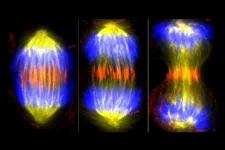
(Press-News.org) It is a scary fact that one in two women and one in three men in the United States will develop some form of cancer in their lifetime. One of the hallmarks of many cancers is the occurrence of errors during the cell division process called mitosis. Therefore, critical to enhancing treatments or perhaps even finding a cure for cancer and other diseases, is developing a better understanding of how mitosis works in both healthy and diseased cells.
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute’s Scott Forth, Ph.D., assistant professor of biological sciences and member of the Shirley Ann Jackson, Ph.D. Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies, has made understanding the cell’s complicated mechanical tasks, such as those needed for mitosis, his life’s work. Recently, he was awarded a $1.6 million grant over five years by the National Institutes of Health to further his research.
With this grant, Forth will explore the mechanical code that underlies the assembly and function of force-generating cytoskeletal networks, using mitosis as a model biological process. One way that cells prepare to divide into two is by duplicating their contents, including chromosomes. Cells then assemble their cytoskeletal networks to produce forces that physically segregate chromosomes into each of two new cells. Errors in this process are linked to cancer.
“Though decades of research has identified a majority of the biological 'parts' that are involved, we still do not understand the mechanical rules that dictate how all of these tiny individual pieces work together as ensembles to accomplish goals like the reliable segregation of DNA into two new daughter cells,” said Forth.
Within the cytoskeleton are micron-scale microtubule networks that need both motor and non-motor proteins to move and organize filaments into proper, functional mechanical units that produce the forces needed to pull chromosomes apart. To better understand how they work, Forth will employ a variety of techniques such as biochemical reconstitution, single-molecule fluorescence microscopy, optical trapping, and live-cell imaging. Biochemical reconstitution employs purified proteins to mimic intracellular processes outside of the cell, and optical trapping is a method for measuring the tiny forces that proteins can generate. Fluorescence microscopy will be used at the same time to watch individual molecules respond to these forces, while live cell imaging will be performed to confirm these biophysical measurements in real dividing cells.
With this grant, Forth hopes to gain three new insights. First, his lab will determine the mechanical and functional differences between bridging fibers in metaphase, when chromosomes are first being properly centered within the cell, and the central spindle microtubule network in anaphase, when chromosomes are being pulled away from each other. Second, he will determine the molecular mechanisms that regulate how microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) cluster to form novel cellular “building blocks,” and decipher the functional role of MAP clusters in regulating microtubule organization. Third, his lab will determine how complexes of motor and non-motor MAPs collectively regulate microtubule organization during later stages of mitosis to help ensure proper division of the two cells.
“Dr. Forth’s work in cellular physics informs our understanding of diseases, such as cancer, that occur when cell structures fail,” said Curt Breneman, Ph.D., dean of Rensselaer’s School of Science. “With this grant, Dr. Forth will gain new insights into molecular mysteries that may forge a path to the development of new diagnostics and treatments.”
About Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute:
Founded in 1824, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute is America’s first technological research university. Rensselaer encompasses five schools, over 30 research centers, more than 140 academic programs including 25 new programs, and a dynamic community made up of over 6,800 students and 110,000 living alumni. Rensselaer faculty and alumni include upwards of 155 National Academy members, six members of the National Inventors Hall of Fame, six National Medal of Technology winners, five National Medal of Science winners, and a Nobel Prize winner in Physics. With nearly 200 years of experience advancing scientific and technological knowledge, Rensselaer remains focused on addressing global challenges with a spirit of ingenuity and collaboration. To learn more, please visit www.rpi.edu.
Contact:
Katie Malatino
Sr. Communications Specialist
malatk@rpi.edu
838-240-5691
For general inquiries: newsmedia@rpi.edu
Visit the Rensselaer research and discovery blog: https://everydaymatters.rpi.edu/
Follow us on Twitter: @RPINews
END
Rensselaer researcher to investigate the mechanics of mitosis to combat cancer
Scott Forth receives $1.6 million grant to explore how chromosomes are segregated during cell division
2023-06-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mason College of Public Health researchers reveal how digital contact tracing applications can be utilized now that the pandemic is over
2023-06-20
During the pandemic, contact tracing apps kept Americans informed of potential exposure risk with the goal of reducing infections. But did apps like this help reduce the spread of COVID and how might we improve these apps for use in future outbreaks?
Contact tracing is a pivotal part of pandemic preparedness. Evidence-based research on best practices for contact tracing is important because when employed inefficiently contact tracing drains resources. Used effectively, contact tracing slows the spread of disease and saves lives. In the past, contact tracing was done through health ...
UNCG spin-off launches national study to help prevent opioid misuse
2023-06-20
Prevention Strategies received a grant from the National Institutes of Health to pursue the study and develop a commercially viable intervention tool based on prevention science. Known as WorkWell, it is a tailored mobile health app that represents the next generation of evidence-based, technology-aided intervention programs.
