(Press-News.org) The Russian writer and philosopher Leo Tolstoy may have been onto something when he wrote the opening line of Anna Karenina: “Happy families are all alike; every unhappy family is unhappy in its own way.”
A recent study published in Psychological Science and led by a scholar now at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, suggests that when it comes to their brains processing information, people who are not lonely are all alike, but every lonely person processes the world in their own, idiosyncratic way.
Copious research shows that loneliness is detrimental to well-being and is often accompanied by self-reported feelings of not being understood by others. A recent report from the United States Surgeon General’s office referred to loneliness as a public health crisis in reaction to the growing number of adults suffering from this condition. Even before the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, approximately half of U.S. adults reported experiencing measurable levels of loneliness.
Loneliness is idiosyncratic
While she was a postdoctoral fellow at UCLA, Elisa Baek, assistant professor of psychology at USC Dornsife, sought to better understand what contributes to such feelings of disconnection and being misunderstood. Baek and her team used a neuroimaging technique called functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to examine the brains of 66 first-year college students while they watched a series of video clips. The videos ranged in topic from sentimental music videos to party scenes and sporting events, providing a diverse array of scenarios for analysis.
Before being scanned, the participants, who ranged in age from 18 to 21, were asked to complete the UCLA Loneliness Scale, a survey that measures a person’s subjective feelings of loneliness and feelings of social isolation.
Based on the survey results, the researchers separated the participants into two groups: lonely and “nonlonely” (those not experiencing loneliness). They then scanned each participant’s brain using fMRI as the participant watched the videos.
Comparing the brain imaging data between the two groups, the researchers discovered that lonelier individuals exhibited more dissimilar and idiosyncratic brain processing patterns than their non-lonely counterparts.
This finding is significant because it reveals that neural similarity, which refers to how similar the brain activity patterns of different individuals are, is linked to a shared understanding of the world. This shared understanding is important for establishing social connections. People who suffer from loneliness are not only less similar to society’s norm of processing the world, but each lonely person differs in unique ways, as well. That uniqueness may further impact the feelings of isolation and lacking social connections.
Baek said, “It was surprising to find that lonely people were even less similar to each other.” The fact that they don’t find commonality with lonely or nonlonely people makes achieving social connection even more difficult for them.
“The ‘Anna Karenina principle’ is a fitting description of lonely people, as they experience loneliness in an idiosyncratic way, not in a universally relatable way,” she added.
Loneliness isn’t about having or not having friends
So, does idiosyncratic processing in lonely individuals cause loneliness, or is it a result of loneliness?
The researchers observed that individuals with high levels of loneliness — regardless of how many friends or social connections they had — were more likely to have idiosyncratic brain responses. This raised the possibility that being surrounded by people who see the world differently from oneself may be a risk factor for loneliness, even if one socializes regularly with them.
The study also suggests that because social connections or disconnections fluctuate over time, it may influence the extent to which an individual processes the world idiosyncratically.
Looking forward, Baek said she is interested in examining people who have friends and are socially active but still feel lonely. In addition, the researchers are looking at what particular situations lonely individuals process differently. For example, do lonely people show idiosyncrasies when processing unexpected events or ambiguous social contexts in which things can be interpreted differently?
About the study:
Funding for the study came from the National Science Foundation and the National Institute of Mental Health.
END
Brain scans reveal that lonely people process the world in unique ways
USC Dornsife psychology researcher compares brain images of people who are lonely with those of people who are not lonely and discovers significant differences in their brain processing patterns.
2023-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
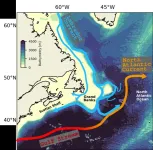
What controls the pathways of the Labrador Current?
2023-06-28
Changes to the flow of the Labrador Current along the coast of Newfoundland and Labrador to Nova Scotia are leading to sudden warmings or drops in the oxygen levels of the waters in several regions including the St. Lawrence Gulf and Estuary. This change has dire consequences for marine ecosystems and fisheries. To better predict what could happen in the future, researchers from McGill University set out to answer the question: what controls the pathway of the Labrador Current?
The Labrador Current supplies cold, oxygen rich waters
The Labrador Current is a cold water current in the North Atlantic Ocean that flows south along the coast of Newfoundland ...
Among professional fighters, new criteria can identify who may develop CTE
2023-06-28
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 28, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a degenerative brain disease linked to repeated head impacts that athletes get from contact sports. However, the definitive diagnosis of the disease can be made only after death through an autopsy.
New research criteria for identifying who may be more likely to develop the disease proved accurate in distinguishing a group who would have changes in brain volume and cognitive skills years later, according to a study published in the June 28, ...
