(Press-News.org) The NHS will be “flying blind” in its attempts to meet its legal, and moral, obligation to eliminate ethnic inequalities in health and care until longstanding problems with the quality of ethnicity data are resolved, warns an expert in The BMJ today.
Inequalities in health and care between ethnic groups have been documented for decades, explains Sarah Scobie at the Nuffield Trust. But she argues that analysis by broad ethnic groups (white, Asian, black, and mixed) can mask substantial variation within them.
An accompanying infographic presents some of these disparities across a range of measures throughout the life course.
In the UK, there are stark and persistent inequalities in stillbirths and infant death rates for Asian, black, and mixed ethnic groups compared with white people, but this pattern is not consistent across all measures, she explains.
For example, death from any cause (“all cause mortality”) in England and Wales for people aged 10 and over between 2017 and 2019 was higher for the white ethnic group (1,058 per 100,000 population) than the black African group (645 per 100,000 population), according to data from the Office for National Statistics.
Wide variations in patterns of illness are also apparent, she adds. For instance, contacts with mental health services are lowest for Asian groups, but these groups have higher rates of cardiovascular disease.
And while evidence shows that health services have responded for some conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, she notes that there are persistent inequalities in mental health, and maternal and infant mortality, with black groups having the worst outcomes, pointing to entrenched challenges.
She explains that the causes of ethnic inequality are multifaceted and include inequalities in socioeconomic status and the effects of structural racism, affecting access to jobs, housing, and other resources, as well as differences in where people live, with ethnic groups concentrated in cities. For example, a fifth (20%) of Asian and black children are born in the most deprived 10% of neighbourhoods, compared with 12% of white children.
Ethnic inequalities are also intrinsically linked to deprivation, and there are major differences within broad ethnic groups, she adds. For example, only 7% of children of Indian ethnicity are eligible for free school meals, the lowest of any group, whereas 29% of children of Bangladeshi ethnicity are eligible. The group with the highest proportion of eligible children is white travellers of Irish heritage (63%), compared with 22% for white British children.
Scobie acknowledges that there are big gaps in what we know about ethnic variations in health, such as access to planned care and for some parts of the life course, including in young adults and for end-of-life care.
“The stark differences in the health effects of the covid-19 pandemic drew attention to longstanding ethnic inequalities, giving hope that these would receive a stronger focus in health policy,” she writes. “But momentum to tackle health inequalities seems to be stalling.”
And while NHS England has adopted an approach to tackle inequalities that considers ethnic and socioeconomic differences, as well as other protected characteristics, vulnerable groups and clinical areas, Scobie believes that “longstanding problems with the quality of ethnicity data hamper progress to understand and tackle ethnic inequalities across healthcare.”
“Until this changes, the NHS will be “flying blind” in its attempts to meet its legal, and moral, obligation to eliminate ethnic inequalities in care,” she concludes.
A linked opinion article asks: How can we make better use of ethnicity data to improve healthcare services?
[Ends]
END
NHS “flying blind” in attempt to tackle ethnic inequalities in care, warns expert
Higher quality data needed to understand and address “stark and persistent” inequalities across the life course
2023-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Timing of childhood adversity is associated with unique epigenetic patterns in adolescents
2023-06-14
BOSTON—Childhood adversity—circumstances that threaten to a child’s physical or psychological well-being--has long been associated with poorer physical and mental health throughout life, such as greater risks of developing cardiac disease, cancer, or depression. It remains unclear, however, when and how the effects of childhood adversity become biologically embedded to influence health outcomes in children, adolescents, and adults.
A team of researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), previously showed that exposure to adversity between ages 3 to 5 has a ...
Lockdown children played on, study finds, despite being stuck at home
2023-06-14
Children displayed a resilient capacity to continue playing during peak COVID-19, a study has found, even though their options to do so became more limited while under stay-at-home orders.
The research, by academics at the University of Cambridge, interviewed children themselves about their playing habits during the pandemic. Without disputing the consensus that COVID-19 impeded children’s healthy development, it does suggest that they were able to adapt their play habits to their changed circumstances.
Children largely expressed ...
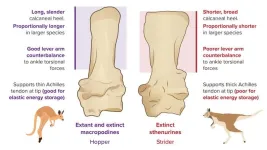
Skipping evolution: some kangaroos didn’t hop, scientists explain
2023-06-14
Extinct kangaroos used alternative methods to their famous hop according to comprehensive analysis from University of Bristol and the University of Uppsala scientists.
