(Press-News.org) As the world faces more climate variability and extremes in the face of global warming, sudden environmental changes add an extra layer of stress to food production in the United States and around the world. It is critical, then, to figure out how the areas in which crops are planted and harvested respond to these stressors, which can bring on ‘shocks’ in production – or, put differently, sudden and statistically significant crop declines.
These production shocks are a big concern in terms of food stability and many crops in the United States—such as corn, cotton, soybeans, and wheat — are all experiencing more frequent production reductions as a result of these shocks.
A new study published in the Nature Sustainability scientific journal and led by the University of Delaware’s Dongyang Wei looked at these production shocks and, specifically, how they are affected by variations in planted and harvested areas.
Kyle Davis, assistant professor in the Department of Geography and Spatial Sciences and the Department of Plant and Soil Sciences, as well as a resident faculty member with UD’s Data Science Institute, is coordinating author on the paper.
Wei, a doctoral candidate in the Department of Geography and Spatial Sciences, said prior studies have focused on crop yield and how the yield variability affects production but very few studies have looked at the role of planted and harvested areas. Because production is the combined result of how much area a farmer plants (the planted area), how much of that area they can harvest (the harvested area) and the yield of the crop in that area, it is important to evaluate all three of these factors when assessing production stability.
“What we did was to focus on the U.S., the world’s largest producer and exporter of cereal grains, to see how these three components—crop yield, planted area, and harvested area—affected food production stability and to what degree they are related to climate extremes,” said Wei.
For the study, the researchers looked at county-level data on seven crops: barley, corn, cotton, sorghum, soybeans, spring wheat, and winter wheat.
These are the main crops that are grown in the United States, accounting for about 70 percent of the country’s total cropland. In addition to being widely produced, they have a lot of readily available data that covers a long time period. As a result, the researchers were able to look at data sets from 1978-2020.
“Agriculture is one of the sectors most directly exposed to the effects of climate change,” said Davis. “Understanding how the stability of crop production is influenced by variations in yield, planted area, and harvested area – and how these influences may differ between crops – is critical to more effectively adapting agriculture in the face of rising climate change and extreme climate events. Dongyang’s research is an important contribution to our understanding on this topic.”
Using time-series data and statistical methods to detect how frequently shocks occur, they found that shocks in planted and harvested areas co-occur with more than half of the production shocks for the study crops.
They then looked at the extent to which each of the three components contribute to the size of a production shock and found that while yield fluctuations contribute more than the other two components for corn, cotton, soybean and winter wheat, changes in planted and harvested areas play a more important role in the magnitude of production shocks for barley, sorghum and winter wheat.
Wei said this is important because it shows that researchers should focus on all three variables instead of simply focusing on the yield and ignoring the planted and harvested areas.
“We want to raise the importance of considering all three of the components when we are facing rising climate variability and climate disruptions on the food systems,” said Wei. “Yield is important, but an exclusive focus on yield stability severely constrains the solution space. If we want to have greater flexibility in adapting agriculture to climate change, we should focus on ways to stabilize planted and harvested areas too. The producers’ decisions on cropping patterns can play a crucial role in stabilizing food production.”
END
Shock to the crop system
New study evaluates how climate shocks impact the planted and harvested areas for crops
2023-06-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers demystify the unusual origin of the Geminids meteor shower
2023-06-15
The Geminids meteoroids light up the sky as they race past Earth each winter, producing one of the most intense meteor showers in our night sky.
Mysteries surrounding the origin of this meteoroid stream have long fascinated scientists because, while most meteor showers are created when a comet emits a tail of ice and dust, the Geminids stem from an asteroid — a chunk of rock that normally does not produce a tail. Until recently, the Geminids had only been studied from Earth.
Now, Princeton researchers used observations from NASA’s Parker Solar Probe mission to deduce that it was likely a violent, ...
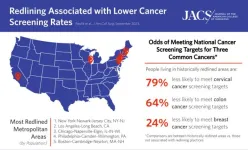
Historic redlining practices cast a long shadow on cancer screening rates
2023-06-15
Key Takeaways
Banned since 1968, the legacy of redlining persists: There continue to be instances of discrimination affecting people in these historically redlined areas.
Redlining was associated with lower odds of hitting screening targets for all three types of cancer: 24% lower odds in breast cancer, 64% lower odds in colorectal, and 79% lower odds in cervical cancer, compared with non-redlined areas.
Actionable initiatives to improve cancer screening rates: Questionnaires to determine barriers to cancer screening, mobile cancer screening ...
