(Press-News.org)
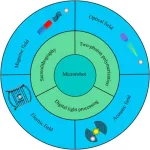
A review paper by scientists at the Beijing Institute of Technology summarized the recent research on field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization.
The new review paper, published on Jun. 6 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, provided an overview the photopolymerization technologies utilized in the fabrication of field-controlled microrobots and introduced the photopolymerized microrobots actuated by different field forces and their functions.
“Field-controlled microrobots have attracted extensive research in the biological and medical fields due to the prominent characteristics including high flexibility, small size, strong controllability, remote manipulation, and minimal damage to living organisms.” explained study author Xiaoming Liu, a professor at the Beijing Institute of Technology.
Microrobots have become one of the most promising tools in the biomedical field due to their increasing abilities of minimally invasive surgery, targeted therapy, and cell manipulation. “Employing photopolymerization in the fabrication of field-controlled microrobots provides an ideal solution”, said study authors. Thus, they reviewed the photopolymerization technologies utilized in the fabrication of field-controlled microrobots and introduced the photopolymerized microrobots actuated by different field forces and their functions.
Photopolymerization technology promotes the progress of field-controlled microrobots in many terms, including manipulation accuracy, function, flexibility, and size. "The requirements on the structure, material, and size of field-controlled microrobots also positively accelerate the development of photopolymerization technology,” said Liu.
The study authors discussed recent advances in actuating microrobots via magnetic, optical, acoustic, and electric fields and the respectively utilized photopolymerization methods. Microrobots controlled by optical tweezer, for example, the joint microrobot based on two-photon polymerization enables indirect manipulation of biological cells.
Looking forward, the main future developing directions of the field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization, including the smart materials and capabilities for real applications. Besides, the development of field-assisted photopolymerization technology may improve multi-material fabricating capabilities and the producibility of complex designs. It is also critical to select suitable and effective control methods to meet the requirements of complex environments and tasks in vivo clinical. Collaborative control of microrobots through multiple combinations of physics may be a viable approach.
“The improvement of printing technology, the development of new materials, and the rational design of multiple control methods, field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization with better performance will usher in vigorous development.” said Liu. The review paper calls for researchers, medical professionals, engineers, and other experts to collaboratively marshal the research on field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization into practical applications in clinical settings.
Authors of the paper include Xiyue Liang, Zhuo Chen, Yan Deng, Dan Liu, Xiaoming Liu, Qiang Huang, and Tatsuo Arai.
National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants 62273052, 61873037, and 61903039; and the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFA0701102).
The paper, "Field-Controlled Microrobots Fabricated by Photopolymerization" was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on June 6, 2023, at DOI: https://doi.org/10.34133/cbsystems.0009.
END
Main Points
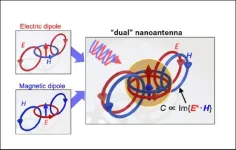
The research group proposed and tested a nano-antenna that uses the specific optical resonance of dielectric nanoparticles to form a near field of circularly polarized light.
This technique bolsters the circularly polarized light-selective response of chiral molecules.
The results of this study should provide applications in chirality analysis and asymmetric photochemical reactions for biomolecules, chemical substances, and pharmaceuticals.
Research Background
“Chirality” refers to the property of a substance that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. Since the mirror image isomers of chiral molecules ...
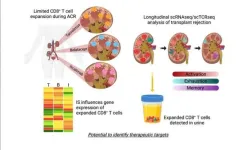
CINCINNATI -- Imagine a day when a urine test could inform a doctor precisely why a kidney transplant patient was experiencing organ rejection and suggest the best medication for specifically addressing the problem.
That day took a leap closer to reality thanks to a remarkable set of single-cell analyses that have identified the most specific cellular signatures to date for kidney transplant rejection. The findings were detailed May 25, 2023, in JCI The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The study results reflect eight years of teamwork led by experts at Cincinnati Children’s and the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine with contributions ...
