(Press-News.org) Major fungal infections have become more common across the globe, and one unexpected phenomenon among the rise of fungi is life-threatening infections as a result of a complication of certain immunotherapies and small molecule kinase inhibitors.
A scientist at the Hackensack Meridian Center for Discovery and Innovation (CDI) has identified the specific mechanistic cause of one such phenomenon, which will likely save lives into the future, via a new publication.
The paper “C5a-licensed phagocytes drive sterilizing immunity during systemic fungal infection” appeared in the journal Cell on May 22.
“Our findings will assist clinicians in their understanding of how these life-threatening infections are emerging,” said Jigar Desai, Ph.D., assistant member of the CDI, assistant professor of medical sciences at the Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine, and first author of the paper. “These findings may help doctors and scientists alike better understand how some of these cases arise - and how to avoid them.”
The team of scientists established that the C5a protein, the penultimate effector constituent of the complement pathway, is key to the body's innate ability to fight systemic fungal infections. Additionally, the team also identified enhanced complement pathway signature acts as a predictive biomarker for systemic candidiasis. With the use of animal models, patient data and sera, the team showed how C5a and its downstream effects are crucial for the body’s immune cells, specifically neutrophils and macrophages, to clear the fungus Candida albicans, when it has overtaken the body’s natural defenses.
Desai and the team - which includes colleagues from the National Institutes of Health, Duke University, and Mount Sinai, among others - showed this in stages, both in animal models and in patient serum, by isolating what roles the C5 plays.
In addition to uncovering induced complement signature as a potential biomarker for systemic candidiasis, this work will be highly impactful in the clinical setting, where complement C5-targeted therapeutics, such as the anti-C5 monoclonal antibodies eculizumab/ravulizumab (as well as the C5a receptor inhibitor, avacopan) are the treatment of choice. In these settings, findings from this work emphasizes the importance of vigilant surveillance for opportunistic fungal infections, where early diagnosis can improve patient outcomes.
"Our findings establish a new paradigm in immunobiology, demonstrating for the first time the direct critical role of cell-intrinsic complement generation for effective host defense against Candida,” write the authors. "The multifaceted translation of our work shows promise for the development of individualized risk stratification and prognostication strategies in patients at-risk for invasive fungal disease."
Desai, a fungal expert who joined the CDI last year, has had other recent publications.
In two papers in 2022 he and colleagues showed a particular genetic deficiency may weaken certain people to the onslaught of a certain plant pathogenic fungus, and also explore how systemic candidiasis may actually carry enhanced mortality following the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Those papers were published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, and Cell Host and Microbe.
“Jigar Desai is uncovering novel insights into life-threatening fungal diseases,” said David Perlin, Ph.D., chief scientific officer and executive vice president of the CDI, who is also an expert in fungal infections. “As we know, this is an emerging health problem, and it’s key to have his work drive our understanding forward.”
END
Fungal infections an unintended consequence of advanced immunotherapy, research shows
The Desai Lab shows how clinical use of some monoclonal antibodies may cause life-threatening systemic fungal infections
2023-06-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How microgrids can help communities adapt to wildfires
2023-06-15
– By Dan Mullen
Wildfires have become increasingly frequent due to climate change, with record occurrences in areas not historically prone to them. In California, wildfires and regional power shutoffs have cost billions and taken lives. For some 46 million Americans living next to forests – at what scientists call the “wildland-urban interface” (WUI) – the risks of wildfire can be especially acute.
Microgrids can build resilience in vulnerable communities. By using small-scale, local energy sources and disconnecting from regional grids during emergencies, they can deliver essential services to keep homes and communities ...
Quantum interference of light : an anomalous phenomenon found
2023-06-15
In a paper published in Nature Photonics, the research team from the Center for Quantum Information and Communication – Ecole polytechnique de Bruxelles of Université libre de Bruxelles, has found an unexpected counter-example to common knowledge on photon bunching.
One of the cornerstones of quantum physics is Niels Bohr's complementarity principle, roughly speaking the fact that objects may behave either like particles or like waves. These two mutually exclusive descriptions are well illustrated in the iconic double-slit experiment, ...
