(Press-News.org) Receiving an autism diagnosis in your 20, 30s, 40s, 50s or even 60s may seem daunting, but a new study from psychologists in Bath and London finds that the link between the age at which someone gets diagnosed has little bearing on their quality of life.
So-called ‘late diagnosis’ for autism has hit the headlines recently thanks to autism campaigner Christine McGuiness. Whereas autism is usually diagnosed in childhood, it is increasing being diagnosed in adults and especially among women.
Parents often wonder if their child finding out they are autistic earlier or later will have an impact on their lives in the long term. Whilst many people who discover they are autistic as adults wonder what life would have been like if they had found out earlier.
Against this backdrop the new study – carried out by researchers at the University of Bath and King’s College London – is the first to examine whether the age at which one becomes aware of being autistic is linked to their quality of life, after accounting for other crucial factors such as household income.
The researchers asked 300 autistic adults to report the age at which they first learned they were autistic, as well as detailed information about their socio-demographic background such as current age, sex, ethnicity, relationship status, living status, education level, employment status, household income, and the presence of additional mental health conditions. Participants’ level of autistic personality traits was also measured.
Participants then completed questions on different aspects of their quality of life – including physical, psychological, social, environmental aspects. For example, questions such as: “To what extent do you feel your life to be meaningful?” and “How satisfied are you with the support you get from your friends?”.
The results – published in the journal Autism – found that the relationship between the age at which one becomes aware of being autistic and the different areas of quality of life was not statistically linked after considering other factors. In fact, other factors were more strongly linked to quality of life: Autistic women reported a better quality of life than autistic men, and people who had additional mental health conditions (e.g., anxiety) reported a lower quality of life.
Senior Research Fellow at the University of Bath and Lecturer in Psychology at King’s College London, Dr Lucy Livingston, said: “More and more people are finding out they are autistic for the first time as an adult, which can be a life-changing realisation. Because we know that many autistic people experience a very poor quality of life and wellbeing, this begs the question whether finding out you are autistic earlier in life improves outcomes.
"Our findings did not suggest this. For some people, finding out they are autistic sooner rather than later was linked to a better quality of life. For others, finding out later was better. Overall, there was no overall link between the age they found out and their quality of life.
"There could be many reasons for this. Getting an autism diagnosis does not always lead to any meaningful additional support, so it could be that autistic people who learn they are autistic at an earlier age did not necessarily experience a benefit to their life quality. Equally, a late diagnosis in adulthood can be a positive experience, helping people to make sense of themselves, which may improve their self-reported quality of life. The take-away message is that the impact of an autism diagnosis on someone’s quality of life is different for everyone. And there may be other, individual factors that are more important to focus on.”
Lead Researcher at the University of Bath, Dr Florence Leung, added: "Our findings revealed that having more autistic personality characteristics - irrespective of when you learn you are autistic - was the strongest link to poor outcomes across all areas of quality of life. We are now following up on this finding to look more closely at how different autistic characteristics contribute to quality of life. This will be an important step towards establishing more tailored, more efficacious support for autistic people based on their specific autistic strengths and difficulties and self-evaluation of their quality of life.
"Additionally, being male and having additional mental health conditions was linked with poor quality of life. These observations highlight the importance of considering support strategies that are gender-specific to have a more targeted focus on improving autistic people’s mental health, to improve their life outcomes. There has understandably been quite a lot of discussion on autism and mental health in females in recent years but, based on these findings, we should not overlook the needs to autistic males who might also be struggling.”
Co-author and Associate Professor at the University of Bath, Dr Punit Shah, said: "Our research more generally adds to a better understanding of neurodiversity across the lifespan. Autism, for a long time, was thought about as a childhood condition. Many still think this way. But people may not realise that most autistic people, in the UK for example, are now actually adults. With an ageing society, this pattern will increase over the next few decades, so it is critically important that we conduct more detailed investigations into individual differences amongst autistic adults, as we have done. Such autism research in adults will thereby start to reveal the many different ways in which we can understand and support autistic people right throughout their lives, moving beyond a ‘one size fits all’ approach."
END
Toronto, ON, June 15, 2023 – The rate of hospital encounters for benzodiazepine-related toxicity rose by 67 per cent for young adults (aged 19 to 24) and 44 per cent for youth (aged 18 or below) in Ontario between 2013 and 2020, according to a new study from ICES and Unity Health Toronto.
Though there was an overall decline of 7 per cent in the provincial rate of benzodiazepine toxicity, this was largely driven by reductions in rates among people aged 35 years and older.
