(Press-News.org) About The Study: In critically ill patients with sepsis, compared with intermittent administration, the continuous administration of the antibiotic meropenem did not improve the composite outcome of mortality and emergence of pandrug-resistant or extensively drug-resistant bacteria at day 28.
Authors: Giovanni Landoni, M.D., of the IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute in Milan, Italy, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.10598)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being released to coincide with presentation at the 2023 Critical Care Reviews meeting.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2023.10598?guestAccessKey=b0f75c6d-25ba-4e55-8106-531c0288a645&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=061623
END
Continuous vs intermittent meropenem administration in critically ill patients with sepsis
JAMA
2023-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Japan’s subtropical forests home to a newly discovered beetle species
2023-06-16
A new weevil species was discovered in Japan’s pristine subtropical forests on Ishigaki Island and Yanbaru National Park in Okinawa.
Renowned for their remarkable biodiversity, the Ryukyu Islands are a chain of subtropical islands distributed between mainland Japan and Taiwan that boast a relatively isolated evolutionary history, and are home to a distinctive and fascinating insect fauna.
Researchers at the Okinawan Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have been placing net traps to monitor insects on Okinawa ...
Revolutionary new method can manipulate the shape and packing of DNA
2023-06-16
A human cell harbors roughly 2 meters of DNA, encompassing the essential genetic information of an individual. If one were to unwind and stretch out all the DNA contained within a single person, it would span a staggering distance – enough to reach the sun and back 60 times over. In order to manage such an astounding volume of biological information, the cell compacts its DNA into tightly packed chromosomes.
“Imagine DNA as a piece of paper upon which all our genetic information is written.” Says Minke A.D. Nijenhuis, co-corresponding author. “The paper is folded into a very tight structure in order to fit all of that ...
New insights on bacteria that causes food poisoning
2023-06-16
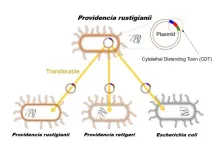
Recently, Providencia spp. which have been detected in patients with gastroenteritis, and similar to enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. O157 and Salmonella spp., have been attracting attention as causative agents of food poisoning. For children with low immunity, food poisoning can be lethal as it causes severe symptoms such as diarrhea and dehydration, so clarifying the source of infection and pathogenic factors of Providencia spp., and establishing preventive methods are urgent issues worldwide.
A joint research group led by Professor Shinji Yamasaki, Dr. Sharda Prasad Awasthi, a Specially Appointed Lecturer, and graduate ...
Alcohol and smoking to blame for premature deaths among night owls, 37-year study suggests
2023-06-16
Staying up late at night has little impact on how long ‘night owls’ live, according to new research published in the peer-reviewed journal Chronobiology International.
Data based on nearly 23,000 twins, however shows that evening types have a slightly increased risk of dying than morning types, but this is largely linked to smoking and drinking.
The study which tracked people over the course of more than 37 years in Finland suggests that lifestyle should be considered.
This is when analyzing the impact on health of chronotype – the body’s natural inclination to sleep at a certain time.
“Our ...
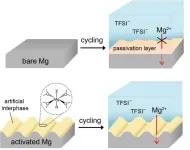
Removing barriers to commercialization of magnesium secondary batteries
2023-06-16
A research team led by Dr. Minah Lee of the Energy Storage Research Center at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology(KIST) has developed a chemical activation strategy of magnesium metal that enables efficient operation of magnesium batteries in common electrolytes that are free of corrosive additives and can be mass-produced.
While the demand for lithium-ion batteries is exploding due to the rapid growth of the electric vehicle and energy storage system(ESS) markets, the supply and demand of their raw materials such as lithium and cobalt ...
Fathers key to supporting breastfeeding and safe infant sleep
2023-06-16
Fathers can make a huge difference in whether an infant is breastfed and placed to sleep safely, according to a recent survey of new fathers via the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) for Dads. This new tool is modeled on the annual surveillance system that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and public health departments have used for more than 35 years to survey new mothers. By utilizing PRAMS for Dads, this article is the first to describe father-reported rates of infant breastfeeding and sleep practices in a state-representative sample. Findings are published in the journal Pediatrics.
Among fathers who wanted their infant’s ...
A facile strategy for comprehensive proteome analysis of urine
2023-06-16
Urine is one of the attractive sources for early and sensitive biomarker discovery since it can accumulate and reflect changes in the human body while being collected non-invasively. However, analysis of the urine proteome presents challenges due to its wide dynamic range, spanning approximately 10 orders of magnitude in protein concentrations. The presence of high-abundance proteins in urine can overshadow potential disease biomarkers, making their identification difficult. Fractionation and depletion ...
Exposure to dioxins can worsen thyroid function
2023-06-16
CHICAGO—Exposure to dioxins can negatively impact thyroid function, according to a study presented Thursday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
Dioxins are highly toxic compounds that are primarily produced by industrial processes, and their persistence in the environment makes them a significant public health concern. They are produced through a variety of incineration processes, including improper municipal waste incineration and burning of trash. They can be released into the air during natural processes, such as forest fires and volcanoes. ...
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals may raise risk of cognitive disorders in future generations, animal study finds
2023-06-16
Adverse cognitive effects linked to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) exposure, a type of endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC), have the potential to be passed down through generations, according to an animal study being presented Thursday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
PCBs can mimic the effect of the hormone estrogen on the body, contributing to a variety of neuroendocrine, metabolic and reproductive problems.
“Endocrine-disrupting chemicals present in our food, air, water and personal products may cause cognitive-behavioral disorders like attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder or overeating in future generations,” ...
IIASA analysis underpins new 2040 climate targets by EU Advisors
2023-06-16
In two new reports, IIASA researchers, with support from colleagues at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), examined the feasibility and fairness of emissions targets and considerations for the European Climate Law. Keywan Riahi, a member of the 15-strong EU Advisory Board and IIASA Energy, Climate, and Environment Program Director, took the lead in conducting the analyses.
The European Scientific Advisory Board on Climate Change is an independent board entrusted with the crucial responsibility of providing transparent and scientific guidance to the EU on setting a new emissions reduction target to be achieved by 2040, as well as budgets for greenhouse ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Continuous vs intermittent meropenem administration in critically ill patients with sepsisJAMA