(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Fifteen years of archaeological work in the Tam Pa Ling cave in northeastern Laos has yielded a reliable chronology of early human occupation of the site, scientists report in the journal Nature Communications. The team’s excavations through the layers of sediments and bones that gradually washed into the cave and were left untouched for tens of thousands of years reveals that humans lived in the area for at least 70,000 years – and likely even longer.
“When we first started excavating the cave, we never expected to find humans in that region,” said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign anthropology professor Laura Shackelford, who led the research with Fabrice Demeter, a professor of anthropology at the University of Copenhagen. “But beginning that first season when we started work there, we found our first modern humans. At the time, that made them the only early modern human fossils in the region.”
While the remains of modern Homo sapiens dating back roughly 197,000 years have been recovered in Israel, genetic studies suggest the main phase of early human migration out of Africa and into Asia occurred much later – around 50,000 years ago, Shackelford said. Her team’s earliest excavations in Tam Pa Ling found bone fragments from modern human remains dating to about 40,000 years ago. But as the excavations dug deeper, the age of sediments and animal remains found alongside human bones dated back much earlier.
In 2019, the team had excavated as far as they could in the cave, reaching bedrock about 23 feet (7 meters) below the surface. The excavations yielded dozens of animal bones and many fragments of human skeletal remains. The deepest human bone recovered – a partial tibia – was resting on bedrock near the bottom of the trench. Analyses of sediments taken not far above this bone indicate the soil was deposited there between 67,000 and 90,000 years ago.
“The entire section of the trench goes from about 30,000 years ago to 80,000 to 100,000 years ago,” Shackelford said. “Flood season after flood season, the sediments and bones washed into the cave and were deposited. They’ve been sitting there ever since.”
The team used a variety of techniques to date the sediments and nonhuman mammal bones found at different depths in the cave. For the soil samples, the researchers relied primarily on a technique called optically stimulated luminescence, which reveals how much time has elapsed since sediments were last exposed to light. Numerous soil samples were collected from the cave in total darkness and taken back to the laboratory for analysis.
The researchers used several other techniques to date the soils, human and animal bones and teeth found at different depths in the trench.
The human remains were fragmentary, but the site yielded two pieces of skull – both from the frontal region of the head – one of which dated to about 35,000 years ago and the other much older, dating to roughly 67,000 years ago, Shackelford said.
At first, a comparison of the physical characteristics of the fossils baffled the researchers, Shackelford said.
"What we saw was that the youngest fossils, the first ones we found, looked old,” she said. “And the oldest fossils that we found at the very bottom looked younger. It was the opposite of what we would expect to find because as you get deeper in time, you think of things becoming more archaic, more like ancestral populations.”
There are two potential explanations for the differences between the older and younger fossils, Shackelford said. One, the older fossil may be from an ancestral population that had more modern characteristics than their descendants, who interbred with people with more archaic features. The other possibility is that the two skulls represent two distinct migrations into the region.
“We don’t know how they’re related, but we have two very different looking groups of humans,” Shackelford said. “The older fossil was most likely part of an early migration – a failed migration because it did not give rise to people who are still alive today.”
The team was unable to extract viable DNA from the human remains, a common problem in studies of ancient remains from tropical sites, Shackelford said.
“I think the only way to settle our questions is with genetic data,” she said. The team is preserving the human fossils in a freezer in the hopes that more refined DNA extraction and analysis techniques will one day yield more answers.
The National Geographic Society supported this research.
Editor’s note:
To reach Laura Shackelford, email llshacke@illinois.edu.
To reach Fabrice Demeter, email f.demeter@sund.ku.dk.
The paper “Early presence of Homo sapiens in southeast Asia by 86-68 kyr at Tam Pa Ling, northern Laos” is available online or from the U. of I. News Bureau.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-38715-y
END
Cave excavation pushes back the clock on early human migration to Laos
2023-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New microcomb device advances photonic technology
2023-06-21
A new tool for generating microwave signals could help propel advances in wireless communication, imaging, atomic clocks, and more.
Frequency combs are photonic devices that produce many equally spaced laser lines, each locked to a specific frequency to produce a comb-like structure. They can be used to generate high-frequency, stable microwave signals and scientists have been attempting to miniaturize the approach so they can be used on microchips.
Scientists have been limited in their abilities to tune these microcombs at a rate to make them effective. But a team of researchers ...
Now, every biologist can use machine learning
2023-06-21
By Lindsay Brownell
(BOSTON) — The amount of data generated by scientists today is massive, thanks to the falling costs of sequencing technology and the increasing amount of available computing power. But parsing through all that data to uncover useful information is like searching for a molecular needle in a haystack. Machine learning (ML) and other artificial intelligence (AI) tools can dramatically speed up the process of data analysis, but most ML tools are difficult for non-ML experts to access and use. Recently, automated machine learning (AutoML) methods have been developed that can automate the design and deployment ...
