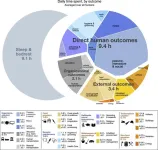
(Press-News.org) Everyone has 24 hours per day. Across the global population of 8 billion people this adds up to approximately 190 billion human hours per day. How those hours are spent determines the impacts we have on our surroundings as well as how we experience life. To find out how people around the world use their time, a research team led by McGill University has gathered and analyzed information about both economic and non-economic activities in order to estimate, for the first time, what a day in the life of the world looks like.
“At present, we are struggling to come to terms with global challenges, and that calls for fresh perspectives on how the world works,” says Eric Galbraith, a professor in Earth System Science at McGill University and the senior author on the study published recently in PNAS. “If we are to sustainably navigate climate change and biodiversity loss, adapt to rapid technological change, and achieve global development goals it is crucial to understand the big picture of how the global human system functions, so that we can see where there is potential for change.”
A holistic, birds-eye view of our collective efforts
“We wanted to know - what does the time allocation of humanity look like, averaged over all people and across all countries?” adds William Fajzel, a PhD student in Earth System Science at McGill University and the first author on the study. “In other words, if the world were a single average person, what would their day look like?”
To find out, the research team looked at time use and labour data gathered for the period from 2000-2019 (to avoid any impacts from the COVID pandemic) from over 140 countries (representing 87% of the world’s population).
Activities and their desired outcomes
The researchers categorized all the things people do in a waking day, including both work and non-work activities, according to what the purpose of the activity was. They used 24 categories that fall into three broad groups:
Intended to alter the external world (including the provision or modification of food, energy, buildings, the maintenance of surroundings, etc.)
Focussed directly on human minds or bodies (including caring for the cleanliness, appearance, mood and health of self and others, as well as education, religion, hobbies, socializing, sports, media, resting, etc.)
Organizing activities within society (such as transportation, trade, finance, law and governance, etc.)
They then manually classified nearly 4 000 unique activities. And made some surprising discoveries.
Most of each day is focussed on ourselves and others
The researchers found that the single largest chunk of time goes towards activities that are human-centered – a little more than 9 hours. Sleep or being in bed accounts for an additional 9 hours (the global estimate includes youth who tend to sleep longer hours). Of the remaining 6 hours, growing and collecting our food, preparing it, commuting and moving around, and allocational tasks (such as trade, finance, sales, law, governance, policing) each occupy around 1 hour. Waste management accounted for just 1 min of the global day, in stark contrast to the 45 minutes spent tidying and maintaining our dwellings. All infrastructure and building construction is accomplished in about 15 minutes.
Surprisingly, time spent in activities like meals, daily travel, hygiene and grooming, and food preparation don’t change in a systematic way with the material wealth of a population. In contrast, the time spent growing and collecting food varied strongly with wealth, from over 1 hour in low-income countries to less than 5 minutes in high-income countries.
Just a tenth of the day is given over to economic activities
Since the study includes both economic and non-economic activities, a portion of the total time in each of the categories described above represents people engaged in economic activity – e.g., doctors and nurses, cooks and agricultural labourers, etc.
The team estimated that the entire global economy occupies around 2.6 hours of the average human day. This economic activity is dominated by agriculture and livestock production, followed by allocational activities like trade, finance and law, and manufacturing. While the total of 2.6 hours may seem small, for the two-thirds of the world’s working-age population (ages 15-64) who make up the labour force this equates to about a 40-hour work week.
The results of the study provide a unique perspective on how economic activities fit into the overall fabric of human life at a global scale. They also suggest that there is plenty of scope to shift time allocation around certain activities, such as extracting materials, provisioning energy, and dealing with wastes, all accomplished within about seven minutes.
“The Global Human Day” by William Fajzel et al was published in PNAS
doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2219564120
END
The global human day – A bird’s eye perspective
How humans around the world spend their time on an average day
2023-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Planned reform of EU pharmaceutical legislation: early market access and robust evidence need not be a contradiction
2023-06-16
The European Commission's stated aim is to improve access to innovative drugs at the national level throughout the EU. Firstly, according to the proposal for the reform of EU pharmaceutical legislation, there are still considerable differences in access between countries. Secondly, drug development has so far only been geared to a limited extent to the actual needs of patients. According to the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), the latter point is in line with the perspective of the ...
Dads are key in supporting breastfeeding, safe infant sleep
2023-06-16
Findings highlight racial disparities in sudden unexpected infant death in the U.S.
Only 16% fathers followed all three AAP-recommended infant sleep practices
Rates of breastfeeding initiation and breastfeeding at eight weeks were much higher among fathers who wanted their infant’s mother to breastfeed than those who did not or had no opinion
CHICAGO --- Fathers can make a huge difference in whether an infant is breastfed and placed to sleep safely, according to a recent survey of new fathers led by scientists at Northwestern University and the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
The study included 250 fathers who ...
