(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this study suggest that Black veterans have lower rates of lung cancer screening that are not fully explained by demographic and socioeconomic variables, underscoring the need for further qualitative studies on barriers to lung cancer screening as well as evidence-based interventions targeted to Black veterans.
Authors: Neelima Navuluri, M.D., M.P.H., of the Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.18795)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.18795?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=061623
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Racial disparities in lung cancer screening among veterans
JAMA Network Open
2023-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Experiences of clinicians contending with health care resource scarcity during COVID-19
2023-06-16
About The Study: The findings of this qualitative study suggest that institutional plans to protect frontline clinicians from the responsibility for allocating scarce resources may be unworkable, especially in a state of chronic crisis. Efforts are needed to directly integrate frontline clinicians into institutional emergency responses and support them in ways that reflect the complex and dynamic realities of health care resource limitation.
Authors: Catherine R. Butler, M.D., M.A., of the University of Washington in Seattle, ...
When is migration successful adaptation to climate change?
2023-06-16
A new study by an international team from Africa, Asia and Europe has put forward three criteria for evaluating the success of migration as adaptation in the face of climate change: well-being, equity and sustainability.
The study shows that while migration is increasingly recognised as an effective way to deal with climate risks, or a form of adaptation, it is far from a silver-bullet solution.
For example, remittances – which include flows of money, ideas, skills and goods between migrants and their places of origin – are thought to be key to facilitating adaptation to climate change.
But, drawing on evidence from every continent ...
CityU researchers invent a low-temperature synthesis method for high-quality tellurium nanomesh for next-generation electronics
2023-06-16
A collaborative team led by researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently invented an innovative method for synthesizing high-quality, semiconducting nanomesh at a lower temperature and production cost than conventional methods. The findings will help enable the large-scale production of nanomesh for next-generation electronics.
Nanomesh is a nano-scale material formed from a network of nanowires. For several decades, one-dimensional materials like nanowires made of crystalline inorganic materials have been widely explored as the main driver for emerging electronics, as they have features like mechanical flexibility, ...
Endocrine Society Scientific Statement distinguishes normal aging from endocrine disease
2023-06-16
CHICAGO—A new Scientific Statement released today by the Endocrine Society highlights the differences between aspects of aging that are normal and sometimes over-treated, and those such as menopausal symptoms and osteoporosis that can be treated and deserve more attention.
“Hormones and Aging: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement,” reviews the current state of research on hormonal changes with age. The statement focuses on common endocrine-related changes in older people including menopause and the development ...
Continuous vs intermittent meropenem administration in critically ill patients with sepsis
2023-06-16
About The Study: In critically ill patients with sepsis, compared with intermittent administration, the continuous administration of the antibiotic meropenem did not improve the composite outcome of mortality and emergence of pandrug-resistant or extensively drug-resistant bacteria at day 28.
Authors: Giovanni Landoni, M.D., of the IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute in Milan, Italy, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.10598)
Editor’s ...
Japan’s subtropical forests home to a newly discovered beetle species
2023-06-16
A new weevil species was discovered in Japan’s pristine subtropical forests on Ishigaki Island and Yanbaru National Park in Okinawa.
Renowned for their remarkable biodiversity, the Ryukyu Islands are a chain of subtropical islands distributed between mainland Japan and Taiwan that boast a relatively isolated evolutionary history, and are home to a distinctive and fascinating insect fauna.
Researchers at the Okinawan Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have been placing net traps to monitor insects on Okinawa ...
Revolutionary new method can manipulate the shape and packing of DNA
2023-06-16
A human cell harbors roughly 2 meters of DNA, encompassing the essential genetic information of an individual. If one were to unwind and stretch out all the DNA contained within a single person, it would span a staggering distance – enough to reach the sun and back 60 times over. In order to manage such an astounding volume of biological information, the cell compacts its DNA into tightly packed chromosomes.
“Imagine DNA as a piece of paper upon which all our genetic information is written.” Says Minke A.D. Nijenhuis, co-corresponding author. “The paper is folded into a very tight structure in order to fit all of that ...
New insights on bacteria that causes food poisoning
2023-06-16
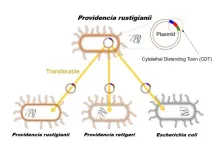
Recently, Providencia spp. which have been detected in patients with gastroenteritis, and similar to enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. O157 and Salmonella spp., have been attracting attention as causative agents of food poisoning. For children with low immunity, food poisoning can be lethal as it causes severe symptoms such as diarrhea and dehydration, so clarifying the source of infection and pathogenic factors of Providencia spp., and establishing preventive methods are urgent issues worldwide.
A joint research group led by Professor Shinji Yamasaki, Dr. Sharda Prasad Awasthi, a Specially Appointed Lecturer, and graduate ...
Alcohol and smoking to blame for premature deaths among night owls, 37-year study suggests
2023-06-16
Staying up late at night has little impact on how long ‘night owls’ live, according to new research published in the peer-reviewed journal Chronobiology International.
Data based on nearly 23,000 twins, however shows that evening types have a slightly increased risk of dying than morning types, but this is largely linked to smoking and drinking.
The study which tracked people over the course of more than 37 years in Finland suggests that lifestyle should be considered.
This is when analyzing the impact on health of chronotype – the body’s natural inclination to sleep at a certain time.
“Our ...
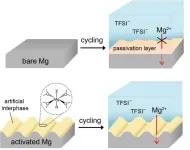
Removing barriers to commercialization of magnesium secondary batteries
2023-06-16
A research team led by Dr. Minah Lee of the Energy Storage Research Center at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology(KIST) has developed a chemical activation strategy of magnesium metal that enables efficient operation of magnesium batteries in common electrolytes that are free of corrosive additives and can be mass-produced.
While the demand for lithium-ion batteries is exploding due to the rapid growth of the electric vehicle and energy storage system(ESS) markets, the supply and demand of their raw materials such as lithium and cobalt ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
[Press-News.org] Racial disparities in lung cancer screening among veteransJAMA Network Open