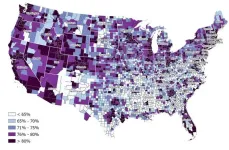
(Press-News.org) Residents in rural counties with limited access to high-speed internet cannot take advantage of increasingly popular online health services.
A new study by the University of Cincinnati highlighted disparities in access to digital technology that could widen the gap in access to health care. The study found that socially vulnerable communities in the United States face more barriers to adequate health care, live in areas with fewer health care resources and have less access to high-speed internet.
The study was published in the journal Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health.
The Biden Administration announced this year it will invest $73 million in outreach grants to provide affordable high-speed internet to more Americans. The program is designed to address a growing gap in access to health care created during the COVID-19 pandemic when providers began offering more health care services over the web.
UC researchers conducted a county-level data visualization and spatial analyses to assess the geospatial association between digital disparities and health care in the contiguous United States.
Study author and UC epidemiologist Diego Cuadros said patients need access to high-speed internet, computers or smart phones and familiarity with technology to use these systems comfortably so they can take advantage of the growing shift to telemedicine and online health services.
The study found that counties with the highest broadband access also had the strongest health care systems, lowest barriers to health care access and lowest social vulnerability.
Cuadros, an associate professor in UC’s College of Arts and Sciences, runs UC’s Digital Epidemiology Laboratory.
His previous research found disparities in easy access to health care across the United States. Many of these same areas have limited access to digital technology such as high-speed internet.
“This finding emphasizes the role that broadband access plays in accessing health care services, particularly during times like the COVID-19 pandemic,” Cuadros said.
“Patients in areas with low broadband access may face greater challenges in obtaining timely and convenient healthcare, leading to potential delays in diagnosis, treatment, and overall healthcare outcomes.”
A vast majority of counties with low broadband access and limited access to health care and social services were rural. About 21 million people, including 14 million rural Americans and more than 1 million Americans living on tribal lands, lack broadband access.
“Telehealth has an awful lot of merit, but the challenge is that telehealth assumes that a person has access to high-speed internet,” said study co-author Neil MacKinnon, provost for Augusta University.
“If someone doesn’t have that access, it can make it difficult for patients and doctors alike. This study shows that because of the digital desert concept, the technology divide really could have health consequences by contributing to a greater health divide in the country.”
University of Washington assistant professor of physiology and biophysics Claudia Moreno, F. DeWolfe Miller at the University of Hawaii, Honolulu, and Ryosuke Omori at Hokkaido University also co-authored the study.
“The study underscores the need for policymakers and health care leaders to prioritize efforts to improve broadband infrastructure, digital literacy and affordability to ensure equitable access to healthcare services for all patients,” Cuadros said.
END
Residents in 'digital deserts' have fewer health care options
Disparities in health care in rural counties could widen as more services go online
2023-06-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Different genes are expressed at different stages during pregnancy, according to scientists
2023-06-13
We have a good understanding of how a woman’s external features can change during pregnancy, but scientists know surprisingly little about what biological changes occur internally.
A new Northwestern Medicine study, published June 5 in the journal Frontiers in Immunology, provides data about immune cells and biological changes (gene expression) in pregnant people at multiple timepoints before and during pregnancy. Using RNA sequencing and computational methods to estimate proportions of different activated types of immune cells in blood the team of scientists showed how pregnancy induces progressive changes in the maternal ...
USC Stem Cell’s journey towards 1,000 mini-kidneys begins with $1 million from KidneyX
2023-06-13
To help patients in need of transplants, artificial kidneys would have to function like their natural counterparts, but they wouldn’t necessarily have to look like them. With a new $1 million prize from the Kidney Innovation Accelerator, or KidneyX, a team of USC Stem Cell scientists led by Nils Lindström in collaboration with Leonardo Morsut are on a quest to build a kidney that resembles the real thing in function, but not in form.
“Nature has taught us that kidneys can come in an ...
Retooling the ribosomal translation machine could expand chemical repertoire of cells
2023-06-13
Synthetic biologists have become increasingly creative in engineering yeast or bacteria to churn out useful chemicals — from fuels to fabrics and drugs — beyond the normal repertoire of microbes.
But a multi-university group of chemists has a more ambitious goal: to retool the cell's polypeptide manufacturing plants — the ribosomes that spin amino acids into protein — to generate polymer chains that are more elaborate than what can now be made in a cell or a test tube.
