(Press-News.org) BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA — The Journal of Applied Remote Sensing (JARS) has honored four of its best papers published in 2022. The awards recognize the journal’s best student paper, as well as papers in interdisciplinary applications, theoretical innovation, and photo-optical instrumentation and design.
JARS is published online in the SPIE Digital Library by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, and optimizes the communication of concepts, information, and progress among the remote-sensing community. Ni-Bin Chang, professor of civil, environmental, and construction engineering at the University of Central Florida, is the journal’s Editor-in-Chief.
“Optical and SAR image fusion method with coupling gain injection and guided filtering,” by Yukai Fu, Shuwen Yang, Heng Yan, Qing Xue, Zhuang Shi, and Xiaoqiang Hu of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, China, was selected for the Best Student Paper. Their research proposed a fusion method of optical and SAR remote sensing images that couples a gain injection method and a guided filter.
“Marine aerosols produced by ocean internal waves,” by James H. Churnside of the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder and NOAA Chemical Sciences Lab, Brian Concannon of the Naval Air Warfare Center Aircraft Division, and James R. Thompson of The MITRE Corporation, was selected for Interdisciplinary Applications. The paper concludes that internal waves affect aerosol production over the ocean under certain environmental conditions.
“Daily monitoring algorithms to detect geostationary imager visible radiance anomalies,” by David R. Doelling and Rajendra Bhatt of NASA Langley Research Center, and Conor Haney, Benjamin Scarino, and Arun Gopalan of Science Systems and Applications, Inc., was selected for Theoretical Innovation. Their study presented daily monitoring algorithms designed to detect certain near-real-time GOES-16 imager anomalies.
“Multiple-instrument-based spectral irradiance of the Moon,” by Hugh H. Kieffer of Celestial Reasonings was selected for Photo-Optical Instrumentation and Design. The paper presents a methodology for incorporating multiple sources of information on lunar spectral irradiance that was applied to generate an improved lunar model useful for instrument radiometric calibration.
“Together, these winning papers showcase the breadth of the remote-sensing field as well as its latest innovations,” said Chang. “And with the inclusion of our relatively new best student paper awardees, we are hearing from the next generation alongside our most experienced scientists.”
The SPIE Digital Library, the world's largest collection of optics and photonics applied research, comprises more than 590,000 publications.
About SPIE
SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, brings engineers, scientists, students, and business professionals together to advance light-based science and technology. The Society, founded in 1955, connects and engages with our global constituency through industry-leading conferences and exhibitions; publications of conference proceedings, books, and journals in the SPIE Digital Library; and career-building opportunities. Over the past five years, SPIE has contributed more than $22 million to the international optics community through our advocacy and support, including scholarships, educational resources, travel grants, endowed gifts, and public-policy development. www.spie.org.
Contact:
Daneet Steffens
Public Relations Manager
daneets@spie.org
+1 360 685 5478
@SPIEtweets
END
Best papers of 2022 announced by SPIE Journal of Applied Remote Sensing
JARS recognizes its top student paper, as well as papers in interdisciplinary applications, theoretical innovation, and photo-optical instrumentation and design
2023-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds human impact on wildlife even in protected areas
2023-06-26
HOUSTON – (June 26, 2023) – By 2030, if the 30 by 30 initiative supported by more than 100 countries is successful, 30% of our land and ocean ecosystems will be designated protected areas meant to safeguard biodiversity and help limit the impacts of climate change.
However, a study by Rice University ecologist Lydia Beaudrot and collaborators reports for the first time that tropical mammals living inside protected areas are not spared the effects of human activity even when it occurs outside of the protected boundaries.
Based on the ...
University of Oklahoma researcher to use NSF CAREER Award to study local community's disaster resilience
2023-06-26
University of Oklahoma assistant professor Xiaochen (Angela) Zhang, Ph.D., has received a prestigious Faculty Early Career Development Award, known as a CAREER award, from the National Science Foundation to study how relationships among non-profits, community groups and local government agencies can improve disaster resilience, resource allocation, and emergency management by enabling organizational interactions, rather than top-down responses.
Zhang, who is an assistant professor of public relations for the Gaylord College ...
Research Brief: Investing in nature improves equity, boosts economy
2023-06-26
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (06/26/2023) — A new study shows that current trends in environmental degradation will lead to large economic losses in the coming decades, hitting the poorest countries hardest. But there is hope: investing in nature can turn those losses into gains.
Researchers from the University of Minnesota and Purdue University published their findings in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The team developed a first-of-its-kind, global earth-economy model to capture interactions ...
New geochemistry research confirms megalodon shark was warm-blooded
2023-06-26
William Paterson University PRESS RELEASE
EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY, JUNE 26, 2023, 3:00 PM EST
WAYNE, NEW JERSEY — A new study shows that the gigantic Megalodon, or megatooth shark, was warm-blooded. This latest research on the Megalodon, which lived in the world’s oceans from 23 million to 3.6 million years ago and measured about 50 feet in length, appears in the peer-reviewed journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study, conceived of and led by Michael Griffiths ...
Megalodon was no cold-blooded killer
2023-06-26
The largest marine predator that ever lived was no cold-blooded killer.
Well, a killer, yes. But a new analysis by environmental scientists from UCLA, UC Merced and William Paterson University sheds light on the warm-blooded animal’s ability to regulate its body temperature — and might help explain why it went extinct.
