(Press-News.org) A stable economic and political environment is necessary for firms to feel secure while making long-term investment decisions, such as those related to investing in foreign countries (also known as foreign direct investment or FDI). Any threat to change legislative procedures in the foreign country can make it difficult for firms to predict the outcomes of such decisions. Populist leaders, who claim to represent the will of the people, often come to power by threatening to alter the established rules and procedures, generating a more uncertain landscape for multinationals.
Due to these changes, firms and investors find it difficult to navigate the uncertain investment climate, and managers are discouraged from making immediate irreversible decisions. Now, in a new Global Strategy Journal study, researchers examine this issue further to understand how the presence of populist rulers affects investment decisions in democratic countries.
“We reasoned that countries with populist leaders at the helm are less likely the target of firms planning to make FDI decisions,” says Margherita Corina, the study’s co-author. Corina and her colleague, Alfonso Carballo Perez, both professors at NEOMA Business School, also hypothesized that countries with strong country-level institutional frameworks and firms with higher levels of international presence can moderate these negative effects. The authors used data from U.S. multinationals in 37 democratic countries from 1999 to 2020 to study and validate their hypothesis.
The study revealed that the presence of populist leaders in government harms firm foreign investment based on the increasing uncertainty generated by populists’ discourses. Elaborating further, Corina says, “Since foreign investment is often not easily reversible and populism threatens to drastically change institutions, firms will be even more cautious in their investment decisions once a populist government takes office in a country. Therefore, managers may prefer to postpone their actions to obtain more information.”
The authors also found that these negative effects can be moderated by a strong institutional environment and the level of firm internationalization. Institutional frameworks with weak protection to foreign investment may create challenges for the expansion of multinational companies in the context of populism since the threats of their rulers can be seen as more credible and generate institutional volatility.
Furthermore, businesses with higher levels of internationalization are better equipped to navigate the challenges posed by populist leaders. This might be due to their experience of operating in foreign markets and their ability to adapt to political and economic changes.
With populism emerging as a persistent global phenomenon, these findings may be particularly important for multinational company managers dealing with political uncertainty.
“Given the irreversible nature of investment decisions, managers may find it difficult to make investment decisions in countries where populist leaders target multinational organizations. Firms may be better able absorb any risk by diversifying to other countries,” explains Carballo.
In summary, this study offers important insights regarding the nexus between populism and global strategies. It also suggests ways in which firms can become more adaptable to an uncertain investment climate under populist governments, such as by leveraging strong institutional frameworks in the foreign country and by drawing on the experiences from internationalization to make better-informed decisions. Future research is needed for informed and effective decision-making in an increasingly uncertain global landscape.
The Global Strategy Journal, published by the Strategic Management Society, is the world’s leading journal for managerially oriented global strategy research.
END
The impact of populism on multinational corporations’ investment
2023-06-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Is the U.S. ready for an African swine fever outbreak?
2023-06-22
In a new study, researchers from North Carolina State University used a computer model to understand how African swine fever (ASF) might spread among swine farms in the southeastern U.S. – and examined the effectiveness of existing response plans. They found that although control actions would help, an outbreak could still prove persistent and costly.
ASF is a highly contagious viral disease in pigs, with a mortality rate that can reach 100%. Additionally, infected pigs may not show symptoms before they die, potentially allowing the ...
NFL and NFL Players Association fund Emory University-led study of innovative pain management solutions
2023-06-22
The National Football League and the NFL Players Association (NFLPA) announced today they are awarding a grant to Emory University researchers to study innovative, first-of-their-kind, alternative pain management methods that could benefit NFL players and society at large. The researchers will investigate mindfulness-based intervention in sports medicine injuries.
The $200,000 grant was awarded by the NFL-NFLPA Joint Pain Management Committee (PMC), which aims to facilitate research to better understand and improve potential alternative pain management treatments for NFL players.
Emory’s winning ...
Research links increase in depression, COVID diagnosis in student-athletes
2023-06-22
Background
COVID-19 survivors may experience persistent neuropsychological disruptions such as lower satisfaction with life (SWLS), depression, and anxiety. While student-athletes are at low risk for severe COVID complications, the effect of COVID on mental health remains to be elucidated.