The $20 million research enterprise centered at the University of California, Berkeley, is ...
Sickle cell disease is 11 times more deadly than previously recorded
2023-06-13
A new analysis provides a more complete picture of sickle cell disease mortality burden by combining disease prevalence data in different age groups and trends in overall survival when factoring in resulting secondary conditions.
When looking across all deaths, sickle cell disease is a leading cause of mortality in children under 5 years as well as in youth 5–14 years and adults 15–49 years.
Half a million babies were born with sickle cell disease in 2021, and 79% of these infants were in sub-Saharan Africa.
The largest increases ...
New approaches to evaluating water interventions around the globe
2023-06-13
Billions of people around the world face water insecurity. Although there are numerous projects from governments, NGOs, and private corporations who are committed to providing safely managed water and sanitation by 2030, a new study advocates for more holistic evaluation of water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) interventions.
According to the study by Justin Stoler, associate professor in the University of Miami College of Arts and Sciences Department of Geography and Sustainable Development, issues ...
ASCAP introduces slate of AI initiatives to help music creators navigate the future while protecting their work
2023-06-13
NEW YORK, June 13, 2023 – With the potential for artificial intelligence (AI) to create both massive disruption and great opportunity within the music industry, ASCAP — the only US PRO that operates on a not-for-profit basis — is introducing a slate of AI initiatives to help music creators navigate the future while protecting their work. These newly announced initiatives include: adoption by the ASCAP Board of Directors of a set of key ASCAP AI principles, creator education, startup incubation and policy development. Building upon ASCAP’s strong ...
Study in mice links heat-damaged DNA in food to possible genetic risks
2023-06-13
Researchers have newly discovered a surprising and potentially significant reason why eating foods frequently cooked at high temperatures, such as red meat and deep-fried fare, elevates cancer risk. The alleged culprit: DNA within the food that’s been damaged by the cooking process.
As shown for the first time known to the authors, this study by Stanford scientists and their collaborators at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the University of Maryland, and Colorado State University reveals that components of heat-marred DNA can be absorbed during digestion and incorporated into the DNA of the consumer. That uptake directly ...
UC Irvine neuroscientists develop ‘meta-cell’ to move Alzheimer’s fight forward
2023-06-13
Irvine, Calif., June 13, 2023 – University of California, Irvine neuroscientists probing the gene changes behind Alzheimer’s disease have developed a process of making a “meta-cell” that overcomes the challenges of studying a single cell. Their technique has already revealed important new information and can be used to study other diseases throughout the body. Details about the meta-cell – created by researchers with the UCI Institute for Memory Impairments and Neurological Disorders, known as UCI MIND – were published in the online journal Cell Press.
Technologies called transcriptomics that study sets of RNA within organisms ...
What’s an underrated way to study decisions? Think out loud
2023-06-13
Think fast: if you’re running a race and overtake the person in second place, what position are you in? Many people instinctively respond that you’re in first place. However, upon reflection, some people realize the correct answer is that you’re now in second place: the former number-two runner slipped into third as you overtook them.
Trick questions of this kind are invaluable to cognitive scientists because they shed light on the cognitive quirks that shape our decision-making. “These aren’t just trick questions,” explained Nick Byrd, a philosopher-scientist and Intelligence Community Fellow who led the research at Stevens ...
Pass the salt: This space rock holds clues as to how Earth got its water
2023-06-13
Sodium chloride, better known as table salt, isn't exactly the type of mineral that captures the imagination of scientists. However, a smattering of tiny salt crystals discovered in a sample from an asteroid has researchers at the University of Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory excited, because these crystals can only have formed in the presence of liquid water.
Even more intriguing, according to the research team, is the fact that the sample comes from an S-type asteroid, a category known to mostly lack hydrated, or water-bearing, minerals. The discovery strongly suggests ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
Fertility preservation in people with cancer
A universal 'instruction manual' helps immune cells protect our organs
Fifteen-year results from SWOG S0016 trial suggest follicular lymphoma is curable
The breasts of a breastfeeding mother may protect a newborn from the cold – researchers offer a new perspective on breast evolution
More organ donations now come from people who die after their heart stops beating
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
[Press-News.org] Residents in 'digital deserts' have fewer health care optionsDisparities in health care in rural counties could widen as more services go online