Midgut gland of scallops: a valuable source of fucosylated heparan sulfate
2023-06-15
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), including chondroitin sulfate (CS), heparan sulfate (HS), heparin, and hyaluronan are linear and acidic polysaccharides found in the extracellular matrix of all animal tissues. GAGs are widely used as functional ingredients in health products, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, and are prepared from biological samples such as shark cartilage and porcine intestinal mucosa. Consequently, the demand for new sources of GAGs is ever-present. For example, the supply source of the anticoagulant heparin—generally prepared from porcine intestinal mucosa in China—was threatened by African swine fever in 2018.
GAGs derived from marine invertebrates—animals ...
University of Cincinnati research finds potential therapy for rare but devastating lung disease
2023-06-15
A treatment for a rare cancer-like lung disease found in women of childbearing age may have been discovered by University of Cincinnati researchers.
The rare lung disease is called lymphangioleiomyomatosis or LAM, and the cause of it is unknown with no cure established. New UC research, funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, discovered that two existing drugs show signs of being effective in treating LAM and could lead to the development of a cure.
The study was published in Science Advances,
“The exact number of women with LAM is unknown but it is estimated that for every 1 million women in the world, three to seven ...
Insilico Medicine’s transformer-based aging clock provides insights into aging, disease, and new therapeutic targets
2023-06-15
Clinical stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”) has announced a new multimodal transformer-based aging clock that is capable of processing diverse data sets and providing insights into biomarkers for aging, mapping them to genes relevant to both aging and disease, and discovering new therapeutic targets designed to slow or reverse both aging and aging-related diseases. The company calls the aging clock Precious1GPT, in a nod to the powerful “One Ring” in Lord of the Rings. The findings were published in the June 13 issue of the journal Aging.
Insilico has been ...
Hip fracture burden to nearly double worldwide by 2050
2023-06-15
An international group of researchers led by the Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, LKS Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), and including Douglas P Kiel, MD, MPH, Director Musculoskeletal Research Center, Marcus Institute for Aging Research, Hebrew SeniorLife, and Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, evaluated the secular trends in hip fracture incidence, treatment patterns following a hip fracture, and all-cause mortality in 19 countries and regions from 2005 to 2018. While the age- and sex-standardised hip fracture incidence rates decreased ...
Research findings „Study on Adult Learning and Education“
2023-06-15
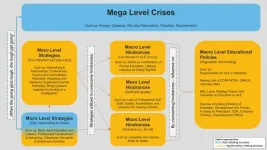
From August 2022 until October 2022, interviews with 25 experts from the selected countries were conducted and then analyzed trough a Ground Theory approach. From this, a model emerged, showing how factors and actors at different societal levels - mega, macro, meso and micro - interact to shape adult learning and education in different contexts.
Mega level comparisons show that overarching issues such as war and conflict, historical and systemic discrimination, disease and extreme poverty as well as political authoritarianism act both as an impetus and as barriers to ALE activities.
Comparative analysis shows that at the macro level, with ...
New tool uncovers COVID-19 susceptibility mechanism
2023-06-15
Researchers have discovered a mechanism for COVID-19 susceptibility using a newly created tool. The tool, GASPACHO, captures dynamic changes in gene expression along the innate immune response, allowing researchers to identify genes and molecular pathways associated with disease risk that have previously been too complex to detect or interpret.
Using GASPACHO (GAuSsian Processes for Association mapping leveraging Cell HeterOgeneity), researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the National Center for Child Health and Development in Japan, Tel Aviv University and their collaborators have identified a gene variant that affects COVID-19 susceptibility. ...
Jefferson Lab oversight roles filled by DOE
2023-06-15
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The U.S. Department of Energy has selected Craig Ferguson to lead the Thomas Jefferson Site Office (TJSO) at the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility in Newport News, Va. As TJSO manager, Ferguson will lead in the oversight and contract management of Jefferson Lab. Additionally, Donté Davis has been confirmed as TJSO deputy manager, a role he first stepped into earlier this year.
Ferguson is familiar with Jefferson Lab and its mission, having already served in a leadership role at the lab. In 2005-2008, he was the lab’s associate director for environment, safety, health & quality.
“I am excited to return ...
High-quality child care contributes to later success in science, math
2023-06-15
Children who receive high-quality child care as babies, toddlers and preschoolers do better in science, technology, engineering and math through high school, and that link is stronger among children from low-income backgrounds, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Our results suggest that caregiving quality in early childhood can build a strong foundation for a trajectory of STEM success,” said study author Andres S. Bustamante, PhD, of the University of California Irvine. “Investing in quality child care and early childhood education could help ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] Shock to the crop systemNew study evaluates how climate shocks impact the planted and harvested areas for crops