Safety and immunogenicity of SYS6006 were evaluated in healthy adults after three doses of COVID-19 inactivated vaccines
2023-06-30
(Press-News.org)
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has resulted in more than 600 million confirmed cases and 6.5 million deaths worldwide. mRNA-based vaccines have emerged as a leading platform for COVID-19 protection and are extensively investigated in basic and clinical trials. SYS6006 (CSPC Pharmaceutical Group) is a newly investigational COVID-19 mRNA vaccine encoding a full-length S protein sequence of the prototype SARS-CoV-2 strain and incorporating the key mutations of main epidemic variants. In March 2023, it has been authorized for emergent use in China by the national medicinal product agency (NMPA) of China. Yet, the data from clinical trials have not been published before. Moreover, the third dose of inactivated vaccine of COVID-19 has been proposed as the initial boosting regimen, and the second heterologous booster (the fourth dose of the vaccine) is worth investigating.
By enrolling eligible healthy subjects and convalescent COVID-19 patients, researchers from Shanghai Xuhui Central Hospital have worked and unveiled the first clinical safety and efficacy profile of SYS6006. Eighteen eligible participants, who had completed three doses of inactivated COVID-19 vaccines, received a fourth boosting dose of SYS6006-20 μg. Eighteen convalescent COVID-19 patients were enrolled for the collection of serum samples as a comparator of immunogenicity. The incidence of adverse events within 30 days after the boosting was collected and reported. The titers of anti-RBD antibodies of the Omicron strain (BA.2 and BA.4/5) in serum and titers of neutralizing antibodies against pseudovirus of the Omicron strain (BA.2 and BA.4/5) were evaluated from baseline (day 0) until day 180 post-vaccination. Besides, specific T-cell responses against SARS-CoV-2 were measured by detecting the production of interferon gamma (IFN-γ) positive spots with ELISpot assay. This study entitled “Safety and immunogenicity of a modified COVID-19 mRNA vaccine, SYS6006, as a fourth-dose booster following three doses of inactivated vaccines in healthy adults: an open-labeled phase 1 trial” is published online in Life Metabolism in 2023.
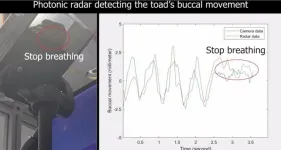
In this study, no serious adverse events were reported within 30 days after vaccination. No Grade 3 fever or serious adverse event was reported in the SYS6006 group. Notably, SYS6006 elicited higher titers and longer increases in anti-RBD antibodies and neutralizing antibodies (>90 days) compared with the convalescent group (P <0.0001) against Omicron strain (BA.2 and BA.4/5). Besides, higher positive spots of T-cell-secreting IFN-γ were observed in the SYS6006 group than those in the convalescent group (P <0.05).
These results demonstrated that a modified mRNA vaccine SYS6006 was safe and highly immunogenic as a heterologous booster in healthy Chinese adults. The strong enhancement of antibody titers after heterologous boosting is encouraging, along with the broad-spectrum neutralizing activity of these antibodies against variants of concern, such as Omicron BA.2 and BA.4/5. The titers in the SYS6006 group were higher than those in the convalescent patients. These findings suggest the flexible use of the mRNA vaccine as a booster regimen, which could accelerate the end of the pandemic.
###
Reference: Yuzhou Gui et al. (2023). Safety and immunogenicity of a modified COVID-19 mRNA vaccine, SYS6006, as a fourth-dose booster following three doses of inactivated vaccines in healthy adults: an open-labeled phase 1 trial. Life Metabolism https://academic.oup.com/lifemeta/advance-article/doi/10.1093/lifemeta/load019/7159154
About Higher Education Press
Founded in May 1954, Higher Education Press Limited Company (HEP), affiliated with the Ministry of Education, is one of the earliest institutions committed to educational publishing after the establishment of P. R. China in 1949. After striving for six decades, HEP has developed into a major comprehensive publisher, with products in various forms and at different levels. Both for import and export, HEP has been striving to fill in the gap of domestic and foreign markets and meet the demand of global customers by collaborating with more than 200 partners throughout the world and selling products and services in 32 languages globally. Now, HEP ranks among China’s top publishers in terms of copyright export volume and the world’s top 50 largest publishing enterprises in terms of comprehensive strength.
About Life Metabolism
Life Metabolism is a fully open access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes one volume per year online, providing a platform for the publication of works of high significance and broad interest in all areas of metabolism. Life Metabolism welcomes several different article types, including original article, review article, research highlight, letter, editorial, perspective, and so on. Once a paper is accepted, Life Metabolism can publish a precopyedited, preproofed version of the paper online within 48 hours of receiving a signed licence, and this will be replaced by a copyedited, proofed version of the paper as soon as it is ready. The Editors-in-Chief are professors Peng Li at Tsinghua University and John R Speakman at University of Aberdeen, UK. In the first three years, there will be no publication costs for publishing in Life Metabolism, and Open Access fees will be waived.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-30
Protein aggregates accumulate during aging and are linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease. A new study by the Nyström lab at Gothenburg University, in collaboration with the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing in Germany, describes a novel, engineered approach that makes protein aggregates amenable to spatial manipulations in both budding yeast and human cells.
