(Press-News.org) With malaria becoming increasingly drug-resistant, a team of UCF researchers is looking to use cancer drugs to accelerate the discovery of new life-saving therapies for the disease.
In a study funded by a 5-year $3.8 million grant from the National Institutes of Health, UCF molecular parasitologist Debopam Chakrabarti and cancer molecular biologist Ratna Chakrabarti are partnering with Nathanael Gray, co-leader of the cancer therapeutics research program at Stanford University and Elizabeth Winzeler, a malaria drug development expert from the University of California San Diego, to test cancer drugs for malaria-fighting properties. Their most recent findings were recently published in the ACS Infectious Diseases journal.
Caused by parasites belonging to Plasmodium species and transmitted by the bite of infected mosquitoes, malaria is life-threatening and is one of the world’s most common infectious diseases. It is responsible for over 600,000 deaths per year, predominantly in sub-Saharan Africa. About 80 percent of these deaths are children under age 5.
“Over time, genetic mutation of the malaria parasite makes it resistant to current drugs,” Chakrabarti says. “The World Health Organization reported that malaria parasites are increasingly becoming resistant to the current therapy used to treat malaria, which was discovered in the 1990s. So, new and more effective drugs for malaria are long overdue as about 30 years have gone by since we have had a new class of compounds in the market against malaria.”
But drug discoveries can take years, even decades, Chakrabarti explained, as compounds go through many phases of testing for efficacy and safety.
“One of the ways we can accelerate the discovery of new treatment options is to use existing drugs that are already approved by the Food and Drug Administration,” Chakrabarti saiys. “This is called taking a piggyback approach, looking at existing drugs that are already on the market to see if they have anti-malarial properties. This will help to shorten the initial stages of drug discovery which is usually quite time-consuming.”
To meet the urgent need for new drugs, the team decided to repurpose protein kinase inhibitors — drugs originally developed for cancer treatment — for an accelerated path to drug therapy for malaria. Protein kinases are enzymes that regulate proteins in the body and are heavily targeted for cancer and other disease therapies by the pharmaceutical industry. Protein kinases are very important for the malaria parasite’s life cycle and as such make good drug targets.
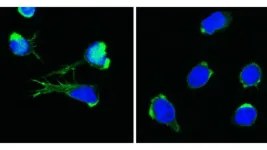
As part of the study, Ph.D. candidate Monica Bohmer, working under Chakrabarti’s supervision, tested a range of anti-cancer protein kinase inhibitors to identify inhibitors that are known to target human Polo-like kinase, a type of protein kinase that plays an important role in cell division in humans. She discovered that a group of inhibitors, specifically BI-2536, a known human Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor, exhibited strong anti-malarial properties.
“While the malaria parasite plasmodium does not have Polo-like kinases, the protein kinase inhibitors targeted another family of proteins called NEK, which also regulate cell division,” Bohmer says. “They also targeted other stress-response pathways which helped to kill the parasite.”
She added that future studies will explore the functions of these NEK proteins in the parasite.
“Overall, this study provides valuable insights for the potential of repurposing of protein kinase inhibitors for malaria treatment,” Chakrabarti says “while also underscores the need for further research to identify additional targets and optimize the efficacy of these inhibitors.”
Chakrabarti has been researching malaria at UCF for more than 25 years. A professor and head of the Molecular Microbiology division in the Burnett School of Biomedical Sciences, he joined the university in 1995 and was one of the first UCF faculty members to receive an NIH grant. He received his doctorate in biochemistry from the University of Calcutta and did post-doctoral training in molecular biology at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
END
Cancer drugs show potential in fight against malaria
In a study funded by a 5-year $3.8 million grant from the National Institutes of Health, UCF researchers are partnering with scientists at Stanford University and the University of California San Diego to test cancer drugs for malaria-fighting properties
2023-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newly discovered genetic defect disrupts blood formation and immune system
2023-06-21
(Vienna, 21.06.2023) In the quest to find the origin of the puzzling symptoms in four children, researchers from St. Anna Children's Cancer Research Institute, the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW), and the Medical University of Vienna have discovered a completely new disease, linking disruptions of blood formation, the immune system, and inflammation. This groundbreaking discovery provides the basis for a better understanding of similar diseases. It is a milestone that the researchers have now published ...
New study reveals number and strength of head impacts, not concussions, drive CTE risk in football
2023-06-21
Does a football player’s number of concussions drive the risk of developing chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)? In a new study of 631 deceased football players, the largest CTE study to date, scientists found that the number of diagnosed concussions alone was not associated with CTE risk. Instead, football players’ odds of developing CTE were related to both how many head impacts they received and how hard the head impacts were.