University of Toronto Engineering researchers are using electric fields to control the movement of defects in crystals
2023-06-21
An international team of researchers, led by University of Toronto Engineering Professor Yu Zou, is using electric fields to control the motion of material defects. This work has important implications for improving the properties and manufacturing processes of typically brittle ionic and covalent crystals, including semiconductors — a crystalline material that is a central component of electronic chips used for computers and other modern devices.
In a new study published in Nature Materials, researchers from ...
Assessment of a peer support group intervention for undocumented Latinx immigrants with kidney failure
2023-06-21
About The Study: This study of 23 undocumented immigrants with kidney failure receiving emergency dialysis found that a peer support group intervention achieved feasibility and acceptability. The findings suggest that a peer support group may be a patient-centered strategy to build camaraderie and provide emotional support in kidney failure, especially for socially marginalized uninsured populations who report limited English proficiency.
Authors: Lilia Cervantes, M.D., of the University of Colorado, Anschutz Medical Campus, in Aurora, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Biodegradable gel shows promise for cartilage regeneration
2023-06-21
A gel that combines both stiffness and toughness is a step forward in the bid to create biodegradable implants for joint injuries, according to new UBC research.
Mimicking articular cartilage, found in our knee and hip joints, is challenging. This cartilage is key to smooth joint movement, and damage to it can cause pain, reduce function, and lead to arthritis. One potential solution is to implant artificial scaffolds made of proteins that help the cartilage regenerate itself as the scaffold biodegrades. How well the cartilage regenerates is linked to how well a scaffold can mimic the biological properties of cartilage, and to date, researchers have struggled ...
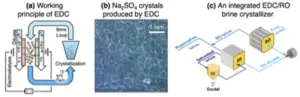
New study in Nature Water demonstrates a vastly more sustainable, cost-effective method to desalinate industrial wastewater
2023-06-21
Vanderbilt researchers are part of a team that has developed a cutting-edge method that seeks to make the removal of salt from hypersaline industrial wastewater far more energy-efficient and cost-effective.
While desalination through reverse osmosis has made tremendous strides—allowing for salt removal from seawater for less than a penny per gallon—it still falls short in eliminating saline in wastewater from industries like mining, oil and gas and power generation and in inland brackish water. The industrial brines are currently injected into deep geological formations or transferred to a evaporation ponds, and both disposal methods are facing more regulatory and ...
Researchers reveal mechanism of protection against breast and ovarian cancer
2023-06-21
In a new paper published today in Nature, researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have outlined the structure and function of a protein complex which is required to repair damaged DNA and protect against cancer.
Every time a cell replicates, mistakes can happen in the form of mutations, but specialised proteins exist to repair the damaged DNA.
People with mutations in a DNA repair protein called BRCA2 are predisposed to breast, ovarian and prostate cancers, which often develop at a young age. In the clinic, these cancers are treated with a drug that inhibits PARP, ...
Atoms realize a Laughlin state
2023-06-21
The discovery of the quantum Hall effects in the 1980's revealed the existence of novel states of matter called "Laughlin states", in honor of the American Nobel prize winner who successfully characterized them theoretically. These exotic states specifically emerge in 2D materials, at very low temperature and in the presence of an extremely strong magnetic field. In a Laughlin state, electrons form a peculiar liquid, where each electron dances around its congeners while avoiding them as much as possible. Exciting such a quantum liquid generates collective states that physicists associate to fictitious particles, whose ...
Ovarian cancer study identifies key genes for potential treatments
2023-06-21
New research is increasing our understanding about why some women with the most lethal form of ovarian cancer respond much better to treatment than others.
Researchers at Imperial College London have confirmed that the tumours of some women with high-grade serious ovarian cancer (HGSOC) contain a type of lymphoid tissue – known as tertiary lymphoid structures, or TLS – and that the presence of this tissue gives women a significantly better prognosis. They have also identified genes in HGSOC ...
Detection of an echo emitted by our Galaxy's black hole 200 years ago
2023-06-21
An international team of scientists has discovered that Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*)1, the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way, emerged from a long period of dormancy some 200 years ago. The team, led by Frédéric Marin2, a CNRS researcher at the Astronomical Strasbourg Observatory (CNRS/University of Strasbourg), has revealed the past awakening of this gigantic object, which is four million times more massive than the Sun. Their work is published in Nature on 21 June. Over a period of one year at the beginning of the 19th century, the black ...