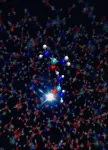
(Press-News.org) New images from the James Webb Space Telescope have revealed, for the first time, starlight from two massive galaxies hosting actively growing black holes – quasars – seen less than a billion years after the Big Bang. A new study in Nature this week finds the black holes have masses close to a billion times that of the Sun, and the host galaxy masses are almost one hundred times larger, a ratio similar to what is found in the more recent universe. A powerful combination of the Subaru Telescope and the JWST has paved a new path to study the distant universe.
The existence of such massive black holes in the distant universe has created more questions than answers for astrophysicists. How could these black holes grow to be so large when the universe was so young? Even more puzzling, observations in the local universe show a clear relation between the mass of supermassive black holes and the much larger galaxies in which they reside. The galaxies and the black holes have completely different sizes, so which came first: the black holes or the galaxies? This is a “chicken-or-egg” problem on a cosmic scale.
An international team of researchers, led by Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU) Project Researcher Xuheng Ding and Professor John Silverman, and Peking University Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics (PKU-KIAA) Kavli Astrophysics Fellow Masafusa Onoue have started to answer this question with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched in December 2021. Studying the relation between host galaxies and black holes in the early universe allows scientists to watch their formation, and see how they are related to one another.
Quasars are luminous, while their host galaxies are faint, which has made it challenging for researchers to detect the dim light of the galaxy in the glare of the quasar, especially at great distances. Before the JWST, the Hubble Space Telescope was able to detect host galaxies of luminous quasars when the universe was just under 3 billion years old, but no younger.
The superb sensitivity and the ultra-sharp images of the JWST at infrared wavelengths finally allowed researchers to push these studies to the time when the quasars and galaxies first formed. Just a few months after JWST started regular operations, the team observed two quasars, HSC J2236+0032 and HSC J2255+0251, at redshifts 6.40 and 6.34 when the universe was approximately 860 million years old. These two quasars were discovered in a deep survey program of the 8.2m-Subaru Telescope on the summit of Maunakea in Hawai’i. The relatively low luminosities of these quasars made them prime targets for measurement of the host galaxy properties, and the successful detection of the hosts represents the earliest epoch to date at which starlight has been detected in a quasar.
The images of the two quasars were taken at infrared wavelengths of 3.56 and 1.50 micron with JWST’s NIRCam instrument, and the host galaxies became apparent after carefully modeling and subtracting glare from the accreting black holes. The stellar signature of the host galaxy was also seen in a spectrum taken by JWST’s NIRSPEC for J2236+0032, further supporting the detection of the host galaxy.
Analyses of the host galaxy photometry found that these two quasar host galaxies are massive, measuring 130 and 34 billion times the mass of the Sun, respectively. Measuring the speed of the turbulent gas in the vicinity of the quasars from the NIRSPEC spectra suggests that the black holes that power them are also massive, measuring 1.4 and 0.2 billion times the mass of the Sun. The ratio of the black hole mass to host galaxy mass is similar to those of galaxies in the more recent past, suggesting that the relationship between black holes and their hosts was already in place 860 million years after the Big Bang.
Ding, Silverman, Onoue and their colleagues will continue this study with a larger sample using scheduled Cycle 1 JWST observations, which will then further constrain models for the coevolution of black holes and their host galaxies. The team recently learned that they have been awarded additional time for JWST in its next cycle to study the host galaxy of J2236+0032 in much more detail.
Details of this study will be published in Nature on June 28.
END
Starlight and the first black holes: researchers detect the host galaxies of quasars in the early universe
2023-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Life after death: Hawaiʻi astronomers find a planet that shouldn’t exist
2023-06-28
Maunakea, Hawaiʻi - When our Sun reaches the end of its life, it will expand to 100 times its current size, enveloping the Earth. Many planets in other solar systems face a similar doom as their host stars grow old. But not all hope is lost, as astronomers from the University of Hawaiʻi Institute for Astronomy (UH IfA) have made the remarkable discovery of a planet’s survival after what should have been certain demise at the hands of its sun.
The Jupiter-like planet 8 UMi b, officially named Halla, ...
Genetic variant linked with faster progression of multiple sclerosis
2023-06-28
Contact: Bess Connolly, 203-432-1324 or elizabeth.connolly@yale.edu
Embargoed For Release: 11 A.M. ET June 28, 2023
Genetic variant linked with faster progression of multiple sclerosis
New Haven, Conn. — A study of more than 22,000 people with multiple sclerosis (MS) has for the first time identified a genetic variant associated with faster progression of the disease, an accumulation of disability that can rob patients of their mobility and independence over time.