Many neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease are associated with the aggregation of misfolded proteins ...
2023-06-30
As businesses become increasingly global, changes are also taking place at an extraordinary pace. Compliance is critical for large economies, industry regulations, and enterprise operations.
BGI Genomics prioritizes compliance management and strictly follow laws, regulations, and international practices while conducting business globally. BGI Genomics recently completed the rigorous evaluation of BSI, a major worldwide standard, testing, and certification authority. It was awarded the GB/T 35770-2022/ISO 37301:2021 Compliance Management System accreditation, making it the first enterprise in the industry to do so. ...
2023-06-30
Constant monitoring of vital health signs is needed in a variety of clinical environments such as intensive care units, for patients with critical health conditions, health monitoring in aged care facilities and prisons, or in safety monitoring situations where drowsiness can cause accidents.
This is now mostly achieved via wired or invasive contact systems. However, these are either inconvenient or, for patients with burns or for infants with insufficient skin area, are unsuitable.
Scientists at the University of Sydney Nano Institute and the NSW Smart Sensing ...
2023-06-30
Exploding populations of wild pigs and macaque monkeys in Southeast Asia are threatening native forests and disease outbreaks in livestock and people, according to research led by The University of Queensland.
Dr Matthew Luskin, from UQ’s School of the Environment, and his team collated and analysed species population data from across the region, some of it collected with a network of cameras.
“Macaques and wild pigs are taking over Southeast Asia’s disturbed forests,” Dr Luskin said.
“Humans are largely to blame for this by altering forests with logging ...
2023-06-30
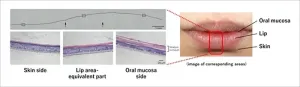
Niigata, Japan - KOSÉ Corporation (Headquarters: Chuo-ku, Tokyo; President: Kazutoshi Kobayashi) has developed in collaborative research with Professor Kenji Izumi and his colleagues at Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences (Faculty of Dentistry) a three-dimensional epithelial model that reproduces the human lip area from the oral mucosa to the lips and surrounding skin, using cell culture.
The lips are one of the most important elements that determine the impressions of the face, and they are also an area where many people suffer from problems, ...
2023-06-30
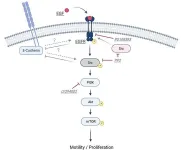
Niigata, Japan—Scientists have made significant progress in understanding the signals involved in regulating oral keratinocyte cell motility and proliferative capacity, offering new insights into potential pharmacological manipulation for regenerative medicine. A recent study, published in FEBS Open Bio, elucidated the role of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its downstream signaling cascade in controlling the behavior of oral keratinocytes.
Oral keratinocytes, which play a crucial role in the formation of the oral mucosa epithelial cell sheet, have long been enigmatic in terms of their signaling ...
2023-06-30
Long COVID is not a single condition, and should not be treated as such, according to new data collected in nationwide study released May 31 in the Open Forum of Infectious Diseases.
The study looked at persistent symptoms experienced by patients with COVID-19 both at three- and six-month intervals. In all, 5,963 patients participated in the study, with 4,504 of the participants testing positive for COVID-19 and 1,459 testing negative. Many of the participants, 2,000 in all, came from King County through the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The four major symptom categories for people who tested positive for COVID-19 included:
Minimal ...
2023-06-30
Sophia Antipolis, 30 June 2023: Loneliness is a bigger risk factor for heart disease in patients with diabetes than diet, exercise, smoking and depression, according to research published today in European Heart Journal, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“The quality of social contact appears to be more important for heart health in people with diabetes than the number of engagements,” said study author Professor Lu Qi of Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, New Orleans, US. “We should not downplay the important of loneliness ...
2023-06-30
ST. LOUIS - Research published in Outlook on Agriculture has shown that the population relative to available climate-suitable areas in Kenya has increased, posing a threat to the country’s economy and food security.
The study, “Spatial changes to climate suitability and availability of agropastoral farming systems across Kenya (1980-2020),” was published online on May 29.
The research team analyzed Kenya’s farming systems and climate zones between 1980-2020. Over that time, the population ...
2023-06-30
The current status and future perspectives on the successful industrialization of biobased succinic acid are discussed in a comprehensive review article in the peer-reviewed journal Industrial Biotechnology. Click here to read the article now.
Succinic acid is one of the most important platform chemicals, with applications as a pharmaceutical ingredient, food additive, precursor of various chemicals, and raw material for biobased polymers. There is increasing demand for the sustainable production of succinic acid and its derivatives.
Sang Yup Lee, from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), and coauthors, review ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Safety and immunogenicity of SYS6006 were evaluated in healthy adults after three doses of COVID-19 inactivated vaccines