Electrosynthesis of 15N-labeled amino acids from 15N-nitrite and ketonic acids
2023-06-30
(Press-News.org)
15N isotope-labeled amino acids (15N-amino acids) provide a safe and effective tracer tool for studying the synthesis of natural products, protein metabolism, and disease diagnosis and treatment in living organisms. In addition, it is an important synthetic block for the synthesis of 15N-labeled drugs. Currently, 15N-labeled amino acids are generally synthesized by microbial fermentation and chemical reduction amination of ketoacids, but these methods usually require complex steps, high temperature conditions or the use of toxic cyanide, causing energy and environmental problems. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop a green and mild method for the synthesis of 15N-amino acids.
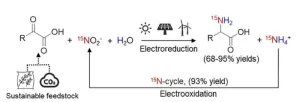
Recently, Zhang’s group reported an electrochemical method to synthesize 15N-amino acids from 15N-nitrite and ketonic acids over a commercial nickel foam (NF) cathode in an aqueous solution under ambient conditions. 15N-alanine with a 93% yield was achieved. Impressively, 15N-ammonium, the major byproduct, could be electrooxidized to 15N-nitrite with a yield of 93%, realizing the recycling property and atomic economy of 15N-nitrite. A 15N-nitrite→15NH2OH→15N-oxime→15N-amino acid pathway was revealed by a series of control experiments, in situ attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (in situ A TR-SEIRAS) spectroscopy, and online differential electrochemical mass spectrometry (DEMS). Furthermore, the method was suitable for synthesizing six 15N-amino acids with 68%–95% yields, demonstrating the good universality of this method. A hepatitis treatment drug, 15N-tiopronin, was synthesized using 15N-glycine, highlighting the utility of this method.
The study not only offers a strategy for the room-temperature and green synthesis of 15N-amino acids but also opens a sustainable avenue to construct 15N-labeled compounds.
See the article:
Electrosynthesis of 15N-labeled amino acids from 15N-nitrite and ketonic acids
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-023-1613-x
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-30
Subtropical mode water (STMW) is a vertically homogeneous thermocline water mass, serving as heat, carbon, and oxygen silos in the ocean interior and providing memory of climate variability for climate prediction. Understanding physics governing STMW formation is thus of broad scientific significance and has received much attention. Traditionally, it has been considered that STMW is constructed by basin-scale atmospheric forcing. Due to the limitations resulting from sparse sampling of observations and coarse ...
2023-06-30
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a serious neurological disease that usually causes permanent disability. Approximately 2.9 million people are affected worldwide, 240,000 in Germany alone. The exact cause of the disease is not yet clear, but a central feature is a loss of the insulating protective layer of axons – the neuronal connections in the central nervous system – which is triggered by autoimmune processes. The coating of the axons, known as myelin, is formed by highly specialised glial cells (i.e. oligodendrocytes) and enables the rapid transmission ...
2023-06-30
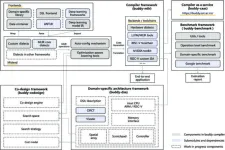
Co-design, that is, designing software and hardware simultaneously, is one way of attempting to meet the computing-power needs of today’s artificial intelligence applications. Compilers, which translate instructions from one representation to another, are a key piece of the puzzle. A group of researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences summarized existing compiler technologies in deep learning co-design and proposed their own framework, the Buddy Compiler.
The group’s review paper was published June 19 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Although others have summarized optimizations, hardware architectures, co-design approaches, and compilation ...
2023-06-30
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has resulted in more than 600 million confirmed cases and 6.5 million deaths worldwide. mRNA-based vaccines have emerged as a leading platform for COVID-19 protection and are extensively investigated in basic and clinical trials. SYS6006 (CSPC Pharmaceutical Group) is a newly investigational COVID-19 mRNA vaccine encoding a full-length S protein sequence of the prototype SARS-CoV-2 strain and incorporating the key mutations of main epidemic variants. In March 2023, it has been authorized for emergent use in China by the national medicinal ...
2023-06-30
Protein aggregates accumulate during aging and are linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease. A new study by the Nyström lab at Gothenburg University, in collaboration with the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing in Germany, describes a novel, engineered approach that makes protein aggregates amenable to spatial manipulations in both budding yeast and human cells.
Many neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease are associated with the aggregation of misfolded proteins ...
2023-06-30
As businesses become increasingly global, changes are also taking place at an extraordinary pace. Compliance is critical for large economies, industry regulations, and enterprise operations.
BGI Genomics prioritizes compliance management and strictly follow laws, regulations, and international practices while conducting business globally. BGI Genomics recently completed the rigorous evaluation of BSI, a major worldwide standard, testing, and certification authority. It was awarded the GB/T 35770-2022/ISO 37301:2021 Compliance Management System accreditation, making it the first enterprise in the industry to do so. ...
2023-06-30
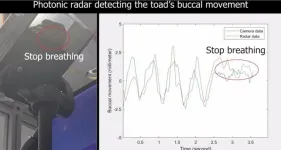
Constant monitoring of vital health signs is needed in a variety of clinical environments such as intensive care units, for patients with critical health conditions, health monitoring in aged care facilities and prisons, or in safety monitoring situations where drowsiness can cause accidents.
This is now mostly achieved via wired or invasive contact systems. However, these are either inconvenient or, for patients with burns or for infants with insufficient skin area, are unsuitable.
Scientists at the University of Sydney Nano Institute and the NSW Smart Sensing ...
2023-06-30
Exploding populations of wild pigs and macaque monkeys in Southeast Asia are threatening native forests and disease outbreaks in livestock and people, according to research led by The University of Queensland.
Dr Matthew Luskin, from UQ’s School of the Environment, and his team collated and analysed species population data from across the region, some of it collected with a network of cameras.
“Macaques and wild pigs are taking over Southeast Asia’s disturbed forests,” Dr Luskin said.
“Humans are largely to blame for this by altering forests with logging ...
2023-06-30
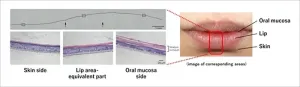
Niigata, Japan - KOSÉ Corporation (Headquarters: Chuo-ku, Tokyo; President: Kazutoshi Kobayashi) has developed in collaborative research with Professor Kenji Izumi and his colleagues at Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences (Faculty of Dentistry) a three-dimensional epithelial model that reproduces the human lip area from the oral mucosa to the lips and surrounding skin, using cell culture.
The lips are one of the most important elements that determine the impressions of the face, and they are also an area where many people suffer from problems, ...
2023-06-30
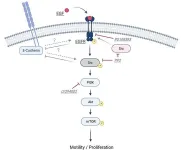
Niigata, Japan—Scientists have made significant progress in understanding the signals involved in regulating oral keratinocyte cell motility and proliferative capacity, offering new insights into potential pharmacological manipulation for regenerative medicine. A recent study, published in FEBS Open Bio, elucidated the role of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its downstream signaling cascade in controlling the behavior of oral keratinocytes.
Oral keratinocytes, which play a crucial role in the formation of the oral mucosa epithelial cell sheet, have long been enigmatic in terms of their signaling ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Electrosynthesis of 15N-labeled amino acids from 15N-nitrite and ketonic acids