Study finds combustion from gas stoves can raise indoor levels of chemical linked to a higher risk of blood cell cancers
2023-06-16
(Press-News.org)
A chemical linked to a higher risk of leukemia and other blood cell cancers creeps into millions of homes whenever residents light their gas stoves. A new Stanford-led analysis finds that a single gas cooktop burner on high or a gas oven set to 350 degrees Fahrenheit can raise indoor levels of the carcinogen benzene above those in secondhand tobacco smoke. Benzene also drifts throughout a home and lingers for hours in home air, according to the paper published June 22 in Environmental Science & Technology.
“Benzene forms in flames and other high-temperature environments, such as the flares found in oil fields and refineries. We now know that benzene also forms in the flames of gas stoves in our homes,” said study senior author Rob Jackson, the Michelle and Kevin Douglas Provostial Professor and professor of Earth system science at the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability. “Good ventilation helps reduce pollutant concentrations, but we found that exhaust fans were often ineffective at eliminating benzene exposure.”
Worse than secondhand smoke
Overall, the researchers found that indoor concentrations of benzene formed in the flames of gas stoves can be worse than average concentrations from secondhand smoke, that benzene can migrate into other rooms far from the kitchen, and that concentrations measured in bedrooms can exceed national and international health benchmarks. They also found residential range hoods are not always effective at reducing concentrations of benzene and other pollutants, even when the hoods vent outdoors.
The new paper is the first to analyze benzene emissions when a stove or oven is in use. Previous studies focused on leaks from stoves when they are off, and did not directly measure resulting benzene concentrations. The researchers found gas and propane burners and ovens emitted 10 to 50 times more benzene than electric stoves. Induction cooktops emitted no detectable benzene whatsoever. The rates of benzene emitted during combustion were hundreds of times higher than benzene emission rates identified in other recent studies from unburned gas leaking into homes.
The researchers also tested whether foods being cooked emit benzene and found zero benzene emissions from pan-frying salmon or bacon. All benzene emissions the investigators measured came from the fuel used rather than any food cooked.
A previous Stanford-led study showed that gas-burning stoves inside U.S. homes leak methane with a climate impact comparable to the carbon dioxide emissions from about 500,000 gasoline-powered cars. They also expose users to pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide, which can trigger respiratory diseases. A 2013 meta-analysis concluded that children who live in homes with gas stoves had a 42% greater risk of asthma than children living in homes without gas stoves, and a 2022 analysis calculated that 12.7% of childhood asthma in the U.S. is attributable to gas stoves.
“I’m renting an apartment that happens to have an electric stove,” said study lead Yannai Kashtan, a graduate student in Earth system science. “Before starting this research, I never thought about it twice, but the more we learn about pollution from gas stoves, the more relieved I am to be living without a gas stove.”
Jackson is also a senior fellow at the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment and the Precourt Institute for Energy. Study co-authors also include Metta Nicholson and Colin Finnegan, environmental science research professionals in Stanford’s Earth System Science Department; Zutao Ouyang, a physical science research associate in Stanford’s Earth System Science Department; and researchers at PSE Healthy Energy, the University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Lab.
The study was funded by the High Tide Foundation.
To read all stories about Stanford science, subscribe to the biweekly Stanford Science Digest.
How to reduce exposure to pollutants from gas stoves
Beyond ensuring proper ventilation with a range hood or open window, relatively low-cost approaches to reducing exposure to pollutants from gas stoves include:
Use portable induction cooktops, which can be found for less than $50 new.
Use electric kitchenware, such as tea kettles, toaster ovens, and slow cookers.
Where available, take advantage of state and local rebates as well as low- or no-interest loans (such as these programs for California and the San Francisco Bay Area) to offset the cost of replacing gas appliances.
Federal tax credits are available now, and federal rebates should be available later this year or sometime in 2024 to help offset the cost of replacing gas appliances.
-30-
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-16
Leaf arrangements in the earliest plants differ from most modern plants, overturning a long-held theory regarding the origins of a famous mathematical pattern found in nature, research shows.
The findings indicate that the arrangement of leaves into distinctive spirals, that are common in nature today, were not common in the most ancient land plants that first populated the earth’s surface.
Instead, the ancient plants were found to have another type of spiral. This negates a long held theory about the evolution of plant leaf spirals, indicating that they evolved ...
