Breaking barriers: Advancements in meta-holographic display enable ultraviolet domain holograms
2023-06-14
(Press-News.org)
The term meta means a concept of transcendence or surpassing, and when applied to materials, metamaterials encompass artificially engineered substances that exhibit properties not naturally found in the environment. Metasurfaces, characterized by their thinness and lightness, have garnered considerable interest as a potential component for incorporation into portable augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices to facilitate holographic generation. Nonetheless, it is important to note that metasurfaces have inherent limitations, such as their restricted capacity to store information and their capability to generate holograms solely within the visible spectrum.
The research team comprising Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and the Department of Chemical Engineering and Joohoon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) have achieved the generation of meta-holograms applicable to both the visible and ultraviolet spectral regions. The research findings have been published in the inside front cover of Nanoscale Horizons, an esteemed international journal.
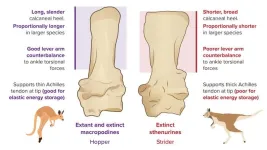
The restriction of hologram generation to the visible spectral range has been primarily attributed to light absorption exhibited by most objects in the ultraviolet regime. However, the research team has effectively addressed this challenge by incorporating a thin layer of specially formulated gas compositions into the metasurfaces, thereby achieving significant improvements in holographic transmission efficiency within both the visible and ultraviolet regimes.
Furthermore, the team has accomplished the encoding of two distinct holographic phase profiles onto a single metasurface. The polarization characteristics of light govern its propagation through space. Leveraging this phenomenon, the team’s approach enables the provision of holographic information both for clockwise circularly polarized light and counter-clockwise circularly polarized light, effectively doubling the amount of information encoded onto metasurfaces.
To facilitate practical implementation, the team employed liquid crystal, a commonly used component in cellphones and LCD displays, which enables convenient manipulation of the light’s spin direction. The experimental results demonstrated that in the absence of an electric field, the light exhibits clockwise spinning, thereby generating a type A hologram. Conversely, the application of an electric field induces a different light spinning direction, resulting in the generation of a type B hologram. In essence, the research team engineered a device capable of presenting distinct holograms based on the presence or absence of an electric field.
Professor Junsuk Rho – who led the research – emphasized this breakthrough by commenting, “This study is significant in that it overcomes the limitations associated with meta-holograms solely applicable to the visible regime and we have achieved the concurrent generation of meta-holograms in both the visible and the UV domains.” He added, “This proposed metasurface can have promising applications in security technologies such as anti-counterfeiting measures, identifications, and passports.”
The study was conducted with the support from the STEAM Research Program (Center for Nano-optics-based Smart Data Security Technology) of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and a program of POSCO’s Industry-Academic Integrated Research Center.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-14
The Bhopal gas explosion in 1984—one of India’s worst industrial disasters—may have heightened the risk of disability and cancer in later life among future generations, curbed their educational attainment, and prompted a fall in the proportion of male births the following year, suggests research in the open access journal BMJ Open.
The disaster is likely to have affected people across a substantially more extensive area than previous evidence suggested, say the researchers.
During the incident, toxic ...
2023-06-14
The NHS will be “flying blind” in its attempts to meet its legal, and moral, obligation to eliminate ethnic inequalities in health and care until longstanding problems with the quality of ethnicity data are resolved, warns an expert in The BMJ today.
Inequalities in health and care between ethnic groups have been documented for decades, explains Sarah Scobie at the Nuffield Trust. But she argues that analysis by broad ethnic groups (white, Asian, black, and mixed) can mask substantial variation within them.
An accompanying infographic presents some of these disparities across a range ...
2023-06-14
BOSTON—Childhood adversity—circumstances that threaten to a child’s physical or psychological well-being--has long been associated with poorer physical and mental health throughout life, such as greater risks of developing cardiac disease, cancer, or depression. It remains unclear, however, when and how the effects of childhood adversity become biologically embedded to influence health outcomes in children, adolescents, and adults.
A team of researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), previously showed that exposure to adversity between ages 3 to 5 has a ...
2023-06-14
Children displayed a resilient capacity to continue playing during peak COVID-19, a study has found, even though their options to do so became more limited while under stay-at-home orders.
The research, by academics at the University of Cambridge, interviewed children themselves about their playing habits during the pandemic. Without disputing the consensus that COVID-19 impeded children’s healthy development, it does suggest that they were able to adapt their play habits to their changed circumstances.
Children largely expressed ...
2023-06-14
Extinct kangaroos used alternative methods to their famous hop according to comprehensive analysis from University of Bristol and the University of Uppsala scientists.
Although hopping is regarded as a pinnacle of kangaroo evolution, the researchers highlight that other kinds of large kangaroos, in the not too distant past, likely moved in different ways such as striding on two legs or traversing on all fours.
In the review, published in Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology, the team shows that there are other ways to be an evolutionary ...
2023-06-14
Artificial night-time light confuses a colour-changing coastal woodlouse, new research shows.
The sea slater is an inch-long woodlouse that lives around the high-tide line and is common in the UK and Europe.
Sea slaters forage at night and can change colour to blend in and conceal themselves from predators.
The new study, by the University of Exeter, tested the effects of a single-point light source (which casts clear shadows) and “diffuse” light (similar to “skyglow” found near towns and cities).
While the single light did not interfere with the sea slaters’ camouflage, diffuse light caused them to turn ...
2023-06-14
A new study suggests that between 2005 and 2014, for almost all births in England, being born outside of working hours did not carry a significantly higher risk of death to the baby from anoxia (lack of oxygen) or trauma, when compared to births during working hours.
The finding runs contrary to an assumed, wider ‘weekend effect,’ with previously reported research suggesting a significantly higher risk of death for births outside of working hours or at weekends.
The current study from City, University of London ...
2023-06-14
The bright lights of big cities are wonders of the modern world; intended to help us work, stay safe and enjoy the world around us long after the sun has set. While artificial light has been great for increasing human productivity, some nocturnal animals, and even people, pay a price for this illumination. From increasing the amount of time that predators are active to disrupting migrations, light pollution affects many animals; but how do animals that use their own luminescence to lure food or attract mates fair against this new, brighter background? Female common glow-worms (Lampyris noctiluca) emit a green glow from their abdomen to ...
2023-06-13
URBANA, Ill. — Meat processing plants in the U.S. have garnered considerable public attention in recent years, often focusing on production and labor issues. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the vulnerability of large, concentrated plants, as major shutdowns led to reduced output and higher meat prices for consumers.
Policy makers have launched initiatives at the state and federal levels to increase meat processing capacity and industry resilience, often favoring small and medium-sized plants. But little research exists to determine what factors make plants more likely to succeed. A new study from the University of ...
2023-06-13
Philadelphia, June 13, 2023— Class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC-I) proteins play an essential role in the immune system of all jawed vertebrates. The MHC-I displays peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell on the cell surface, “presenting” them to the immune system, which is constantly scanning the body for foreign or toxic antigens. When foreign peptides are identified, they trigger a cascade that allows cytotoxic T cells to eliminate intruders. This process has been exploited in the development of both vaccines ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Breaking barriers: Advancements in meta-holographic display enable ultraviolet domain holograms