The study, conducted by researchers at Mass General Brigham, Harvard Medical School, and Boston University (BU), was published today in Nature Communications. It ...
ASPB Journals launch Author Travel Awards
2023-06-21
ROCKVILLE, MD - Authors whose work has been published in Plant Physiology or The Plant Cell, leading international society journals published by the American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB), have a new option to support their travel to share their research with the scientific community. Funded by Plant Physiology and The Plant Cell, US$1,000 travel awards will be awarded to authors who have received invitations to give an oral presentation at any conference or scientific meeting around the world. Five US$1,000 awards are available in 2023 with more awards anticipated for 2024 ...
Scientists discover mechanism affecting heart development in Down syndrome
2023-06-21
Infants born with Down syndrome, the genetic condition caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21, or trisomy 21, are highly predisposed to congenital heart defects. It is estimated that nearly half of newborns with Down syndrome have a congenital heart malformation, and Down syndrome is recognized as the most common cause of congenital heart abnormalities. Despite many research efforts over several decades, the mechanisms by which trisomy 21 prevents proper formation of the heart during embryonic development have remained unknown.
A recent study by scientists ...
Combining twistronics with spintronics could be the next giant leap in quantum electronics
2023-06-21
Twistronics isn’t a new dance move, exercise equipment, or new music fad. No, it’s much cooler than any of that. It is an exciting new development in quantum physics and material science where van der Waals materials are stacked on top of each other in layers, like sheets of paper in a ream that can easily twist and rotate while remaining flat, and quantum physicists have used these stacks to discover intriguing quantum phenomena.
Adding the concept of quantum spin with twisted double bilayers of an antiferromagnet, it is possible to have tunable moiré magnetism. This suggests a new class of material platform for the next step in twistronics: ...
Omega-3 fatty acids linked to slower decline in ALS
2023-06-21
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 21, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS - People with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) who eat more foods high in certain omega-3 fatty acids like flaxseed oil, walnuts, canola oil and pumpkin seeds may have a slower physical decline from the disease and may have a slightly extended survival. The study, which looked at the survival of people with ALS over the course of 18 months, was published in the June 21, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Researchers also found an omega-6 ...
Is TBI a chronic condition?
2023-06-21
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 21, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People with TBI may continue to improve or decline years after their injury, making it a more chronic illness, according to a study published in the June 21, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our results dispute the notion that TBI is a one-time event with a stagnant outcome after a short period of recovery,” said study author Benjamin L. Brett, PhD, of the Medical College ...
Omega-3 fatty acids linked with slower progression of ALS
2023-06-21
Key points:
In an 18-month study, people living with ALS who had higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids in their blood were found to have slower decline in physical functionality and lower risk of premature death compared to those with lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids.
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)—an omega-3 fatty acid found in many nuts, seeds, and oils—showed the strongest link to slower disease progression. Those with higher levels of ALA had a 50% lower risk of dying during the study period compared to those with lower levels of ALA.
Embargoed for release: Wednesday, June 21, 2023, 4:00 PM ET
Boston, MA—Consuming omega-3 fatty acids—particularly ...
A UCI-led study found that plant extracts used by indigenous people hold promise in treatment of ataxia
2023-06-21
Irvine, CA – June 21, 2023 – A University of California, Irvine-led team of researchers have discovered that extracts from plants used by the Kwakwaka’wakw First Nations peoples in their traditional botanical medicine practices are able to rescue the function of ion channel proteins carrying mutations that cause human Episodic Ataxia.
The study, “Native American ataxia medicines rescue ataxia-linked mutant potassium channel activity via binding to the voltage sensing domain” was published in June in Nature Communications.
“Episodic Ataxia 1 (EA1) is a movement disorder caused by inherited mutations ...
An app can transform smartphones into thermometers that accurately detect fevers
2023-06-21
If you’ve ever thought you may be running a temperature yet couldn’t find a thermometer, you aren’t alone. A fever is the most commonly cited symptom of COVID-19 and an early sign of many other viral infections. For quick diagnoses and to prevent viral spread, a temperature check can be crucial. Yet accurate at-home thermometers aren’t commonplace, despite the rise of telehealth consultations.
There are a few potential reasons for that. The devices can range from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Cancer drugs show potential in fight against malariaIn a study funded by a 5-year $3.8 million grant from the National Institutes of Health, UCF researchers are partnering with scientists at Stanford University and the University of California San Diego to test cancer drugs for malaria-fighting properties