New biotech venture PHIOGEN, a spinoff of BCM’s TAILOR Labs, to tackle the global threat of antimicrobial resistance
2023-06-15
The new biotech venture PHIOGEN is a spin-off company from Baylor College of Medicine’s TAILOR Labs, one of the United States only academic phage therapy cores with a decade’s worth of revolutionary research related to bacteriophages, viruses that infect and destroy bacteria.
The company made its debut at the 6th World Conference on Targeting Phage Therapy in Paris, June 1-2, 2023.
PHIOGEN’s R&D efforts are led by phage researcher Dr. Anthony ...
How will a warming world impact the Earth’s ability to offset our carbon emissions?
2023-06-15
Washington, DC—As the world heats up due to climate change, how much can we continue to depend on plants and soils to help alleviate some of our self-inflicted damage by removing carbon pollution from the atmosphere?
New work led by Carnegie’s Wu Sun and Anna Michalak tackles this key question by deploying a bold new approach for inferring the temperature sensitivity of ecosystem respiration—which represents one side of the equation balancing carbon dioxide uptake and carbon dioxide output in terrestrial environments. Their findings are published in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
“Right now, plants in the terrestrial ...
New research shows the benefits of teaching pupils about mental health in the classroom
2023-06-15
Giving schools the right resources and training to teach pupils about mental health really can have a positive impact on young people’s wellbeing.
New research by Welsh academics has just been published demonstrating the benefits of improving pupils’ mental health literacy and reducing the stigma around mental health issues at a crucial stage in a young person’s life.
Most mental health problems start in the teenage years with a recent survey identifying that two in five young people report mental health symptoms. However, due to poor knowledge ...
Tethering of shattered chromosomal fragments paves way for new cancer therapies
2023-06-15
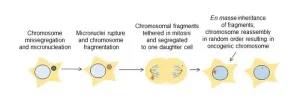
Healthy cells work hard to maintain the integrity of our DNA, but occasionally, a chromosome can get separated from the others and break apart during cell division. The tiny fragments of DNA then get reassembled in random order in the new cell, sometimes producing cancerous gene mutations.
This chromosomal shattering and rearranging is called “chromothripsis” and occurs in the majority of human cancers, especially cancers of the bones, brain and fatty tissue. Chromothripsis was first ...
Diagnosis of rare, genetic muscle disease improved by new approach
2023-06-15
It’s not easy to distinguish between the dozens of subtypes of limb girdle muscular dystrophy — a rare, genetic muscle disease characterized by weakness in the hips and shoulders that causes difficulty walking and lifting the arms. Until now, determining the subtype has not been critical in caring for patients, because no specific treatments have been available. But gene therapies are on the horizon, and such therapies are targeted to specific genetic variants, so pinpointing the genetic roots of each patient’s disease has taken on a new importance.
In new research, a team at Washington University ...
Analysis of race and ethnicity, socioeconomic factors, and tooth decay among children
2023-06-15
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study, large proportions of disparities in time to first tooth decay associated with race and ethnicity were explained by insurance type and dental procedure types among children and adolescents. These findings can be applied to develop targeted strategies to reduce oral health disparities.
Authors: Sung Eun Choi, S.M., Ph.D., of the Harvard School of Dental Medicine in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.18425)
Editor’s ...
Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in the US
2023-06-15
About The Study: In 2021, it is estimated that 9.6 million people in the U.S. (26% of those with diabetes) had diabetic retinopathy and 1.84 million people (5% of those with diabetes) had vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy. There was marked variation in prevalence across states and the number of people living with diabetes-related eye disease grew substantially since prevalence was last estimated in 2004 and may grow in the coming decades due to the increasing burden of diabetes among youth and adults.
Authors: Elizabeth A. Lundeen, Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Use of wearable activity trackers to improve patient physical activity, other outcomes in adults who are hospitalized
2023-06-15
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 studies and 1,900 participants, interventions that used wearable activity trackers with patients who are hospitalized were associated with higher physical activity levels, less sedentary behavior, and better physical functioning compared with usual care.
Authors: Carol Maher, Ph.D., of the University of South Australia in Adelaide, South Australia, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
[Press-News.org] Fungal infections an unintended consequence of advanced immunotherapy, research showsThe Desai Lab shows how clinical use of some monoclonal antibodies may cause life-threatening systemic fungal infections