Objective
Compare patient-reported mental health outcomes for incoming collegiate athletes who did (COVID+) and did not (COVID-) have COVID-19.
Methods
79 COVID+ (79/178, 44.4%, 18.90±0.16 years) and 99 COVID- (99/178, 55.6%,18.95±0.16 ...
Heat spots reveal growth rate of a galaxy 12 billion years ago
2023-06-22
An international team of astronomers has drawn a temperature map of the dust drifting within one of the oldest spiral galaxies of the Universe which provides new insights into how fast the galaxy is growing. Until now researchers have only been able to measure the temperature of most distant galaxies in broad terms, without showing how temperatures vary in individual areas.
This research, described in a paper published today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS) shows unambiguous temperature variation within the distant galaxy indicating two distinct heat sources – a supermassive black hole at the centre of the galaxy, and the heat generated ...
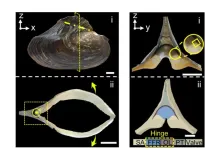
Scientists learn from hinge in bivalve about fatigue resistance of materials
2023-06-22
Recently, flexible and foldable devices have developed at a dramatic rate. More and more foldable devices appear in people's lives. Long-term service requires the folded parts to endure repeated deformation which might cause fatigue damage to the devices. Consequently, the damage will affect the normal function of the devices. Inspired by the hinge of bivalve Cristaria plicata, which experiences hundreds of thousands of repeating opening-and-closing valve motions throughout the bivalve’s lifetime, a research team led by Prof. YU Shuhong collaborating with Prof. WU Hengan from the University of Science and Technology of China ...
Bias in AI algorithms could be mitigated by implementing new checklist
2023-06-22
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Digital Health: https://journals.plos.org/digitalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pdig.0000278
Article Title: Bias in artificial intelligence algorithms and recommendations for mitigation
Author Countries: Jordan, United States, Canada
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
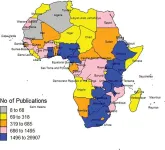
Africa's share of global HIV research output has increased from 5.1% to 31.3% over the last 35 years, but is still low compared to its relative burden of infections
2023-06-22
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0000544
Article Title: HIV research output in African Countries between 1986–2020
Author Countries: Nigeria, USA, UK
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
How might generative AI models distort human beliefs?
2023-06-22
Generative AI models such as ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Midjourney all have features that may distort human beliefs through their transmission of false information and stereotyped biases, according to Celeste Kidd and Abeba Birhane. In this Perspective, they discuss how research on human psychology can explain why generative AI could be particularly powerful in distorting beliefs. The capabilities of generative AI have been exaggerated at this point, they suggest, leading to a belief that these models exceed human capabilities. People are predisposed to adopt the information of knowledgeable, confident agents like generative AI ...
Large herbivores slow Arctic tundra diversity losses associated with sea ice decline
2023-06-22
Tundra diversity, including plants, lichens and fungi, declined over a 15-year experiment in the Arctic due to warming temperatures mediated by the disappearance of sea ice, according to Eric Post and colleagues. However, the presence of large herbivores such as caribou and musk oxen slowed this decline, by affecting the plant understory with their different browsing behaviors, the researchers concluded. Their findings offer support for the idea that encouraging herbivore diversity in the tundra could temper some of the impacts of climate warming. Post et al. observed the interacting effects of warming temperatures, sea ice changes, tundra diversity and herbivore exclusion in ...
Hard and soft materials form a fatigue-resistant fan in the mussel’s hinge
2023-06-22
How does a mussel shell open and shut easily and without damage for hundreds of thousands of cycles during the bivalve’s lifetime? Such fatigue-resistant materials would be useful in electronics, aerospace and tissue engineering designs, where components need to operate repeatedly without failure. Xiang-Sen Meng and colleagues took a closer look at the hinge on the shell of the bivalve Cristaria plicata, and found that the answer lies in a combination of design and materials that resist brittle fracture over time. Microscopic observations by Meng et al. show that the hinge gets its ...