Benzodiazepines are commonly prescribed to treat anxiety ...
The climate crisis is turning the temperature up all over the world, but in southern Africa, the rise has been particularly concerning. Wild animals dependent on delicate ecosystems which are already dry, so that food and water scarcity limits their ability to cope with increased heat, are at serious risk. Scientists studied the behavior of three different species of antelope with overlapping ranges in Namibia to try to understand how animals of different sizes and behaviors adapt to the heat.
“Even the indigenous wildlife, adapted to hot and arid conditions, shows sensitivity to extreme heat,” said Paul Berry of the University of Potsdam, lead author of the study in ...
Teacher talk seems intuitive – the expert imparts knowledge onto novices, who passively receive expertise like a car or machine receives parts at every station on an assembly line. In reality, an effective teacher in an era of dynamic and higher literacies is less of a factory worker and more of an active negotiator who tries to understand where their students are coming from in order to reach them. The language classroom amplifies this challenge where the negotiation not only centers on the knowledge itself but the means of communication for that knowledge. ...
New research shows that some of the best tools to decrease COVID-19 mortality rates weren’t found in the ER, but rather at the bank.
A study of COVID-19 mortality rates across 142 nations has demonstrated a surprisingly strong link between access to formal financial services and lower COVID-19 mortality rates. In fact, it’s proved to be as strong a predictor of lower COVID-19 death rates as several comorbidities are of higher COVID-19 death rates.
“The reduction is surprisingly large, similar in magnitude to, but opposite in direction from, the mortality risks associated with higher rates of lung cancer and hypertension,” says Todd Watkins, ...
Men were significantly more vulnerable than women to overdose deaths involving opioid and stimulant drugs in 2020-2021, according to a new study analyzing death records data from across the United States. The study found that men had a 2–3 times greater rate of overdose mortality from opioids (like fentanyl and heroin) and psychostimulants (like methamphetamine and cocaine). While it has been known that men use drugs at higher rates than women, the researchers found that this alone does not explain the gap in overdose deaths, noting that biological, behavioral, and social factors likely ...
Sea sponges are essential to marine ecosystems. They play critical roles in the ocean, as they provide shelter and food to a plethora of marine creatures, recycle nutrients by filtering thousands of litres of sea water daily, and are hosts to microbes that may be the key to some of the most pressing medical challenges we face today.
Now, scientists from UNSW have discovered that when a tropical sea sponge is exposed to warmer temperatures, it loses an important microbe, which could explain why the sponge tissue dies. The latest study, published today in ISME Communications, has revealed that by exposing sea sponges ...
Journals from BMJ Press Release:
Embargoed 23:30 hours UK (BST) time Wednesday 14 June 2023
Please click on links for full articles and contact authors direct for further comment - details can be found under Notes for Editors. Please remember to credit the relevant journal - this assures your audience it is from a reputable source.
BRITISH JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE
Externally peer reviewed? Yes
Evidence type: Consensus Statement
Subjects: People
Latest Consensus Statement on Concussion in Sport includes:
-New and updated age appropriate tools to aid identification ...
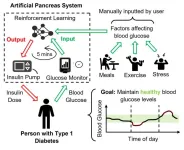
The same type of machine learning methods used to pilot self-driving cars and beat top chess players could help type-1 diabetes sufferers keep their blood glucose levels in a safe range.
Scientists at the University of Bristol have shown that reinforcement learning, a type of machine learning in which a computer program learns to make decisions by trying different actions, significantly outperforms commercial blood glucose controllers in terms of safety and effectiveness. By using offline reinforcement learning, where the algorithm learns from patient records, the researchers improve ...
Insulin production has, for the last 50 or so years, come with some risks to the patient. Even so, the medication is lifesaving for the estimated 537 million adults living with diabetes worldwide, with that number expected to grow.
Recent clinical studies show that injection via insulin pens can cause insulin to reach the bloodstream so quickly that hypoglycemia, or blood sugar levels that dip below the healthy range, may result. Automated insulin pumps can deliver precise insulin and minimize this risk but are expensive and available only to a small portion of diabetes patients around the world.
Now, a plant-based, oral delivery of proinsulin could address these drawbacks, ...
Staffing levels likely drive the differences in hospitalizations and emergency department visits among nursing homes, the researchers report in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Studies show that nursing homes serving high proportions of Black residents may experience poor healthcare outcomes. To better understand the environmental and structural characteristics of nursing homes that may lead to these outcomes, the researchers examined data from 14,121 U.S. nursing homes using multiple ...