these human pilots accomplish their mission.
A machine, on the other hand, would struggle to complete the same pulse-pounding task. To an autonomous aircraft, for instance, the most straightforward path toward the target is in conflict with what the machine needs ...
Mass General Hospital researchers uncover why light-to-moderate drinking is tied to better heart health
2023-06-12
BOSTON – A new study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, offers an explanation for why light-to-moderate alcohol consumption may be associated with lower risk of heart disease. For the first time, researchers found that alcohol, in light to moderate quantities, was associated with long-term reductions in stress signaling in the brain. This impact on the brain’s stress systems appeared to significantly account for the reductions in cardiovascular events seen in light to moderate drinkers participating in the ...
NIH grant backs study focused on Alzheimer’s in women
2023-06-12
HOUSTON – (June 12, 2023) – Two-thirds of the people suffering from Alzheimer’s disease are women, yet most research has ignored differences between the sexes.
To help fill this gap, Rice University postdoctoral fellow Hannah Ballard will look at how Alzheimer’s risk, estrogen levels and menopausal status interact with memory-related brain function and behavioral outcomes in women age 35-80.
Supported by a three-year grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Ballard’s research could help identify the physiological factors ...
Self-esteem of kids with short stature tied to social supports, not height
2023-06-12
Philadelphia, June 12, 2023—Challenging the assumption that short stature negatively impacts children and adolescents’ self-esteem, a new study by researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) has found that in otherwise healthy short youth, quality of life and self-esteem are associated with coping skills and how supported they feel and not the degree of their short stature. The findings were published in The Journal of Pediatrics.
“There is a notion among some parents and caregivers that short stature will negatively impact their children in terms of self-esteem and social adjustment, so they seek out growth hormone ...
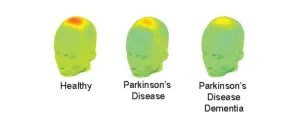
Brain waves may predict cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease
2023-06-12
A few minutes of data recorded from a single electrode placed on top of the head may be sufficient to predict thinking problems, including dementia, in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). The finding from a new University of Iowa study might help improve diagnosis of cognitive disability in PD and develop new biomarkers and targeted therapies for cognitive symptoms of the disease.
“Cognitive decline, including dementia, is a significant and underappreciated symptom of Parkinson’s disease. ...
The Face Game: A citizen science project to learn how Artificial Intelligence will choose to appear to humans
2023-06-12
Online, profile pictures of human faces are everywhere, and they play a crucial role in shaping the first impression we make on others. Right now, AI gives people the digital tools to transform their online appearance in any way they desire, often making themselves look younger or more attractive. But this is just the beginning: AI is not only helping us play this face game amongst ourselves, but it is also learning the game from us and quietly deciding which face it will showcase as itself when interacting with us.
To better understand these mechanisms, researchers from the Max Planck ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
[Press-News.org] Evolutionary fuel: Researchers study maintenance of an ancient chromosomal inversionThe complexity of evolutionary processes affecting an inversion in stick insects provides resilience against loss of genetic variation, and may foster long-term survival