(Press-News.org) A team of researchers led by Feng Zhang at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and the McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT has uncovered the first programmable RNA-guided system in eukaryotes — organisms that include fungi, plants, and animals.
In a study in Nature, the team describes how the system is based on a protein called Fanzor. They showed that Fanzor proteins use RNA as a guide to target DNA precisely, and that Fanzors can be reprogrammed to edit the genome of human cells. The compact Fanzor systems have the potential to be more easily delivered to cells and tissues as therapeutics than CRISPR/Cas systems, and further refinements to improve their targeting efficiency could make them a valuable new technology for human genome editing.
CRISPR/Cas was first discovered in prokaryotes (bacteria and other single-cell organisms that lack nuclei) and scientists including Zhang’s lab have long wondered whether similar systems exist in eukaryotes. The new study demonstrates that RNA-guided DNA-cutting mechanisms are present across all kingdoms of life.
“CRISPR-based systems are widely used and powerful because they can be easily reprogrammed to target different sites in the genome,” said Zhang, senior author on the study and a core institute member at the Broad, an investigator at MIT’s McGovern Institute, the James and Patricia Poitras Professor of Neuroscience at MIT, and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator. “This new system is another way to make precise changes in human cells, complementing the genome editing tools we already have.”
Searching the domains of life
A major aim of the Zhang lab is to develop genetic medicines using systems that can modulate human cells by targeting specific genes and processes. “A number of years ago, we started to ask, ‘What is there beyond CRISPR, and are there other RNA-programmable systems out there in nature?’” said Zhang.
Two years ago, Zhang lab members discovered a class of RNA-programmable systems in prokaryotes called OMEGAs, which are often linked with transposable elements, or “jumping genes”, in bacterial genomes and likely gave rise to CRISPR/Cas systems. That work also highlighted similarities between prokaryotic OMEGA systems and Fanzor proteins in eukaryotes, suggesting that the Fanzor enzymes might also use an RNA-guided mechanism to target and cut DNA.
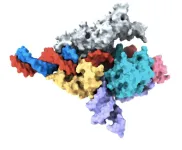
In the new study, the researchers continued their study of RNA-guided systems by isolating Fanzors from fungi, algae, and amoeba species, in addition to a clam known as the Northern Quahog. Co-first author Makoto Saito of the Zhang lab led the biochemical characterization of the Fanzor proteins, showing that they are DNA-cutting endonuclease enzymes that use nearby non-coding RNAs known as ωRNAs to target particular sites in the genome. It is the first time this mechanism has been found in eukaryotes, such as animals.
Unlike CRISPR proteins, Fanzor enzymes are encoded in the eukaryotic genome within transposable elements and the team’s phylogenetic analysis suggests that the Fanzor genes have migrated from bacteria to eukaryotes through so-called horizontal gene transfer.
“These OMEGA systems are more ancestral to CRISPR and they are among the most abundant proteins on the planet, so it makes sense that they have been able to hop back and forth between prokaryotes and eukaryotes,” said Saito.
To explore Fanzor’s potential as a genome editing tool, the researchers demonstrated that it can generate insertions and deletions at targeted genome sites within human cells. The researchers found the Fanzor system to initially be less efficient at snipping DNA than CRISPR/Cas systems, but by systematic engineering, they introduced a combination of mutations into the protein that increased its activity 10-fold. Additionally, unlike some CRISPR systems and the OMEGA protein TnpB, the team found that a fungal-derived Fanzor protein did not exhibit “collateral activity,” where an RNA-guided enzyme cleaves its DNA target as well as degrading nearby DNA or RNA. The results suggest that Fanzors could potentially be developed as efficient genome editors.
Co-first author Peiyu Xu led an effort to analyze the molecular structure of the Fanzor/ωRNA complex and illustrate how it latches onto DNA to cut it. Fanzor shares structural similarities with its prokaryotic counterpart CRISPR-Cas12 protein, but the interaction between the ωRNA and the catalytic domains of Fanzor is more extensive, suggesting that the ωRNA might play a role in the catalytic reactions. “We are excited about these structural insights for helping us further engineer and optimize Fanzor for improved efficiency and precision as a genome editor,” said Xu.
