Association of preoperative high-intensity interval training with cardiorespiratory fitness, postoperative outcomes among adults undergoing major surgery
JAMA Network Open
2023-06-30
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: The results of this systematic review and meta-analysis of 12 studies including 832 patients suggest that preoperative high-intensity interval training may improve cardiorespiratory fitness and reduce postoperative complications. These findings support including high-intensity interval training in pre-habilitation programs before major surgery.
Authors: John C. Woodfield, Ph.D., of the University of Otago in Dunedin, New Zealand, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.20527)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.20527?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=063023
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-30
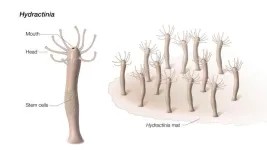
Insights into healing and aging were discovered by National Institutes of Health researchers and their collaborators, who studied how a tiny sea creature regenerates an entire new body from only its mouth. The researchers sequenced RNA from Hydractinia symbiolongicarpus, a small, tube-shaped animal that lives on the shells of hermit crabs. Just as the Hydractinia were beginning to regenerate new bodies, the researchers detected a molecular signature associated with the biological process of aging, also known as senescence. According to the study published in Cell Reports, Hydractinia demonstrates that the fundamental biological processes of healing and aging are intertwined, ...
2023-06-30
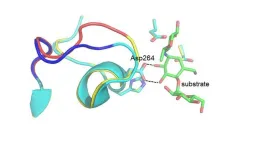
For the first time, researchers have succeeded in predicting how to change the optimum temperature of an enzyme using large computer calculations. A cold-adapted enzyme from an Antarctic bacterium was used as a basis. The study is to be published in the journal Science Advances and is a collaboration between researchers at Uppsala University and the University of Tromsø.
The type of cold-adapted enzymes used by the researchers for their study can be found in bacteria and fish that live in icy water, for example. Evolution has shaped ...
2023-06-30
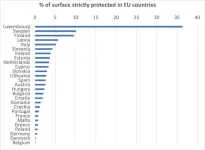
The goal of fully protecting 10% of the EU's land area is ambitious for European countries that have been profoundly shaped by millennia of human transformation. A recently published study, coordinated by the University of Bologna, has carried out the first analysis at European level on the strictly protected areas (classified by the IUCN as integral reserves, wilderness areas and national parks) across the EU, studying how extensive integral protection is across biogeographical regions, countries and elevation gradients.
"We have discovered – explains Prof. Roberto Cazzolla Gatti, conservation ...
2023-06-30
This study is led by Dr. Jiali Liu (State Key Laboratory of Animal Biotech Breeding, College of Biological Sciences, China Agricultural University).
Meiotic recombination-related gene (e.g., DMC1, HFM1, MEIOB, MAJIN, C14ORF39/SIX6OS1, STAG3, SYCE1, SYCP2-3, TERB1-2) mutations have been identified in human subfertility or infertility. Surprisingly, most patients have been found to have aberrant splicing of genes such as MEIOB, C14ORF39/SIX6OS1, STAG3, and SYCE1. Therefore, it is imperative to understand ...
2023-06-30
Patients with limited hand function are soon set to benefit from an intelligent neuro-orthosis that will enable them to lead independent lives again. Prof. Dr. Alessandro Del Vecchio, a neuroscientist at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), is working on this aim in two new projects and has received over 1.3 million euros of funding from the Free State of Bavaria. The main focus of this research during the next three years will involve wireless measurements of muscle impulses and the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to make the intended movements.
Around 50 million people worldwide suffer from neuromotor impairments to their hands caused ...
2023-06-30
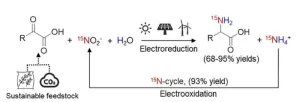
15N isotope-labeled amino acids (15N-amino acids) provide a safe and effective tracer tool for studying the synthesis of natural products, protein metabolism, and disease diagnosis and treatment in living organisms. In addition, it is an important synthetic block for the synthesis of 15N-labeled drugs. Currently, 15N-labeled amino acids are generally synthesized by microbial fermentation and chemical reduction amination of ketoacids, but these methods usually require complex steps, high temperature conditions or the use of toxic cyanide, causing energy and environmental ...
2023-06-30
Subtropical mode water (STMW) is a vertically homogeneous thermocline water mass, serving as heat, carbon, and oxygen silos in the ocean interior and providing memory of climate variability for climate prediction. Understanding physics governing STMW formation is thus of broad scientific significance and has received much attention. Traditionally, it has been considered that STMW is constructed by basin-scale atmospheric forcing. Due to the limitations resulting from sparse sampling of observations and coarse ...
2023-06-30
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a serious neurological disease that usually causes permanent disability. Approximately 2.9 million people are affected worldwide, 240,000 in Germany alone. The exact cause of the disease is not yet clear, but a central feature is a loss of the insulating protective layer of axons – the neuronal connections in the central nervous system – which is triggered by autoimmune processes. The coating of the axons, known as myelin, is formed by highly specialised glial cells (i.e. oligodendrocytes) and enables the rapid transmission ...
2023-06-30
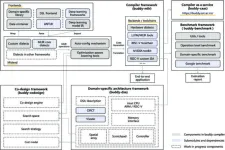
Co-design, that is, designing software and hardware simultaneously, is one way of attempting to meet the computing-power needs of today’s artificial intelligence applications. Compilers, which translate instructions from one representation to another, are a key piece of the puzzle. A group of researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences summarized existing compiler technologies in deep learning co-design and proposed their own framework, the Buddy Compiler.
The group’s review paper was published June 19 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Although others have summarized optimizations, hardware architectures, co-design approaches, and compilation ...
2023-06-30
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has resulted in more than 600 million confirmed cases and 6.5 million deaths worldwide. mRNA-based vaccines have emerged as a leading platform for COVID-19 protection and are extensively investigated in basic and clinical trials. SYS6006 (CSPC Pharmaceutical Group) is a newly investigational COVID-19 mRNA vaccine encoding a full-length S protein sequence of the prototype SARS-CoV-2 strain and incorporating the key mutations of main epidemic variants. In March 2023, it has been authorized for emergent use in China by the national medicinal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Association of preoperative high-intensity interval training with cardiorespiratory fitness, postoperative outcomes among adults undergoing major surgery
JAMA Network Open