After analyzing isotopes in the tooth enamel of the ancient shark, which went extinct about 3.6 million years ago, the scientists concluded the megalodon could maintain a body temperature that was about ...
UCalgary study provides insight into how an infectious parasite uses immune cells as a Trojan Horse
2023-06-26
University of Calgary researchers have discovered how Leishmania parasites hide within the body to cause Leishmaniasis. The tiny parasites are carried by infected sand flies. Considered a tropical disease, one to two million people in more than 90 countries are infected every year. Effects range from disfiguring skin ulcers to enlarged spleen and liver and even death.
This chronic disease has been difficult to detect in the early stages. Scientists realized that the parasite was somehow manipulating immune cells but this process had not been well understood.
“This is the first study that shows how the parasite stalls the process of regular ...
Poop and prey help researchers estimate that gray whales off Oregon Coast consume millions of microparticles per day
2023-06-26
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Oregon State University researchers estimate that gray whales feeding off the Oregon Coast consume up to 21 million microparticles per day, a finding informed in part by poop from the whales.
Microparticle pollution includes microplastics and other human-sourced materials, including fibers from clothing. The finding, just published in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science, is important because these particles are increasing exponentially and predicted to continue doing so in the coming decades, according to researchers Leigh Torres and Susanne Brander.
Microparticle pollution is a threat to the health of ...
A smarter way to monitor critical care patients
2023-06-26
Surgical and intensive care patients face a higher risk of death and longer hospital stays because they are susceptible to both hypotension and hemodynamic instability – or unstable blood flow.
These potential complications require round-the-clock monitoring of several cardiac functions by nurses and physicians, but there’s currently no singular, convenient device on the market that can measure the most vital aspects of a patient’s cardiovascular health.
Ramakrishna Mukkamala, professor of bioengineering at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering, and Aman Mahajan, ...
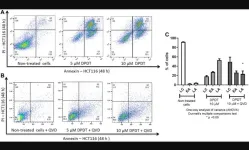
DPDT anticancer activity in human colon cancer HCT116 cells
2023-06-26
“Altogether, our results show that DPDT preferentially targets HCT116 colon cancer cells likely through DNA topoisomerase I poisoning.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 26, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on June 21, 2023, entitled, “Diphenyl ditelluride anticancer activity and DNA topoisomerase I poisoning in human colon cancer HCT116 cells.”
Diphenyl ditelluride (DPDT) is an organotellurium (OT) compound with pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, antigenotoxic and antimutagenic activities when applied at low concentrations. However, ...
Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging announces 2023 fellows
2023-06-26
Chicago, Illinois – The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging recognized ten new SNMMI Fellows today during a plenary session at the society’s 2023 Annual Meeting, held June 24-27. The SNMMI Fellowship was established in 2016 to recognize distinguished service to the society as well as exceptional achievement in the field of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. It is among the most prestigious formal recognitions available to long-time SNMMI members.
In keeping with tradition, SNMMI’s 2022-23 president, Munir Ghesani, MD, FACNM, FACR, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists show how to predict world’s deadly scorpion hotspots
ASU researchers to lead AAAS panel on water insecurity in the United States
ASU professor Anne Stone to present at AAAS Conference in Phoenix on ancient origins of modern disease
Proposals for exploring viruses and skin as the next experimental quantum frontiers share US$30,000 science award
ASU researchers showcase scalable tech solutions for older adults living alone with cognitive decline at AAAS 2026
Scientists identify smooth regional trends in fruit fly survival strategies
Antipathy toward snakes? Your parents likely talked you into that at an early age
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for Feb. 2026
Online exposure to medical misinformation concentrated among older adults
Telehealth improves access to genetic services for adult survivors of childhood cancers
Outdated mortality benchmarks risk missing early signs of famine and delay recognizing mass starvation
Newly discovered bacterium converts carbon dioxide into chemicals using electricity
Flipping and reversing mini-proteins could improve disease treatment
Scientists reveal major hidden source of atmospheric nitrogen pollution in fragile lake basin
Biochar emerges as a powerful tool for soil carbon neutrality and climate mitigation
Tiny cell messengers show big promise for safer protein and gene delivery
AMS releases statement regarding the decision to rescind EPA’s 2009 Endangerment Finding
Parents’ alcohol and drug use influences their children’s consumption, research shows
Modular assembly of chiral nitrogen-bridged rings achieved by palladium-catalyzed diastereoselective and enantioselective cascade cyclization reactions
Promoting civic engagement
AMS Science Preview: Hurricane slowdown, school snow days
Deforestation in the Amazon raises the surface temperature by 3 °C during the dry season
Model more accurately maps the impact of frost on corn crops
How did humans develop sharp vision? Lab-grown retinas show likely answer
Sour grapes? Taste, experience of sour foods depends on individual consumer
At AAAS, professor Krystal Tsosie argues the future of science must be Indigenous-led
From the lab to the living room: Decoding Parkinson’s patients movements in the real world
Research advances in porous materials, as highlighted in the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Sally C. Morton, executive vice president of ASU Knowledge Enterprise, presents a bold and practical framework for moving research from discovery to real-world impact
Biochemical parameters in patients with diabetic nephropathy versus individuals with diabetes alone, non-diabetic nephropathy, and healthy controls
[Press-News.org] Best papers of 2022 announced by SPIE Journal of Applied Remote SensingJARS recognizes its top student paper, as well as papers in interdisciplinary applications, theoretical innovation, and photo-optical instrumentation and design