Blood test aids in predicting lung cancer mortality risk
2023-06-28
HOUSTON ― A blood-based test developed by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center can efficiently predict an individual’s risk of dying from lung cancer when combined with a personalized risk model.
According to new data published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, a blood-based four-protein panel (4MP), when combined with a lung cancer risk model (PLCOm2012), can better identify those at high risk of dying from lung cancer than the current U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) criteria.
These findings build upon previous MD Anderson research demonstrating the ...
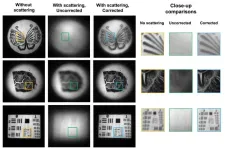
NeuWS camera answers ‘holy grail problem’ in optical imaging
2023-06-28
HOUSTON – (June 28, 2023) – Engineers from Rice University and the University of Maryland have created full-motion video technology that could potentially be used to make cameras that peer through fog, smoke, driving rain, murky water, skin, bone and other media that reflect scattered light and obscure objects from view.
“Imaging through scattering media is the ‘holy grail problem’ in optical imaging at this point,” said Rice’s Ashok Veeraraghavan, co-corresponding author of an open-access study published today in Science Advances. ...
Research reveals sources of CO2 from Aleutian-Alaska Arc volcanoes
2023-06-28
Scientists have wondered what happens to the organic and inorganic carbon that Earth’s Pacific Plate carries with it as it slides into the planet’s interior along the volcano-studded Ring of Fire.
A new study suggests a notable amount of such subducted carbon returns to the atmosphere rather than traveling deep into Earth’s mantle.
The finding can improve long-term projections about Earth’s climate.
A study led by a University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute scientist has shown that volcanoes of the Aleutian-Alaska Arc return more subducted slab carbon to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide than previously thought. This occurs ...
Cancerous brain tumor cells may be at ‘critical point’ between order and disorder, study suggests
2023-06-28
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive form of brain cancer. Despite decades of major efforts and clinical trials, the tumor’s survival rate has remained stagnant.
For years, scientists understood the cells in these tumors as static and relatively fixed. But recent studies have uncovered that glioblastomas contain active cells moving in complex patterns known as “oncostreams”, which determine how aggressively the tumors grow.
Research led by Michigan Medicine and the University of Michigan, published in Science Advances, suggests that glioblastoma ...
A dog’s breed can affect pain sensitivity, but not necessarily the way your vet may think
2023-06-28
Dog breeds differ in pain sensitivity, but these differences don’t always match up with the beliefs people – including veterinarians – hold about breed-specific pain sensitivity. The results appear in a new study from North Carolina State University, which also found that a dog’s temperament (specifically in the way they interact with strangers) may influence the way veterinarians view breed pain sensitivity.
“Veterinarians have a fairly strong consensus in their ratings of pain sensitivity ...
Controversy in Facebook posts linked to speed of spread among users
2023-06-28
A new analysis of nearly 60 million Facebook posts investigates how users’ interest in posts evolves over time, suggesting that the amount of controversy generated by a post is strongly linked to the speed with which it reaches a broad audience—regardless of the specific topic being discussed. Gabriele Etta of Sapienza Università di Roma, Italy, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 28, 2023.
This study adds to mounting research examining the influence ...
Kindness meditation helps people with depression recall positive memories, study finds
2023-06-28
A meditation that guides people to practice unconditional kindness to themselves and others helps people with a history of depression recall specific personal memories, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Amanda Lathan and Barbara Dritschel of the University of St. Andrews, UK.
Autobiographic memory is essential to human functioning in areas such as self-concept, emotion regulation and problem-solving. Research has suggested that, among the cognitive processes disrupted by depression, the retrieval of autobiographical memory is often impaired.
In the new ...
Intranasal insulin treatment might boost cognition in people with mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer's Disease, according to meta-analysis of 29 studies across multiple disorders
2023-06-28
Intranasal insulin treatment might boost cognition in people with mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer's Disease, according to meta-analysis of 29 studies across multiple disorders
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0286887
Article Title: Outcomes and clinical implications of intranasal insulin on cognition in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Author Countries: Canada
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Study: Anxiety, gloom often accompany intellectual deficits
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
Increasing the number of coronary interventions in patients with acute myocardial infarction does not appear to reduce death rates
Tackling uplift resistance in tall infrastructures sustainably
Novel wireless origami-inspired smart cushioning device for safer logistics
Hidden genetic mismatch, which triples the risk of a life-threatening immune attack after cord blood transplantation
[Press-News.org] Brain scans reveal that lonely people process the world in unique waysUSC Dornsife psychology researcher compares brain images of people who are lonely with those of people who are not lonely and discovers significant differences in their brain processing patterns.