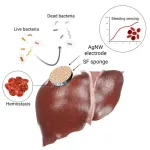
(LOS ANGELES) – June 28, 2023 - A multi-faceted device for effectively treating deep, non-compressible, and irregularly-shaped wounds has been engineered by the scientists at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI). As outlined in their recent paper in Advanced Science, the device provides rapid hemorrhage management, has minimal inflammatory effects, and provides infection control. It also has tunable biodegradation rates, making it usable for both internal and external use, and features sensing capabilities for long-term hemorrhage monitoring. This versatile device is highly beneficial ...
From growls to pulses to booms, whales, fish and crustaceans all produce sounds. In fact, more than 800 species of fish are capable of making noises for a variety of functions such as courtship and mating, defending their turf or responding to threats. Each of these species has a characteristic waveform that is unique to their “calls.” As such, detecting structures in these signals can be used to identify the sounds of different species.
Classifying sounds produced by fish will help to understand how they respond to environmental changes ...
With a flick of a switch, current technologies allow you to quickly change materials from being dark to light, or cold to hot, just by blocking or transmitting specific wavelengths. But now, inspired by squid skin, researchers in ACS Nano report a soft film that can regulate its transparency across a large range of wavelengths — visible, infrared and microwave — simultaneously. They demonstrated the material in smart windows and in health monitoring and temperature management applications.
Unique to the skin of squid and other cephalopods, iridocytes and chromatophores reversibly ...
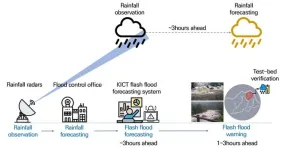
Korea has recently seen a surge in localized torrential rain and floods due to global warming. Frequent flash floods are hard to forecast and, when forecast, the accuracy is low. This often leads to major disasters that take hundreds of lives, as seen in Germany and China (Henan) in July 2021. Floods are one of the deadliest types of natural disasters, but climate change has made the forecasting of them even more challenging.
Researchers at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) have developed a system that can forecast ...
Reston, VA (July 28, 2023)—The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) hosted nearly 8,000 physicians, technologists, pharmacists, laboratory professionals, scientists and others at its 2023 Annual Meeting, themed “Eye on the Patient,” held in Chicago, Illinois.
“This year’s meeting offered attendees world-class scientific research, education, and exhibits as well as one-of-a-kind networking opportunities that will ultimately help us serve our patients better,” said Helen ...
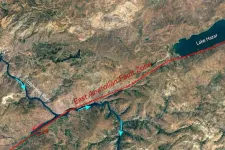
An international team led by the University of Minnesota Twin Cities has, for the first time, accurately determined the age and formation process of the East Anatolian fault, which runs from eastern to south-central Turkey and was involved in the creation of the Anatolian tectonic plate.
The fault zone was the site of two devastating earthquakes that occurred in Turkey and Syria in February 2023. While the researchers’ findings won’t help predict timing or size of earthquakes, it allows geologists to learn more about how long the area has been seismically active and how major earthquakes have shaped the landscape over time, which can help drive ...
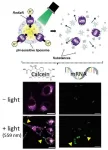
Artificial lipid bilayer vesicle liposomes, also called proteoliposomes, are specialized systems capable of incorporating various molecules, such as chemicals and drugs. Their unique properties make them ideal carriers for delivering substances inside cells. However, they must possess the dual characteristics of high stability in extracellular environments and low stability in intracellular environments.
Several techniques have been developed to regulate the stability of liposomes in a condition-dependent manner, with pH-sensitive liposomes being widely employed. A standard measure of acidity or basicity, the ...
Copenhagen, Denmark: Women with adenomyosis – a chronic condition that can cause pelvic pain and heavy menstrual bleeding – are at increased risk of infertility as well as problems in pregnancy and during birth, according to research presented at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
Data from the first study of its kind based on more than nine million women show that mothers-to-be with adenomyosis experienced higher rates of complications.
The greatest risk was for caesarean section delivery – ...