(Press-News.org) CHICAGO—The percent of metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), the leading global cause of liver disease, is increasing in U.S. adults, according to a study presented Friday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
Mexican Americans consistently had the highest percentage of MAFLD, especially in 2018, although the prevalence of increase was higher among Whites, the study found.
MAFLD, previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is fast becoming the most common indication for liver transplantation. It is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and a common type of liver cancer. If untreated, MAFLD can lead to liver cancer and liver failure.
“MAFLD affects Hispanics at a higher prevalence relative to Blacks and Whites. This racial/ethnic disparity is a public health concern,” said researcher Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D., Chair of the Department of Internal Medicine at Charles R. Drew University of Medicine & Science in Los Angeles, Calif. “Overall, the increase in MAFLD is concerning, as this condition can lead to liver failure and cardiovascular diseases and has an important health disparity.”
The researchers analyzed data for 32,726 participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 1988 to 2018. “We found that overall, both MAFLD and obesity increased with time, with the increase in MAFLD greater than the increase in obesity,” Friedman said.
“The percent of people with MAFLD increased from 16% in 1988 to 37% in 2018 (a 131% increase) while the percent of obesity rose from 23% in 1988 to 40% in 2018 (a 74% increase),” said the study’s first author Magda Shaheen, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., M.S., of Charles R. Drew University of Medicine & Science. “The prevalence of MAFLD increased faster than the prevalence of obesity, suggesting that the increase in the other risk factors such as diabetes and hypertension may also contribute to the increase in the prevalence of MAFLD.”
Among Mexican Americans, the percent of MAFLD was higher at all times compared to the overall population. The percent increase of MAFLD in 2018 relative to 1988 was 133% among Whites, 61% among Mexican Americans and 56% among Blacks.
“In summary, MAFLD is increasing with time and more efforts are needed to control this epidemic,” Shaheen said.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
Prevalence of metabolic associated fatty liver disease is increasing
2023-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
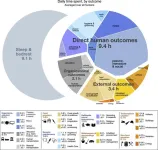
The global human day – A bird’s eye perspective
2023-06-16
Everyone has 24 hours per day. Across the global population of 8 billion people this adds up to approximately 190 billion human hours per day. How those hours are spent determines the impacts we have on our surroundings as well as how we experience life. To find out how people around the world use their time, a research team led by McGill University has gathered and analyzed information about both economic and non-economic activities in order to estimate, for the first time, what a day in the life of the world looks like.
“At present, we are struggling to come to terms with global challenges, and that calls for fresh perspectives on how the world ...
Planned reform of EU pharmaceutical legislation: early market access and robust evidence need not be a contradiction
2023-06-16
The European Commission's stated aim is to improve access to innovative drugs at the national level throughout the EU. Firstly, according to the proposal for the reform of EU pharmaceutical legislation, there are still considerable differences in access between countries. Secondly, drug development has so far only been geared to a limited extent to the actual needs of patients. According to the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), the latter point is in line with the perspective of the ...
Dads are key in supporting breastfeeding, safe infant sleep
2023-06-16
Findings highlight racial disparities in sudden unexpected infant death in the U.S.
Only 16% fathers followed all three AAP-recommended infant sleep practices
Rates of breastfeeding initiation and breastfeeding at eight weeks were much higher among fathers who wanted their infant’s mother to breastfeed than those who did not or had no opinion
CHICAGO --- Fathers can make a huge difference in whether an infant is breastfed and placed to sleep safely, according to a recent survey of new fathers led by scientists at Northwestern University and the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
The study included 250 fathers who ...
AI could replace humans in social science research
2023-06-16
In an article published yesterday in the prestigious journal Science, leading researchers from the University of Waterloo, University of Toronto, Yale University and the University of Pennsylvania look at how AI (large language models or LLMs in particular) could change the nature of their work.
“What we wanted to explore in this article is how social science research practices can be adapted, even reinvented, to harness the power of AI,” said Igor Grossmann, professor of psychology at Waterloo.
Grossmann and colleagues note ...
Research hints at how fungus farming ants keep their gardens healthy
2023-06-16
‘Weed early and often’ is the key to a productive garden. Interestingly, certain species of ants are also avid gardeners, a practice they’ve refined over 50 million years. They too weed their underground fungus gardens, but how they know what to weed out has been a mystery. Now, a multidisciplinary team of scientists report in PNAS on June 15 how ants distinguish the good fungus from the bad.
People rely on sight to identify weeds but ants grow fungus underground in the dark and must have other ways to sense undesirable garden denizens. A team led by Jonathan Klassen, Ph.D., at the ...
Impacts of elevated salinity on microbial interactions within activated sludge microbial community: RMT-based network analysis
2023-06-16
Biological treatment processes are critical for sewage purification, wherein microbial interactions are tightly associated with treatment performance. Previous studies have focused on assessing how environmental factors (such as salinity) affect the diversity and composition of the microbial community but ignore the connections among microorganisms. To fill this gap, an international team of researchers conducted an in-depth analysis of microbial interactions at elevated salinity in activated sludge systems.
Biological ...
Rice University chemist leverages heterogeneity for insight into catalysis, cancer initiation
2023-06-16
HOUSTON – (June 16, 2023) – Rice University chemist Anatoly Kolomeisky has won an award from the National Science Foundation to investigate how heterogeneity affects chemical and biological processes. The goal of his project is to develop analytical models that quantify the role of heterogeneity in various phenomena including catalytic reactions, antimicrobial peptides, early cancer development and lysis, a process describing cellular membrane breakdown.
“We live in a world of heterogeneity,” ...
Significant correlation found between vitreous human biomarkers and Alzheimer’s disease
2023-06-16
BOSTON – New research from Boston Medical Center found a significant correlation between biomarkers in the vitreous humor of the eye and pathologically confirmed cases of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) in post-mortem brain and eye tissue. Published in IOS Press, this exploratory study indicates that biomarkers in the vitreous humor may serve as a proxy for neuropathological disease.
The incidence of dementias like AD continues to rise. As of 2021, 6.2 million North Americans above 65 years of age are suffering from AD, and this number is projected to reach 13.2 million by 2060. Diagnosis of both AD and CTE is based on symptoms, clinical exam ...
Brigid Garelik named Chief Medical Officer of the Children’s Tumor Foundation
2023-06-16
The Children’s Tumor Foundation (CTF) has announced that Brigid Garelik, MD, MPH, has been appointed Chief Medical Officer, overseeing the Foundation’s research and clinical initiatives. In this role, Dr. Garelik will set direction for the Foundation’s innovative R&D programs, developing effective clinical and preclinical strategies in order to deliver treatments to patients. She will also direct the Foundation’s educational programs in support of NF healthcare professionals, growing the NF field, and R&D related patient engagement. She will report to the President of the Children’s Tumor Foundation, Annette Bakker, PhD.
Dr. Garelik is an accomplished ...
Launch of REC@NUS Corporate R&D Laboratory for Next Generation Photovoltaics
2023-06-16
A new SGD 77 million research initiative has been launched today at the National University of Singapore (NUS) to boost innovation and research on advanced solar cell technologies in Singapore. Over the next five years, the REC@NUS Corporate R&D Laboratory for Next Generation Photovoltaics (REC@NUS Corp Lab), which is jointly set up by the Solar Energy Research Institute of Singapore (SERIS) at NUS and REC Solar (REC), will research, develop, and commercialise disruptive solar photovoltaic (PV) technologies based on perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells.
Supported ...