Multiple sclerosis begins as an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the brain and the spinal cord, resulting in symptom flares, called relapses, as well as longer-term degeneration known ...
High-speed proton transaction
2023-06-28
How did life begin on Earth? Experts have long been fascinated by this question and over the years have come up with a variety of theories. One hypothesis is that the origin of life can be traced back to warm little ponds which are thought to have existed on Earth four billion years ago. The water in these ponds probably contained urea molecules; these were exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun, which at that time would have penetrated to the surface of the earth largely unimpeded. This high-energy radiation was able to convert ...
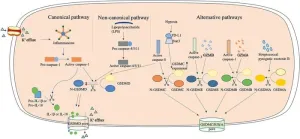
The complex role of pyroptosis in lung cancer: a Chinese Medical Journal Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Review
2023-06-28
Lung cancer, one of the most aggressive forms of cancer, continues to be a leading cause of death worldwide. Although several new therapies have been developed for this disease, it has a poor prognosis in its advanced stages. A primary reason underlying this poor response to treatment is the formation of a tumor microenvironment (TME)— the environment that surrounds a tumor and plays a crucial role in its growth. To develop approaches that can overcome treatment resistance during the advanced stages of this cancer, we need to understand ...
The American Association for Anatomy calls for ethical treatment and justice for human body donors
2023-06-28
ROCKVILLE, MD—JUNE 15, 2023 – In response to the allegations of illicit buying and selling of stolen body parts from Harvard Medical School's body donation program, the American Association for Anatomy (AAA) stands united in strong condemnation of the commercialization of human body donors and any action that violates donor ethics and trust. Our heartfelt support goes out to the affected families.
Any act that violates the principles of respect and dignity owed to every individual, in life or death, undermines the sanctity of ...
Scientists design a nanoparticle that may improve mRNA cancer vaccines
2023-06-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have developed a nanoparticle — an extremely tiny biodegradable container — that has the potential to improve the delivery of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-based vaccines for infectious diseases such as COVID-19, and vaccines for treating non-infectious diseases including cancer.
Results of tests in mice, reported June 20 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show that the degradable, polymer-based nanoparticle carrying an mRNA-based vaccine, when injected into the ...
Undergrad-driven project reveals drought’s effects on painted turtles
2023-06-28
A projected rise in droughts could muddy the waters for painted turtles and some fellow freshwater-dwelling reptiles, says 11 years of data collected by 50-plus undergraduates from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
Two recent studies based on the data suggest that drought can lower the survival odds, slow the growth and even skew the ratio of female-to-male painted turtles inhabiting the ponds of the Cornhusker State. Those outcomes emerged despite the water level of a sampled pond in southwestern Nebraska remaining relatively steady throughout the observed periods ...
One-two punch: Novel drug pairing could beat pancreatic cancer
2023-06-28
Mutations in the KRAS gene are the major driver of pancreatic cancer. The resulting protein controls multiple signaling pathways involved in cell growth and survival. In cancer, the gene is mutated to be permanently “on,” driving cells to excessively multiply and form tumors.
New drugs have recently been developed to inhibit KRAS and appear to be therapeutically promising. However, pancreatic cancer is especially prone to drug resistance. Most drugs only work for a short period of time before the cancer finds its way around them.
Previous experiments revealed a potential reason why: a group ...
Field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization
2023-06-28
A review paper by scientists at the Beijing Institute of Technology summarized the recent research on field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization.
The new review paper, published on Jun. 6 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, provided an overview the photopolymerization technologies utilized in the fabrication of field-controlled microrobots and introduced the photopolymerized microrobots actuated by different field forces and their functions.
“Field-controlled microrobots have attracted extensive research in the ...
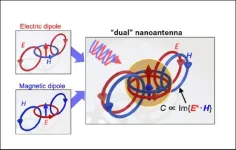
Developing a nano-antenna that forms a near field of circularly polarized light: Promising applications in highly sensitive sensing and asymmetric photochemical reactions for molecular chirality
2023-06-28
Main Points
The research group proposed and tested a nano-antenna that uses the specific optical resonance of dielectric nanoparticles to form a near field of circularly polarized light.
This technique bolsters the circularly polarized light-selective response of chiral molecules.
The results of this study should provide applications in chirality analysis and asymmetric photochemical reactions for biomolecules, chemical substances, and pharmaceuticals.
Research Background
“Chirality” refers to the property of a substance that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. Since the mirror image isomers of chiral molecules ...