Like CRISPR-based systems, the Fanzor system can be easily reprogrammed to target specific genome sites, and Zhang said it could one day be developed into a powerful new genome editing technology for research and therapeutic applications. The abundance of RNA-guided endonucleases like Fanzors further expands the number of OMEGA systems known across kingdoms of life and suggests that there are more yet to be found.
“Nature is amazing. There's so much diversity,” said Zhang. “There are probably more RNA-programmable systems out there, and we're continuing to explore and will hopefully discover more.”
The paper’s other authors include Guilhem Faure, Samantha Maguire, Soumya Kannan, Han Altae-Tran, Sam Vo, AnAn Desimone, and Rhiannon Macrae.
Support for this work was provided by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute; Poitras Center for Psychiatric Disorders Research at MIT; K. Lisa Yang and Hock E. Tan Molecular Therapeutics Center at MIT; Broad Institute Programmable Therapeutics Gift Donors; The Pershing Square Foundation, William Ackman, and Neri Oxman; James and Patricia Poitras; BT Charitable Foundation; Asness Family Foundation; Kenneth C. Griffin; the Phillips family; David Cheng; Robert Metcalfe; and Hugo Shong.
Paper cited
Saito M, Xu P, et al. Fanzor is a eukaryotic programmable RNA-guided endonuclease. Nature. Online June 28, 2023. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06356-2
About Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard
Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard was launched in 2004 to empower this generation of creative scientists to transform medicine. The Broad Institute seeks to describe the molecular components of life and their connections; discover the molecular basis of major human diseases; develop effective new approaches to diagnostics and therapeutics; and disseminate discoveries, tools, methods and data openly to the entire scientific community.
Founded by MIT, Harvard, Harvard-affiliated hospitals, and the visionary Los Angeles philanthropists Eli and Edythe L. Broad, the Broad Institute includes faculty, professional staff and students from throughout the MIT and Harvard biomedical research communities and beyond, with collaborations spanning over a hundred private and public institutions in more than 40 countries worldwide.
About McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT
The McGovern Institute is an inclusive and collaborative community of MIT scientists, engineers, and support staff who work together to unravel the mysteries of the brain. Our researchers are committed to meeting two of the greatest challenges of modern science: understanding how the brain works and discovering new ways to prevent or treat brain disorders. To address this scientific challenge, we study the brain at many levels and collaborate with academic, clinical, and industry partners around the world.
The McGovern Institute was established in 2000 by technology entrepreneur Lore Harp McGovern and the late Patrick J. McGovern, former chairman of International Data Group (IDG). Our director is Robert Desimone, the Doris and Don Berkey Professor of Neuroscience at MIT and former head of intramural research at the National Institute of Mental Health. The McGovern Institute has grown from six founding faculty members to more than 20 distinguished investigators including one Nobel laureate and six members of the National Academy of Sciences.
END
Researchers uncover new CRISPR-like system in animals that can edit the human genome
The first RNA-guided DNA-cutting enzyme found in eukaryotes, Fanzor could one day be harnessed to edit DNA more precisely than CRISPR/Cas systems
2023-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Starlight and the first black holes: researchers detect the host galaxies of quasars in the early universe
2023-06-28
New images from the James Webb Space Telescope have revealed, for the first time, starlight from two massive galaxies hosting actively growing black holes – quasars – seen less than a billion years after the Big Bang. A new study in Nature this week finds the black holes have masses close to a billion times that of the Sun, and the host galaxy masses are almost one hundred times larger, a ratio similar to what is found in the more recent universe. A powerful combination of the Subaru Telescope and the JWST has paved a new path to study the distant universe.
The existence of such massive black holes in the distant universe has created more questions ...
Life after death: Hawaiʻi astronomers find a planet that shouldn’t exist
2023-06-28
Maunakea, Hawaiʻi - When our Sun reaches the end of its life, it will expand to 100 times its current size, enveloping the Earth. Many planets in other solar systems face a similar doom as their host stars grow old. But not all hope is lost, as astronomers from the University of Hawaiʻi Institute for Astronomy (UH IfA) have made the remarkable discovery of a planet’s survival after what should have been certain demise at the hands of its sun.
The Jupiter-like planet 8 UMi b, officially named Halla, ...