AI could replace humans in social science research
2023-06-16
In an article published yesterday in the prestigious journal Science, leading researchers from the University of Waterloo, University of Toronto, Yale University and the University of Pennsylvania look at how AI (large language models or LLMs in particular) could change the nature of their work.
“What we wanted to explore in this article is how social science research practices can be adapted, even reinvented, to harness the power of AI,” said Igor Grossmann, professor of psychology at Waterloo.
Grossmann and colleagues note ...
Research hints at how fungus farming ants keep their gardens healthy
2023-06-16
‘Weed early and often’ is the key to a productive garden. Interestingly, certain species of ants are also avid gardeners, a practice they’ve refined over 50 million years. They too weed their underground fungus gardens, but how they know what to weed out has been a mystery. Now, a multidisciplinary team of scientists report in PNAS on June 15 how ants distinguish the good fungus from the bad.
People rely on sight to identify weeds but ants grow fungus underground in the dark and must have other ways to sense undesirable garden denizens. A team led by Jonathan Klassen, Ph.D., at the ...
Impacts of elevated salinity on microbial interactions within activated sludge microbial community: RMT-based network analysis
2023-06-16
Biological treatment processes are critical for sewage purification, wherein microbial interactions are tightly associated with treatment performance. Previous studies have focused on assessing how environmental factors (such as salinity) affect the diversity and composition of the microbial community but ignore the connections among microorganisms. To fill this gap, an international team of researchers conducted an in-depth analysis of microbial interactions at elevated salinity in activated sludge systems.
Biological ...
Rice University chemist leverages heterogeneity for insight into catalysis, cancer initiation
2023-06-16
HOUSTON – (June 16, 2023) – Rice University chemist Anatoly Kolomeisky has won an award from the National Science Foundation to investigate how heterogeneity affects chemical and biological processes. The goal of his project is to develop analytical models that quantify the role of heterogeneity in various phenomena including catalytic reactions, antimicrobial peptides, early cancer development and lysis, a process describing cellular membrane breakdown.
“We live in a world of heterogeneity,” ...
Significant correlation found between vitreous human biomarkers and Alzheimer’s disease
2023-06-16
BOSTON – New research from Boston Medical Center found a significant correlation between biomarkers in the vitreous humor of the eye and pathologically confirmed cases of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) in post-mortem brain and eye tissue. Published in IOS Press, this exploratory study indicates that biomarkers in the vitreous humor may serve as a proxy for neuropathological disease.
The incidence of dementias like AD continues to rise. As of 2021, 6.2 million North Americans above 65 years of age are suffering from AD, and this number is projected to reach 13.2 million by 2060. Diagnosis of both AD and CTE is based on symptoms, clinical exam ...
Brigid Garelik named Chief Medical Officer of the Children’s Tumor Foundation
2023-06-16
The Children’s Tumor Foundation (CTF) has announced that Brigid Garelik, MD, MPH, has been appointed Chief Medical Officer, overseeing the Foundation’s research and clinical initiatives. In this role, Dr. Garelik will set direction for the Foundation’s innovative R&D programs, developing effective clinical and preclinical strategies in order to deliver treatments to patients. She will also direct the Foundation’s educational programs in support of NF healthcare professionals, growing the NF field, and R&D related patient engagement. She will report to the President of the Children’s Tumor Foundation, Annette Bakker, PhD.
Dr. Garelik is an accomplished ...
Launch of REC@NUS Corporate R&D Laboratory for Next Generation Photovoltaics
2023-06-16
A new SGD 77 million research initiative has been launched today at the National University of Singapore (NUS) to boost innovation and research on advanced solar cell technologies in Singapore. Over the next five years, the REC@NUS Corporate R&D Laboratory for Next Generation Photovoltaics (REC@NUS Corp Lab), which is jointly set up by the Solar Energy Research Institute of Singapore (SERIS) at NUS and REC Solar (REC), will research, develop, and commercialise disruptive solar photovoltaic (PV) technologies based on perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells.
Supported ...
Study finds combustion from gas stoves can raise indoor levels of chemical linked to a higher risk of blood cell cancers
2023-06-16
A chemical linked to a higher risk of leukemia and other blood cell cancers creeps into millions of homes whenever residents light their gas stoves. A new Stanford-led analysis finds that a single gas cooktop burner on high or a gas oven set to 350 degrees Fahrenheit can raise indoor levels of the carcinogen benzene above those in secondhand tobacco smoke. Benzene also drifts throughout a home and lingers for hours in home air, according to the paper published June 22 in Environmental Science & ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] The global human day – A bird’s eye perspectiveHow humans around the world spend their time on an average day