(Press-News.org) The new biotech venture PHIOGEN is a spin-off company from Baylor College of Medicine’s TAILOR Labs, one of the United States only academic phage therapy cores with a decade’s worth of revolutionary research related to bacteriophages, viruses that infect and destroy bacteria.
The company made its debut at the 6th World Conference on Targeting Phage Therapy in Paris, June 1-2, 2023.
PHIOGEN’s R&D efforts are led by phage researcher Dr. Anthony Maresso, founder of TAILOR Labs and associate professor of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor, whose phage therapy work has attracted funding of more than $5 million to date.
The globally renowned research team behind PHIOGEN is housed in the world’s largest medical complex inside the prestigious Texas Medical Center’s Innovation Hub.
PHIOGEN has developed a world-first technology platform that mobilizes the natural power of bacteriophages to tackle critical and life-threatening infections. This marks a significant medical breakthrough for countering the global threat of antimicrobial resistance.
The World Health Organization deems drug resistant infections as one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity with estimates of over 5 million deaths worldwide attributed to antibiotic resistant infections.
The proprietary first-of-its-kind technology platform that is being spearheaded by PHIOGEN is able to discover and screen at-scale naturally occurring bacteriophages, singling out those with elite bacteria-fighting abilities, and directing biological changes to evolve the phage into antimicrobials that overcome resistance.
This creates a new business model for phage therapy as the group is able to create products that treat populations of people instead of on a per patient basis. By optimizing nature’s defenders, the team has produced unprecedented phage treatments which have already successfully saved the lives of several patients in FDA approved, compassionate use cases.
“We receive high-performing phage fighters that are trained and ready to deliver safe and effective treatments for clinical applications,” said Amanda Burkardt, CEO at PHIOGEN.
###
About PHIOGEN
PHIOGEN™ is a trademark of PHIOGEN INC. PHIOGEN is an innovative biotech company housed in the Texas Medical Center Innovation Hub. It is committed to using proven technology to deliver patient-ready bacteriophage products to tackle the most deadly and serious bacterial infections. PHIOGEN’s world-class patented process has received early proof of concept validation through several in vivo studies as well as for patients in FDA-approved compassionate use cases.
Learn more about the clinical successes of phage therapy in this video interview with Dr. Maresso.
END
New biotech venture PHIOGEN, a spinoff of BCM’s TAILOR Labs, to tackle the global threat of antimicrobial resistance
2023-06-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How will a warming world impact the Earth’s ability to offset our carbon emissions?
2023-06-15
Washington, DC—As the world heats up due to climate change, how much can we continue to depend on plants and soils to help alleviate some of our self-inflicted damage by removing carbon pollution from the atmosphere?
New work led by Carnegie’s Wu Sun and Anna Michalak tackles this key question by deploying a bold new approach for inferring the temperature sensitivity of ecosystem respiration—which represents one side of the equation balancing carbon dioxide uptake and carbon dioxide output in terrestrial environments. Their findings are published in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
“Right now, plants in the terrestrial ...
New research shows the benefits of teaching pupils about mental health in the classroom
2023-06-15
Giving schools the right resources and training to teach pupils about mental health really can have a positive impact on young people’s wellbeing.
New research by Welsh academics has just been published demonstrating the benefits of improving pupils’ mental health literacy and reducing the stigma around mental health issues at a crucial stage in a young person’s life.
Most mental health problems start in the teenage years with a recent survey identifying that two in five young people report mental health symptoms. However, due to poor knowledge ...
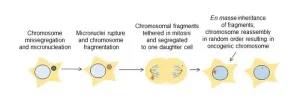
Tethering of shattered chromosomal fragments paves way for new cancer therapies
2023-06-15
Healthy cells work hard to maintain the integrity of our DNA, but occasionally, a chromosome can get separated from the others and break apart during cell division. The tiny fragments of DNA then get reassembled in random order in the new cell, sometimes producing cancerous gene mutations.
This chromosomal shattering and rearranging is called “chromothripsis” and occurs in the majority of human cancers, especially cancers of the bones, brain and fatty tissue. Chromothripsis was first ...
Diagnosis of rare, genetic muscle disease improved by new approach
2023-06-15
It’s not easy to distinguish between the dozens of subtypes of limb girdle muscular dystrophy — a rare, genetic muscle disease characterized by weakness in the hips and shoulders that causes difficulty walking and lifting the arms. Until now, determining the subtype has not been critical in caring for patients, because no specific treatments have been available. But gene therapies are on the horizon, and such therapies are targeted to specific genetic variants, so pinpointing the genetic roots of each patient’s disease has taken on a new importance.
In new research, a team at Washington University ...
Analysis of race and ethnicity, socioeconomic factors, and tooth decay among children
2023-06-15
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study, large proportions of disparities in time to first tooth decay associated with race and ethnicity were explained by insurance type and dental procedure types among children and adolescents. These findings can be applied to develop targeted strategies to reduce oral health disparities.
Authors: Sung Eun Choi, S.M., Ph.D., of the Harvard School of Dental Medicine in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.18425)
Editor’s ...
Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in the US
2023-06-15
About The Study: In 2021, it is estimated that 9.6 million people in the U.S. (26% of those with diabetes) had diabetic retinopathy and 1.84 million people (5% of those with diabetes) had vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy. There was marked variation in prevalence across states and the number of people living with diabetes-related eye disease grew substantially since prevalence was last estimated in 2004 and may grow in the coming decades due to the increasing burden of diabetes among youth and adults.
Authors: Elizabeth A. Lundeen, Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Use of wearable activity trackers to improve patient physical activity, other outcomes in adults who are hospitalized
2023-06-15
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 studies and 1,900 participants, interventions that used wearable activity trackers with patients who are hospitalized were associated with higher physical activity levels, less sedentary behavior, and better physical functioning compared with usual care.
Authors: Carol Maher, Ph.D., of the University of South Australia in Adelaide, South Australia, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Shock to the crop system
2023-06-15
As the world faces more climate variability and extremes in the face of global warming, sudden environmental changes add an extra layer of stress to food production in the United States and around the world. It is critical, then, to figure out how the areas in which crops are planted and harvested respond to these stressors, which can bring on ‘shocks’ in production – or, put differently, sudden and statistically significant crop declines.
These production shocks are a big concern in terms of food stability and many crops in the United States—such as corn, cotton, soybeans, and wheat — are all experiencing more frequent production reductions ...
Researchers demystify the unusual origin of the Geminids meteor shower
2023-06-15
The Geminids meteoroids light up the sky as they race past Earth each winter, producing one of the most intense meteor showers in our night sky.
Mysteries surrounding the origin of this meteoroid stream have long fascinated scientists because, while most meteor showers are created when a comet emits a tail of ice and dust, the Geminids stem from an asteroid — a chunk of rock that normally does not produce a tail. Until recently, the Geminids had only been studied from Earth.
Now, Princeton researchers used observations from NASA’s Parker Solar Probe mission to deduce that it was likely a violent, ...
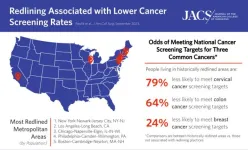
Historic redlining practices cast a long shadow on cancer screening rates
2023-06-15
Key Takeaways
Banned since 1968, the legacy of redlining persists: There continue to be instances of discrimination affecting people in these historically redlined areas.
Redlining was associated with lower odds of hitting screening targets for all three types of cancer: 24% lower odds in breast cancer, 64% lower odds in colorectal, and 79% lower odds in cervical cancer, compared with non-redlined areas.
Actionable initiatives to improve cancer screening rates: Questionnaires to determine barriers to cancer screening, mobile cancer screening ...