(Press-News.org) Safety biomarkers aim to provide an additional tool for detecting acute drug-induced pancreatic injury (DIPI) in phase 1 clinical trials
TUCSON, Ariz., June 13, 2023 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) today announced that the Biomarker Qualification Program (BQP) at the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a Biomarker Letter of Support (LOS) for four pancreatic injury safety biomarkers identified and evaluated by C-Path’s Predictive Safety Testing Consortium's (PSTC) Pancreatic Injury Working Group (PIWG).
This set of biomarkers will help increase the ability to detect and monitor drug-induced pancreatic injury (DIPI) to better inform dosing-related decisions in clinical trials for new drugs.
The biomarkers in question are microRNAs (miRNAs), namely – miR-216a, miR-216b, miR-217, and miR-375. In conjunction with the current standard biomarkers, amylase and lipase, the four novel biomarkers represent sensitive tools to detect DIPI in phase 1 clinical trials, when preclinical information suggests the potential to cause DIPI. Sensitive DIPI biomarkers permit earlier detection of potential injury and determine if a novel therapy can be monitored for potential injury in humans better than the current options. This will improve the accuracy of clinical monitoring and increase the safety of healthy volunteers and patients, also optimizing the overall cost of clinical development of new drugs.
In its LOS, FDA stated, “We support PSTC’s initiative to encourage the voluntary and complementary use of these miRNAs in conjunction with amylase and lipase as exploratory nonclinical and clinical biomarkers of DIPI. We also support PSTC’s generation of additional nonclinical toxicology data and plan for exploratory early clinical studies to enable future formal qualification of these safety biomarkers.”
PSTC Executive Director Nicholas King, M.S. stated, “Collaboration and data sharing between PSTC’s members advanced us to this important step in the path to implementing safety biomarkers with the potential to improve detection of DIPI in drug development.”
Senior Director, Systems Toxicology, Nonclinical Drug Safety at Merck & Co., Inc. and PSTC PIWG Co-Chair Warren Glaab, Ph.D., indicated, “The FDA Letter of Support is a significant milestone demonstrating the added value of emerging safety biomarkers for drug-induced pancreatic injury. This also represents the first endorsement of miRNAs as safety biomarkers to monitor the onset of drug-induced injury. The Letter of Support also provides the foundation for further translation to clinical settings and will further enable clinical qualification of these safety biomarkers.”
Michael Ringenberg, Ph.D., Senior Scientific Director, Pathology, at GlaxoSmithKline and PIWG Co-Chair, said, “Through the identification of promising monitorable parameters, this LOS reinforces our consortia’s commitment to strengthened vigilance over drug safety in patients.”
The LOS for these DIPI biomarkers is posted on the FDA DDT website and is also accessible via C-Path’s PSTC webpage.
As part of the 21st Century Cures Act, passed into law in December 2016, public-private partnerships consisting of government entities, including FDA, the biopharmaceutical industry, healthcare providers, academic researchers and patient advocacy organizations have been encouraged to work together to foster innovation in development of new therapies by qualifying new drug development tools that can accelerate the process of making new therapies available to patients. Since its formation in 2006, C-Path’s Predictive Safety Testing Consortium efforts to improve drug safety monitoring have resulted in two Qualifications of 10 safety biomarkers by the FDA and European Medicines Agency (EMA) and a combined seven sets of Letters of Support from the FDA and EMA.
Any groups that would like to join this effort or obtain information or data that may be useful may contact Nicholas King (nking@c-path.org) or visit https://c-path.org/pstc.
About Critical Path Institute
Critical Path Institute (C-Path) is an independent, nonprofit organization established in 2005 as a public and private partnership. C-Path’s mission is to catalyze the development of new approaches that advance medical innovation and regulatory science, accelerating the path to a healthier world. An international leader in forming collaborations, C-Path has established numerous global consortia that currently include more than 1,600 scientists from government and regulatory agencies, academia, patient organizations, disease foundations, and hundreds of pharmaceutical and biotech companies. C-Path U.S. is headquartered in Tucson, Arizona, C-Path in Europe is headquartered in Amsterdam, Netherlands and C-Path Ltd. operates from Dublin, Ireland with additional staff in multiple other locations. For more information, visit c-path.org.
Critical Path Institute is supported by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and is 55% funded by the FDA/HHS, totaling $17,612,250, and 45% funded by non-government source(s), totaling $14,203,111. The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement by, FDA/HHS or the U.S. Government.
END
C-Path’s PSTC receives positive FDA response for drug-induced pancreatic injury biomarkers
Safety biomarkers aim to provide an additional tool for detecting acute drug-induced pancreatic injury (DIPI) in phase 1 clinical trials
2023-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
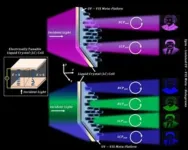
Breaking barriers: Advancements in meta-holographic display enable ultraviolet domain holograms
2023-06-14
The term meta means a concept of transcendence or surpassing, and when applied to materials, metamaterials encompass artificially engineered substances that exhibit properties not naturally found in the environment. Metasurfaces, characterized by their thinness and lightness, have garnered considerable interest as a potential component for incorporation into portable augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices to facilitate holographic generation. Nonetheless, it is important to note that metasurfaces have inherent limitations, such ...
Bhopal explosion may have heightened risk of disability and cancer among future generations
2023-06-14
The Bhopal gas explosion in 1984—one of India’s worst industrial disasters—may have heightened the risk of disability and cancer in later life among future generations, curbed their educational attainment, and prompted a fall in the proportion of male births the following year, suggests research in the open access journal BMJ Open.