Although hopping is regarded as a pinnacle of kangaroo evolution, the researchers highlight that other kinds of large kangaroos, in the not too distant past, likely moved in different ways such as striding on two legs or traversing on all fours.
In the review, published in Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology, the team shows that there are other ways to be an evolutionary ...
Light pollution confuses coastal woodlouse
2023-06-14
Artificial night-time light confuses a colour-changing coastal woodlouse, new research shows.
The sea slater is an inch-long woodlouse that lives around the high-tide line and is common in the UK and Europe.
Sea slaters forage at night and can change colour to blend in and conceal themselves from predators.
The new study, by the University of Exeter, tested the effects of a single-point light source (which casts clear shadows) and “diffuse” light (similar to “skyglow” found near towns and cities).
While the single light did not interfere with the sea slaters’ camouflage, diffuse light caused them to turn ...
Giving birth outside of working hours in England is safe, suggests study
2023-06-14
A new study suggests that between 2005 and 2014, for almost all births in England, being born outside of working hours did not carry a significantly higher risk of death to the baby from anoxia (lack of oxygen) or trauma, when compared to births during working hours.
The finding runs contrary to an assumed, wider ‘weekend effect,’ with previously reported research suggesting a significantly higher risk of death for births outside of working hours or at weekends.
The current study from City, University of London ...
Brighter nights risk extinguishing glow-worm twinkle
2023-06-14
The bright lights of big cities are wonders of the modern world; intended to help us work, stay safe and enjoy the world around us long after the sun has set. While artificial light has been great for increasing human productivity, some nocturnal animals, and even people, pay a price for this illumination. From increasing the amount of time that predators are active to disrupting migrations, light pollution affects many animals; but how do animals that use their own luminescence to lure food or attract mates fair against this new, brighter background? Female common glow-worms (Lampyris noctiluca) emit a green glow from their abdomen to ...
Meat processing plants: What factors are critical for survival?
2023-06-13
URBANA, Ill. — Meat processing plants in the U.S. have garnered considerable public attention in recent years, often focusing on production and labor issues. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the vulnerability of large, concentrated plants, as major shutdowns led to reduced output and higher meat prices for consumers.
Policy makers have launched initiatives at the state and federal levels to increase meat processing capacity and industry resilience, often favoring small and medium-sized plants. But little research exists to determine what factors make plants more likely to succeed. A new study from the University of ...
CHOP researchers develop universal MHC molecules that can be produced rapidly at scale
2023-06-13
Philadelphia, June 13, 2023— Class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC-I) proteins play an essential role in the immune system of all jawed vertebrates. The MHC-I displays peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell on the cell surface, “presenting” them to the immune system, which is constantly scanning the body for foreign or toxic antigens. When foreign peptides are identified, they trigger a cascade that allows cytotoxic T cells to eliminate intruders. This process has been exploited in the development of both vaccines ...
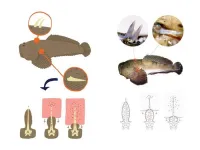
Peptide from venomous fish toxin controls lung inflammation in mice
2023-06-13
A molecule found in the venomous toadfish Thalassophryne nattereri has proved capable of controlling lung inflammation and could be the basis for a more effective asthma drug. The research was supported by FAPESP and conducted by scientists at Butantan Institute in São Paulo, Brazil. An article describing the results is published in the journal Cells.
A welter of fish species live in freshwater, seawater and a mixture of the two, and some of them are venomous. They have spines or stingers connected to venom glands, which ...
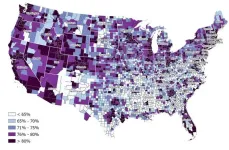
Residents in 'digital deserts' have fewer health care options
2023-06-13
Residents in rural counties with limited access to high-speed internet cannot take advantage of increasingly popular online health services.
A new study by the University of Cincinnati highlighted disparities in access to digital technology that could widen the gap in access to health care. The study found that socially vulnerable communities in the United States face more barriers to adequate health care, live in areas with fewer health care resources and have less access to high-speed internet.
The study was published in the journal Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health.
The Biden Administration announced this year it will invest $73 million in outreach ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] NHS “flying blind” in attempt to tackle ethnic inequalities in care, warns expertHigher quality data needed to understand and address “stark and persistent” inequalities across the life course