(Press-News.org) A molecule found in the venomous toadfish Thalassophryne nattereri has proved capable of controlling lung inflammation and could be the basis for a more effective asthma drug. The research was supported by FAPESP and conducted by scientists at Butantan Institute in São Paulo, Brazil. An article describing the results is published in the journal Cells.
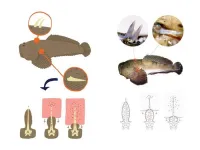
A welter of fish species live in freshwater, seawater and a mixture of the two, and some of them are venomous. They have spines or stingers connected to venom glands, which are a kind of pouch full of molecules, large and small, that are toxins. For these fish, venom is a defensive weapon against predators.
T. nattereri is a case in point. It is a small fish that inhabits calm shallow coastal waters in North and Northeast Brazil. Fishermen call it niquim, an Indigenous word for fish. Its venom apparatus consists of two dorsal and two lateral spines covered by a membrane connected to the venom glands at the base of the fins. When the spine penetrates the victim, the integumentary sheath enclosing the gland presses out the venom into the duct. When stepped on or touched, the animal defends itself by injecting venom, causing intense pain, wounds that swell, and potentially necrosis.
“We started studying the venom of T. nattereri in 1996 because we wanted to analyze its toxins in order to develop a treatment for people injured in accidents,” said Mônica Lopes-Ferreira, a biologist at the Center for Research on Toxins, Immune Response and Cell Signaling (CeTICS), one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDCs) funded by FAPESP.
“We were surprised to discover a small molecule, a peptide, that our studies here at the laboratory showed to have anti-inflammatory properties. An entirely novel molecule no one had ever discovered,” said Lopes-Ferreira, who has a PhD in immunology from the University of São Paulo (USP) and postdoctoral studies in biochemistry and pharmacology at Butantan Institute.
According to the article, mice treated with TnP (T. nattereri peptide) displayed no airway hyperreactivity or lung remodeling. The TnP acted systemically on secondary lymphoid organs and locally on the lungs, inhibiting production of cytokines Th2 and Th17. It also prevented hyperplasia of mucus-producing cells and decreased the thickening and deposition of sub-epithelial collagen. “Our results showed TnP to be a candidate molecule for treatment of airway remodeling associated with inflammatory diseases such as asthma,” the authors write.
“Many diseases cause inflammation. We chose asthma to test TnP using animal models in the laboratory and concluded that it was safe and efficacious. It improved the lung inflammation caused by asthma. This is a Brazilian discovery and we’ve taken care to protect it by filing for a patient,” Lopes-Ferreira said. “We now mean to continue with the research. The more we discover, the more we’ll know about the diseases TnP can treat. It will also be very important to partner with a pharmaceutical company that wants to invest in TnP so that a medical drug can be developed.”
A study supported by FAPESP and reported in October 2016 found that T. nattereri has a molecule with potential action against sclerosis. The results of the study, which was also conducted under the aegis of CeTICS, were published in the journal Toxicon.
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe.
END
Peptide from venomous fish toxin controls lung inflammation in mice
A research group performed tests on animal models with asthma as a reference and demonstrated that the peptide from Thalassophryne nattereri, common in North and Northeast Brazil, is safe and efficacious.
2023-06-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Residents in 'digital deserts' have fewer health care options
2023-06-13
Residents in rural counties with limited access to high-speed internet cannot take advantage of increasingly popular online health services.
A new study by the University of Cincinnati highlighted disparities in access to digital technology that could widen the gap in access to health care. The study found that socially vulnerable communities in the United States face more barriers to adequate health care, live in areas with fewer health care resources and have less access to high-speed internet.
The study was published in the journal Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health.
The Biden Administration announced this year it will invest $73 million in outreach ...
Different genes are expressed at different stages during pregnancy, according to scientists
2023-06-13
We have a good understanding of how a woman’s external features can change during pregnancy, but scientists know surprisingly little about what biological changes occur internally.
A new Northwestern Medicine study, published June 5 in the journal Frontiers in Immunology, provides data about immune cells and biological changes (gene expression) in pregnant people at multiple timepoints before and during pregnancy. Using RNA sequencing and computational methods to estimate proportions of different activated types of immune cells in blood the team of scientists showed how pregnancy induces progressive changes in the maternal ...
