(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study, large proportions of disparities in time to first tooth decay associated with race and ethnicity were explained by insurance type and dental procedure types among children and adolescents. These findings can be applied to develop targeted strategies to reduce oral health disparities.
Authors: Sung Eun Choi, S.M., Ph.D., of the Harvard School of Dental Medicine in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.18425)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.18425?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=061523
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Analysis of race and ethnicity, socioeconomic factors, and tooth decay among children
JAMA Network Open
2023-06-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in the US
2023-06-15
About The Study: In 2021, it is estimated that 9.6 million people in the U.S. (26% of those with diabetes) had diabetic retinopathy and 1.84 million people (5% of those with diabetes) had vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy. There was marked variation in prevalence across states and the number of people living with diabetes-related eye disease grew substantially since prevalence was last estimated in 2004 and may grow in the coming decades due to the increasing burden of diabetes among youth and adults.
Authors: Elizabeth A. Lundeen, Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Use of wearable activity trackers to improve patient physical activity, other outcomes in adults who are hospitalized
2023-06-15
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 studies and 1,900 participants, interventions that used wearable activity trackers with patients who are hospitalized were associated with higher physical activity levels, less sedentary behavior, and better physical functioning compared with usual care.
Authors: Carol Maher, Ph.D., of the University of South Australia in Adelaide, South Australia, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Shock to the crop system
2023-06-15
As the world faces more climate variability and extremes in the face of global warming, sudden environmental changes add an extra layer of stress to food production in the United States and around the world. It is critical, then, to figure out how the areas in which crops are planted and harvested respond to these stressors, which can bring on ‘shocks’ in production – or, put differently, sudden and statistically significant crop declines.
These production shocks are a big concern in terms of food stability and many crops in the United States—such as corn, cotton, soybeans, and wheat — are all experiencing more frequent production reductions ...
Researchers demystify the unusual origin of the Geminids meteor shower
2023-06-15
The Geminids meteoroids light up the sky as they race past Earth each winter, producing one of the most intense meteor showers in our night sky.
Mysteries surrounding the origin of this meteoroid stream have long fascinated scientists because, while most meteor showers are created when a comet emits a tail of ice and dust, the Geminids stem from an asteroid — a chunk of rock that normally does not produce a tail. Until recently, the Geminids had only been studied from Earth.
Now, Princeton researchers used observations from NASA’s Parker Solar Probe mission to deduce that it was likely a violent, ...
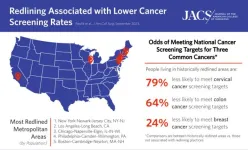
Historic redlining practices cast a long shadow on cancer screening rates
2023-06-15
Key Takeaways
Banned since 1968, the legacy of redlining persists: There continue to be instances of discrimination affecting people in these historically redlined areas.
Redlining was associated with lower odds of hitting screening targets for all three types of cancer: 24% lower odds in breast cancer, 64% lower odds in colorectal, and 79% lower odds in cervical cancer, compared with non-redlined areas.
Actionable initiatives to improve cancer screening rates: Questionnaires to determine barriers to cancer screening, mobile cancer screening ...
Midgut gland of scallops: a valuable source of fucosylated heparan sulfate
2023-06-15
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), including chondroitin sulfate (CS), heparan sulfate (HS), heparin, and hyaluronan are linear and acidic polysaccharides found in the extracellular matrix of all animal tissues. GAGs are widely used as functional ingredients in health products, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, and are prepared from biological samples such as shark cartilage and porcine intestinal mucosa. Consequently, the demand for new sources of GAGs is ever-present. For example, the supply source of the anticoagulant heparin—generally prepared from porcine intestinal mucosa in China—was threatened by African swine fever in 2018.
GAGs derived from marine invertebrates—animals ...
University of Cincinnati research finds potential therapy for rare but devastating lung disease
2023-06-15
A treatment for a rare cancer-like lung disease found in women of childbearing age may have been discovered by University of Cincinnati researchers.
The rare lung disease is called lymphangioleiomyomatosis or LAM, and the cause of it is unknown with no cure established. New UC research, funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, discovered that two existing drugs show signs of being effective in treating LAM and could lead to the development of a cure.
The study was published in Science Advances,
“The exact number of women with LAM is unknown but it is estimated that for every 1 million women in the world, three to seven ...
Insilico Medicine’s transformer-based aging clock provides insights into aging, disease, and new therapeutic targets
2023-06-15
Clinical stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”) has announced a new multimodal transformer-based aging clock that is capable of processing diverse data sets and providing insights into biomarkers for aging, mapping them to genes relevant to both aging and disease, and discovering new therapeutic targets designed to slow or reverse both aging and aging-related diseases. The company calls the aging clock Precious1GPT, in a nod to the powerful “One Ring” in Lord of the Rings. The findings were published in the June 13 issue of the journal Aging.
Insilico has been ...
Hip fracture burden to nearly double worldwide by 2050
2023-06-15
An international group of researchers led by the Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, LKS Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), and including Douglas P Kiel, MD, MPH, Director Musculoskeletal Research Center, Marcus Institute for Aging Research, Hebrew SeniorLife, and Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, evaluated the secular trends in hip fracture incidence, treatment patterns following a hip fracture, and all-cause mortality in 19 countries and regions from 2005 to 2018. While the age- and sex-standardised hip fracture incidence rates decreased ...
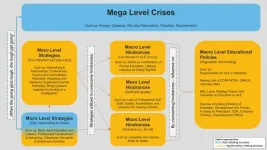
Research findings „Study on Adult Learning and Education“
2023-06-15
From August 2022 until October 2022, interviews with 25 experts from the selected countries were conducted and then analyzed trough a Ground Theory approach. From this, a model emerged, showing how factors and actors at different societal levels - mega, macro, meso and micro - interact to shape adult learning and education in different contexts.
Mega level comparisons show that overarching issues such as war and conflict, historical and systemic discrimination, disease and extreme poverty as well as political authoritarianism act both as an impetus and as barriers to ALE activities.
Comparative analysis shows that at the macro level, with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
[Press-News.org] Analysis of race and ethnicity, socioeconomic factors, and tooth decay among childrenJAMA Network Open