The disaster is likely to have affected people across a substantially more extensive area than previous evidence suggested, say the researchers.
During the incident, toxic ...
NHS “flying blind” in attempt to tackle ethnic inequalities in care, warns expert
2023-06-14
The NHS will be “flying blind” in its attempts to meet its legal, and moral, obligation to eliminate ethnic inequalities in health and care until longstanding problems with the quality of ethnicity data are resolved, warns an expert in The BMJ today.
Inequalities in health and care between ethnic groups have been documented for decades, explains Sarah Scobie at the Nuffield Trust. But she argues that analysis by broad ethnic groups (white, Asian, black, and mixed) can mask substantial variation within them.
An accompanying infographic presents some of these disparities across a range ...
Timing of childhood adversity is associated with unique epigenetic patterns in adolescents
2023-06-14
BOSTON—Childhood adversity—circumstances that threaten to a child’s physical or psychological well-being--has long been associated with poorer physical and mental health throughout life, such as greater risks of developing cardiac disease, cancer, or depression. It remains unclear, however, when and how the effects of childhood adversity become biologically embedded to influence health outcomes in children, adolescents, and adults.
A team of researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), previously showed that exposure to adversity between ages 3 to 5 has a ...
Lockdown children played on, study finds, despite being stuck at home
2023-06-14
Children displayed a resilient capacity to continue playing during peak COVID-19, a study has found, even though their options to do so became more limited while under stay-at-home orders.
The research, by academics at the University of Cambridge, interviewed children themselves about their playing habits during the pandemic. Without disputing the consensus that COVID-19 impeded children’s healthy development, it does suggest that they were able to adapt their play habits to their changed circumstances.
Children largely expressed ...
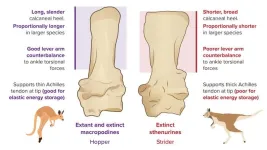
Skipping evolution: some kangaroos didn’t hop, scientists explain
2023-06-14
Extinct kangaroos used alternative methods to their famous hop according to comprehensive analysis from University of Bristol and the University of Uppsala scientists.
Although hopping is regarded as a pinnacle of kangaroo evolution, the researchers highlight that other kinds of large kangaroos, in the not too distant past, likely moved in different ways such as striding on two legs or traversing on all fours.
In the review, published in Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology, the team shows that there are other ways to be an evolutionary ...
Light pollution confuses coastal woodlouse
2023-06-14
Artificial night-time light confuses a colour-changing coastal woodlouse, new research shows.
The sea slater is an inch-long woodlouse that lives around the high-tide line and is common in the UK and Europe.
Sea slaters forage at night and can change colour to blend in and conceal themselves from predators.
The new study, by the University of Exeter, tested the effects of a single-point light source (which casts clear shadows) and “diffuse” light (similar to “skyglow” found near towns and cities).
While the single light did not interfere with the sea slaters’ camouflage, diffuse light caused them to turn ...
Giving birth outside of working hours in England is safe, suggests study
2023-06-14
A new study suggests that between 2005 and 2014, for almost all births in England, being born outside of working hours did not carry a significantly higher risk of death to the baby from anoxia (lack of oxygen) or trauma, when compared to births during working hours.
The finding runs contrary to an assumed, wider ‘weekend effect,’ with previously reported research suggesting a significantly higher risk of death for births outside of working hours or at weekends.
The current study from City, University of London ...
Brighter nights risk extinguishing glow-worm twinkle
2023-06-14
The bright lights of big cities are wonders of the modern world; intended to help us work, stay safe and enjoy the world around us long after the sun has set. While artificial light has been great for increasing human productivity, some nocturnal animals, and even people, pay a price for this illumination. From increasing the amount of time that predators are active to disrupting migrations, light pollution affects many animals; but how do animals that use their own luminescence to lure food or attract mates fair against this new, brighter background? Female common glow-worms (Lampyris noctiluca) emit a green glow from their abdomen to ...
Meat processing plants: What factors are critical for survival?
2023-06-13
URBANA, Ill. — Meat processing plants in the U.S. have garnered considerable public attention in recent years, often focusing on production and labor issues. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the vulnerability of large, concentrated plants, as major shutdowns led to reduced output and higher meat prices for consumers.
Policy makers have launched initiatives at the state and federal levels to increase meat processing capacity and industry resilience, often favoring small and medium-sized plants. But little research exists to determine what factors make plants more likely to succeed. A new study from the University of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A genetic brake that forms our muscles
CHEST announces first class of certified critical care advanced practice providers awarded CCAPP Designation
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop an innovative prussian-blue based electrode for effective and efficient cesium removal
Self-organization of cell-sized chiral rotating actin rings driven by a chiral myosin
Report: US history polarizes generations, but has potential to unite
Tiny bubbles, big breakthrough: Cracking cancer’s “fortress”
A biological material that becomes stronger when wet could replace plastics
Glacial feast: Seals caught closer to glaciers had fuller stomachs
Get the picture? High-tech, low-cost lens focuses on global consumer markets
Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne bacteria remains a public health concern in Europe
Safer batteries for storing energy at massive scale
How can you rescue a “kidnapped” robot? A new AI system helps the robot regain its sense of location in dynamic, ever-changing environments
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
[Press-News.org] C-Path’s PSTC receives positive FDA response for drug-induced pancreatic injury biomarkersSafety biomarkers aim to provide an additional tool for detecting acute drug-induced pancreatic injury (DIPI) in phase 1 clinical trials