USC Stem Cell’s journey towards 1,000 mini-kidneys begins with $1 million from KidneyX
2023-06-13
To help patients in need of transplants, artificial kidneys would have to function like their natural counterparts, but they wouldn’t necessarily have to look like them. With a new $1 million prize from the Kidney Innovation Accelerator, or KidneyX, a team of USC Stem Cell scientists led by Nils Lindström in collaboration with Leonardo Morsut are on a quest to build a kidney that resembles the real thing in function, but not in form.
“Nature has taught us that kidneys can come in an ...
Retooling the ribosomal translation machine could expand chemical repertoire of cells
2023-06-13
Synthetic biologists have become increasingly creative in engineering yeast or bacteria to churn out useful chemicals — from fuels to fabrics and drugs — beyond the normal repertoire of microbes.
But a multi-university group of chemists has a more ambitious goal: to retool the cell's polypeptide manufacturing plants — the ribosomes that spin amino acids into protein — to generate polymer chains that are more elaborate than what can now be made in a cell or a test tube.
The $20 million research enterprise centered at the University of California, Berkeley, is ...
Sickle cell disease is 11 times more deadly than previously recorded
2023-06-13
A new analysis provides a more complete picture of sickle cell disease mortality burden by combining disease prevalence data in different age groups and trends in overall survival when factoring in resulting secondary conditions.
When looking across all deaths, sickle cell disease is a leading cause of mortality in children under 5 years as well as in youth 5–14 years and adults 15–49 years.
Half a million babies were born with sickle cell disease in 2021, and 79% of these infants were in sub-Saharan Africa.
The largest increases ...
New approaches to evaluating water interventions around the globe
2023-06-13
Billions of people around the world face water insecurity. Although there are numerous projects from governments, NGOs, and private corporations who are committed to providing safely managed water and sanitation by 2030, a new study advocates for more holistic evaluation of water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) interventions.
According to the study by Justin Stoler, associate professor in the University of Miami College of Arts and Sciences Department of Geography and Sustainable Development, issues ...
ASCAP introduces slate of AI initiatives to help music creators navigate the future while protecting their work
2023-06-13
NEW YORK, June 13, 2023 – With the potential for artificial intelligence (AI) to create both massive disruption and great opportunity within the music industry, ASCAP — the only US PRO that operates on a not-for-profit basis — is introducing a slate of AI initiatives to help music creators navigate the future while protecting their work. These newly announced initiatives include: adoption by the ASCAP Board of Directors of a set of key ASCAP AI principles, creator education, startup incubation and policy development. Building upon ASCAP’s strong ...
Study in mice links heat-damaged DNA in food to possible genetic risks
2023-06-13
Researchers have newly discovered a surprising and potentially significant reason why eating foods frequently cooked at high temperatures, such as red meat and deep-fried fare, elevates cancer risk. The alleged culprit: DNA within the food that’s been damaged by the cooking process.
As shown for the first time known to the authors, this study by Stanford scientists and their collaborators at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the University of Maryland, and Colorado State University reveals that components of heat-marred DNA can be absorbed during digestion and incorporated into the DNA of the consumer. That uptake directly ...
UC Irvine neuroscientists develop ‘meta-cell’ to move Alzheimer’s fight forward
2023-06-13
Irvine, Calif., June 13, 2023 – University of California, Irvine neuroscientists probing the gene changes behind Alzheimer’s disease have developed a process of making a “meta-cell” that overcomes the challenges of studying a single cell. Their technique has already revealed important new information and can be used to study other diseases throughout the body. Details about the meta-cell – created by researchers with the UCI Institute for Memory Impairments and Neurological Disorders, known as UCI MIND – were published in the online journal Cell Press.
Technologies called transcriptomics that study sets of RNA within organisms ...
What’s an underrated way to study decisions? Think out loud
2023-06-13
Think fast: if you’re running a race and overtake the person in second place, what position are you in? Many people instinctively respond that you’re in first place. However, upon reflection, some people realize the correct answer is that you’re now in second place: the former number-two runner slipped into third as you overtook them.
Trick questions of this kind are invaluable to cognitive scientists because they shed light on the cognitive quirks that shape our decision-making. “These aren’t just trick questions,” explained Nick Byrd, a philosopher-scientist and Intelligence Community Fellow who led the research at Stevens ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
[Press-News.org] Peptide from venomous fish toxin controls lung inflammation in miceA research group performed tests on animal models with asthma as a reference and demonstrated that the peptide from Thalassophryne nattereri, common in North and Northeast Brazil, is safe and efficacious.