2023-06-16
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that Black veterans have lower rates of lung cancer screening that are not fully explained by demographic and socioeconomic variables, underscoring the need for further qualitative studies on barriers to lung cancer screening as well as evidence-based interventions targeted to Black veterans.
Authors: Neelima Navuluri, M.D., M.P.H., of the Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
2023-06-16
About The Study: The findings of this qualitative study suggest that institutional plans to protect frontline clinicians from the responsibility for allocating scarce resources may be unworkable, especially in a state of chronic crisis. Efforts are needed to directly integrate frontline clinicians into institutional emergency responses and support them in ways that reflect the complex and dynamic realities of health care resource limitation.
Authors: Catherine R. Butler, M.D., M.A., of the University of Washington in Seattle, ...
2023-06-16
A new study by an international team from Africa, Asia and Europe has put forward three criteria for evaluating the success of migration as adaptation in the face of climate change: well-being, equity and sustainability.
The study shows that while migration is increasingly recognised as an effective way to deal with climate risks, or a form of adaptation, it is far from a silver-bullet solution.
For example, remittances – which include flows of money, ideas, skills and goods between migrants and their places of origin – are thought to be key to facilitating adaptation to climate change.
But, drawing on evidence from every continent ...
2023-06-16
A collaborative team led by researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently invented an innovative method for synthesizing high-quality, semiconducting nanomesh at a lower temperature and production cost than conventional methods. The findings will help enable the large-scale production of nanomesh for next-generation electronics.
Nanomesh is a nano-scale material formed from a network of nanowires. For several decades, one-dimensional materials like nanowires made of crystalline inorganic materials have been widely explored as the main driver for emerging electronics, as they have features like mechanical flexibility, ...
2023-06-16
CHICAGO—A new Scientific Statement released today by the Endocrine Society highlights the differences between aspects of aging that are normal and sometimes over-treated, and those such as menopausal symptoms and osteoporosis that can be treated and deserve more attention.
“Hormones and Aging: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement,” reviews the current state of research on hormonal changes with age. The statement focuses on common endocrine-related changes in older people including menopause and the development ...
2023-06-16
About The Study: In critically ill patients with sepsis, compared with intermittent administration, the continuous administration of the antibiotic meropenem did not improve the composite outcome of mortality and emergence of pandrug-resistant or extensively drug-resistant bacteria at day 28.
Authors: Giovanni Landoni, M.D., of the IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute in Milan, Italy, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.10598)
Editor’s ...
2023-06-16
A new weevil species was discovered in Japan’s pristine subtropical forests on Ishigaki Island and Yanbaru National Park in Okinawa.
Renowned for their remarkable biodiversity, the Ryukyu Islands are a chain of subtropical islands distributed between mainland Japan and Taiwan that boast a relatively isolated evolutionary history, and are home to a distinctive and fascinating insect fauna.
Researchers at the Okinawan Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have been placing net traps to monitor insects on Okinawa ...
2023-06-16
A human cell harbors roughly 2 meters of DNA, encompassing the essential genetic information of an individual. If one were to unwind and stretch out all the DNA contained within a single person, it would span a staggering distance – enough to reach the sun and back 60 times over. In order to manage such an astounding volume of biological information, the cell compacts its DNA into tightly packed chromosomes.
“Imagine DNA as a piece of paper upon which all our genetic information is written.” Says Minke A.D. Nijenhuis, co-corresponding author. “The paper is folded into a very tight structure in order to fit all of that ...
2023-06-16
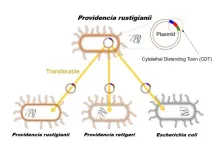
Recently, Providencia spp. which have been detected in patients with gastroenteritis, and similar to enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. O157 and Salmonella spp., have been attracting attention as causative agents of food poisoning. For children with low immunity, food poisoning can be lethal as it causes severe symptoms such as diarrhea and dehydration, so clarifying the source of infection and pathogenic factors of Providencia spp., and establishing preventive methods are urgent issues worldwide.
A joint research group led by Professor Shinji Yamasaki, Dr. Sharda Prasad Awasthi, a Specially Appointed Lecturer, and graduate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study finds combustion from gas stoves can raise indoor levels of chemical linked to a higher risk of blood cell cancers