Treating wastewater using passive processes
It is possible to treat certain types of wastewater—not currently treated—globally using more sustainable and affordable in situ methods
2023-06-13
(Press-News.org)
Human activities have a significant impact on natural waters, aquatic biodiversity and the quality of drinking water resources. For Professor Mathieu Lapointe of the Department of Construction Engineering at École de technologie supérieure (ÉTS), it is possible to treat certain types of wastewater—not currently treated—globally using more sustainable and affordable in situ methods.
In a study carried out by Professor Lapointe and published in the Nature journal, the rate of discharge into the environment of certain types of untreated water—urban and rural runoff, as well as that generated by industry—varies from one country to another. Countries with lower incomes tend to discharge more than those with higher incomes. More specifically, wastewater treatment rates can vary from 4% to 95%, depending on the country.
Water treatment plants are not only costly, they also consume a lot of energy. Moreover, they don’t solve the problems associated with urban waterproofing or the erratic excess rainfall caused by climate change. In addition, agricultural and urban runoff is often considered insufficiently contaminated to justify the cost of using conventional treatment plants. As a result, runoff remains untreated even though it can contaminate aquatic ecosystems.
Professor Lapointe recommends passive, modular, inexpensive, and decentralized solutions capable of retaining certain contaminants. These include bioretention cells, aggregate-decant systems and seepage areas through functionalized soils. He also proposes a greater reliance on “passive ecosystem services,” including microorganisms, oxidation, photodegradation and inactivation, to name a few.
“To treat waters that are not currently treated for techno-economic reasons, such as stormwater runoff, government authorities and environmental organizations would do well to promote passive systems, which can be combined or integrated with more conventional processes for collecting and treating wastewater.
Although more in-depth studies are needed to better assess the advantages and cost-benefits of this solution that combines technology with passive methods, Professor Lapointe is optimistic about the viability of this alternative.
It seems that his peers and the water industry agree with him! His study has been published in Nature (Water), the world’s leading journal for water-related issues.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-13
CHICAGO, IL (June 13, 2023) — Scholastica, a leading academic journal publishing software provider, has announced CRediT Taxonomy support across its products and services in line with ANSI/NISO guidelines. The CRediT Taxonomy, which consists of 14 research contributor roles, helps facilitate transparency around research development processes and ensure proper acknowledgment of all contributors.
With the new CRediT implementation, journals using Scholastica's peer review system can request to have CRediT fields added to their submission form, ...
2023-06-13
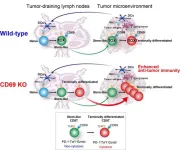
CD8+ T cells, a vital component of the immune system that provides immunity against cancer, have been the focal point of anti-cancer therapies. Recent studies have identified two major subpopulations of these cells present within the tumor—the stem-like cells that do not have anti-tumor activity, and the terminally differentiated CD8+ T cells, which are generated from the stem-like cells and have cytotoxic function on tumor cells. Tumor-draining lymph nodes (TDLNs) have been found to be the primary site for the presence of these cells. However, the molecular mechanisms responsible for the generation of stem-like cells into terminally differentiated ...
2023-06-13
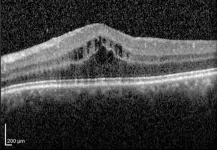
Repeat treatment with corticosteroid injections improved vision in people with persistent or recurrent uveitis-related macular edema better than two other therapies, according to results from a clinical trial funded by the National Eye Institute (NEI). Compared with methotrexate or ranibizumab intravitreal (in-the-eye) injections, the corticosteroid treatment achieved greater reductions in retinal swelling and was the only therapy in the study that improved vision. The report was published today in the journal Ophthalmology. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
“Prior to this study, we didn’t know the best treatment for persistent or recurrent macular edema, a major ...
2023-06-13
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- In collaboration with the Thurgood Marshall College Fund, Binghamton University has announced a New Educational and Research Alliance (New ERA) with six historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs): Alabama A&M University, Central State University, Tuskegee University, Prairie-View A&M University, the University of the District of Columbia and Virginia State University.
The groundbreaking partnership is built on the shared missions of education, research and service, aiming to foster holistic, equitable and sustainable collaborations that will shape the future of academia and beyond.
The strategic alliances formed through this partnership will ...
2023-06-13
How do you study the effects of exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), when it is in everything?! To study the effect of a chemical, toxicologists typically expose animals to various doses of the chemical over a period of time so that they could then study the dose versus effect relationship. Such toxicology studies often employee several types of “blanks” for quality control. Blanks are experiments where the test animals are not given any dose of the chemical being studied (sort of like a placebo in human drug ...
2023-06-13
Tulsa, Okla. – A pioneering study conducted by researchers at the Laureate Institute for Brain Research (LIBR) in Tulsa, Okla., has made significant strides in understanding the elusive gut-brain connection, a complex relationship that has long puzzled scientists due to the difficulty of accessing the body's interior. The study, “Parieto-occipital ERP indicators of gut mechanosensation in humans,” appears in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Nature Communications.
The research team successfully had ...
2023-06-13
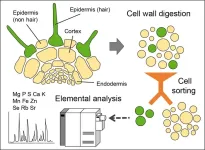
Plant roots play a critical role in taking up, selecting, enriching and retaining a range of different mineral elements thereby supplying distant plant tissues with nutrients while sequestering excessive amounts of metals. To execute such element-specific functions, a range of ion transporters present at roots mediate the uptake, efflux and intracellular compartmentalization of different mineral elements. Most ion transporters show characteristic tissue and cell type-specific localization patterns, which can be altered in response to internal signalling or external cues. To fully ...
2023-06-13
A groundbreaking machine-learning study has unmasked the best drug combinations to prevent COVID-19 from coming back after an initial infection. It turns out these combos are not the same for every patient.
Using real-world data from a hospital in China, the UC Riverside-led study found that individual characteristics, including age, weight, and additional illness determine which drug combinations most effectively reduce recurrence rates. This finding has been published in the journal Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence.
That the data came from China is significant for two reasons. First, when patients are treated for COVID-19 in the U.S, it is ...
2023-06-13
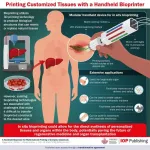
In situ bioprinting, which involves 3D printing biocompatible structures and tissues directly within the body, has seen steady progress over the past few years. In a recent study, a team of researchers developed a handheld bioprinter that addresses key limitations of previous designs, i.e., the ability to print multiple materials and control the physicochemical properties of printed tissues. This device will pave the way for a wide variety of applications in regenerative medicine, drug development and testing, and custom orthotics and prosthetics.
The emergence of regenerative medicine has resulted ...
2023-06-13
Women suffering from the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis temporarily get much better when pregnant. Researchers have now identified the beneficial changes naturally occurring in the immune system during pregnancy. The findings, published in Journal of Neuroinflammation, can show the way to new treatments.
Pregnancy is a very special condition from an immunological point of view. The immune system serves to defend us against foreign substances. However, although half of the genetic material of the foetus ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Treating wastewater using passive processes
It is possible to treat certain types of wastewater—not currently treated—globally using more sustainable and affordable in situ methods