The initial pilot program to test the WorkWell app will focus on construction trade workers and nurses, as well as nursing assistants and technicians. These occupations have been disproportionately impacted by the opioid crisis and have high mortality ratios.
“Opioid-involved overdoses are among the leading causes of death in the United States despite extensive ...
UTHealth Houston study on repeated radiofrequency ablation in combination with chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer supported with $3.3M HHS grant
2023-06-20
A combination strategy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA) with chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer will be studied at UTHealth Houston through a $3.3 million grant from the National Cancer Institute by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The survival rate of pancreatic adenocarcinoma, or pancreatic cancer, remains low, around 10%, because of its poor response to current chemotherapies.
The five-year grant will continue the established six-year clinical and translational research collaboration between Jennifer Bailey-Lundberg, ...
Breast cancer research team pulls in $3 million in national support
2023-06-20
UTHSC researchers working to find new treatments to combat breast cancer metastasis recently pulled in a major national award. Wei Li, PhD, distinguished professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences and director of the Drug Discovery Center in the College of Pharmacy, and Tiffany Seagroves, PhD, professor of Pathology in the College of Medicine, are principal investigators on a $3.07 million grant from the National Cancer Institute for a project to develop a new series of drugs targeting microtubules to stop the spread of breast cancer to the brain and bone. Duane Miller, PhD, professor emeritus, and Zhongzhi Wu, PhD, assistant professor, both in ...
Science in the shadows: NASA selects 5 experiments for 2024 total solar eclipse
2023-06-20
A total solar eclipse will darken a swath of North America as the Moon blocks the light of the Sun for a few minutes on April 8, 2024. In addition to casting a breathtaking, passing shadow over the heads of millions of people, this total solar eclipse gives scientists a unique opportunity to study the Sun, Earth, and their interactions.
NASA will fund five interdisciplinary science projects for the 2024 eclipse to make the most of this opportunity. The projects, which are led by researchers at different academic institutions, will study the Sun and its influence on Earth with a variety of instruments, including cameras aboard high-altitude research planes, ham radios, and ...
Dupilumab lessens disease in COPD patients with type 2 inflammation
2023-06-20
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with type 2 inflammation saw rapid and sustained improvements in their disease after treatment with the monoclonal antibody dupilumab, according to a yearlong, Phase 3 clinical trial reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
These improvements — as measured by a significantly lower annualized rate of acute exacerbations, significantly better lung function and quality of life, and significantly less severe symptoms than placebo-treated adults with COPD — were observed within two to four weeks after the initiation of dupilumab and were sustained throughout the 52-week trial period. This monoclonal antibody ...
Scientists discover new embryonic cell type that self-destructs to protect the developing embryo
2023-06-20
Scientists studying gene activity data of the early human embryo have discovered an overlooked type of cell which self-destructs within days of forming, as part of a quality control process to protect the developing foetus. The findings give insights on what happens at the very first stages of life after fertilisation which could in the future help improve IVF or regenerative medicine treatments.
A new study published on 20 June 2023 in PLoS Biology by an international team of scientists including researchers at the University of Bath, finds that our earliest development in the womb may be rather different to what we have always assumed.
While ...
National Geographic Explorers win award for visualizing arctic climate change
2023-06-20
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: June 20, 2023 - Washington, D.C. - An innovative virtual reality project created by National Geographic Explorers in collaboration with local communities was recognized with the “Best in Category: Visualize” during the XR Prize Challenge: Fight Climate Change earlier this month. The project, “Qikiqtaruk: Arctic at Risk” was selected for the award from across 150 submissions at the Augmented World Expo (AWE) in Santa Clara, California on June 1, 2023.
“Qikiqtaruk: Arctic at Risk” brought together researchers, park rangers, educators and immersive content ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers develop first-of-its-kind adhesive bandage that can detect COVID-19 antibodies
2023-06-20
Abu Dhabi, UAE, June 20, 2023: Researchers at NYU Abu Dhabi have developed a new rapid testing method for COVID-19 – an adhesive bandage that relies on gold nanoparticles to quickly detect the immune antibodies in the bloodstream.
These antibodies, named IgM and IgG, are naturally produced as a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and therefore serve as valuable biomarkers to identify infected individuals and monitor the spread of pandemics. The innovative bandage technology is affordable and easy-to-use, and ...
Alissa Park appointed Dean of UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science
2023-06-20
Ah-Hyung “Alissa” Park has been appointed the Ronald and Valerie Sugar Dean of the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science, effective September 1.
One of the nation’s leading experts on carbon capture and conversion technology, Park is currently the Lenfest Earth Institute Professor of Climate Change and chair of the department of earth and environmental engineering at Columbia University, where she has been a faculty member since 2007. She also is director of the Lenfest Center for Sustainable Energy, an executive committee ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
[Press-News.org] Rensselaer researcher to investigate the mechanics of mitosis to combat cancerScott Forth receives $1.6 million grant to explore how chromosomes are segregated during cell division