Genetic variant linked with faster progression of multiple sclerosis
2023-06-28
Contact: Bess Connolly, 203-432-1324 or elizabeth.connolly@yale.edu
Embargoed For Release: 11 A.M. ET June 28, 2023
Genetic variant linked with faster progression of multiple sclerosis
New Haven, Conn. — A study of more than 22,000 people with multiple sclerosis (MS) has for the first time identified a genetic variant associated with faster progression of the disease, an accumulation of disability that can rob patients of their mobility and independence over time.
Multiple sclerosis begins as an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the brain and the spinal cord, resulting in symptom flares, called relapses, as well as longer-term degeneration known ...
High-speed proton transaction
2023-06-28
How did life begin on Earth? Experts have long been fascinated by this question and over the years have come up with a variety of theories. One hypothesis is that the origin of life can be traced back to warm little ponds which are thought to have existed on Earth four billion years ago. The water in these ponds probably contained urea molecules; these were exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun, which at that time would have penetrated to the surface of the earth largely unimpeded. This high-energy radiation was able to convert ...
The complex role of pyroptosis in lung cancer: a Chinese Medical Journal Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Review
2023-06-28
Lung cancer, one of the most aggressive forms of cancer, continues to be a leading cause of death worldwide. Although several new therapies have been developed for this disease, it has a poor prognosis in its advanced stages. A primary reason underlying this poor response to treatment is the formation of a tumor microenvironment (TME)— the environment that surrounds a tumor and plays a crucial role in its growth. To develop approaches that can overcome treatment resistance during the advanced stages of this cancer, we need to understand ...
The American Association for Anatomy calls for ethical treatment and justice for human body donors
2023-06-28
ROCKVILLE, MD—JUNE 15, 2023 – In response to the allegations of illicit buying and selling of stolen body parts from Harvard Medical School's body donation program, the American Association for Anatomy (AAA) stands united in strong condemnation of the commercialization of human body donors and any action that violates donor ethics and trust. Our heartfelt support goes out to the affected families.
Any act that violates the principles of respect and dignity owed to every individual, in life or death, undermines the sanctity of ...
Scientists design a nanoparticle that may improve mRNA cancer vaccines
2023-06-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have developed a nanoparticle — an extremely tiny biodegradable container — that has the potential to improve the delivery of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-based vaccines for infectious diseases such as COVID-19, and vaccines for treating non-infectious diseases including cancer.
Results of tests in mice, reported June 20 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show that the degradable, polymer-based nanoparticle carrying an mRNA-based vaccine, when injected into the ...
Undergrad-driven project reveals drought’s effects on painted turtles
2023-06-28
A projected rise in droughts could muddy the waters for painted turtles and some fellow freshwater-dwelling reptiles, says 11 years of data collected by 50-plus undergraduates from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
Two recent studies based on the data suggest that drought can lower the survival odds, slow the growth and even skew the ratio of female-to-male painted turtles inhabiting the ponds of the Cornhusker State. Those outcomes emerged despite the water level of a sampled pond in southwestern Nebraska remaining relatively steady throughout the observed periods ...
One-two punch: Novel drug pairing could beat pancreatic cancer
2023-06-28
Mutations in the KRAS gene are the major driver of pancreatic cancer. The resulting protein controls multiple signaling pathways involved in cell growth and survival. In cancer, the gene is mutated to be permanently “on,” driving cells to excessively multiply and form tumors.
New drugs have recently been developed to inhibit KRAS and appear to be therapeutically promising. However, pancreatic cancer is especially prone to drug resistance. Most drugs only work for a short period of time before the cancer finds its way around them.
Previous experiments revealed a potential reason why: a group ...
Field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization
2023-06-28
A review paper by scientists at the Beijing Institute of Technology summarized the recent research on field-controlled microrobots fabricated by photopolymerization.
The new review paper, published on Jun. 6 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, provided an overview the photopolymerization technologies utilized in the fabrication of field-controlled microrobots and introduced the photopolymerized microrobots actuated by different field forces and their functions.
“Field-controlled microrobots have attracted extensive research in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
[Press-News.org] Researchers uncover new CRISPR-like system in animals that can edit the human genomeThe first RNA-guided DNA-cutting enzyme found in eukaryotes, Fanzor could one day be harnessed to edit DNA more precisely than CRISPR/Cas systems