Transplantation of genome-edited iPS cells delivers therapeutic molecules in vivo
2023-07-03
(Press-News.org)
Induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells have a great impact on biology and medicine, and they are expected to improve regenerative medicine. Since 2014 when a sheet of retinal pigment epithelial cells derived from iPS cells was transplanted into patients with age-related macular degeneration, clinical trials have been conducted with various cell types derived from iPS cells. While iPS cells derived from healthy individuals have been used so far, it is expected that transplantation therapy using iPS cells can be enhanced through genetic modification in the future.
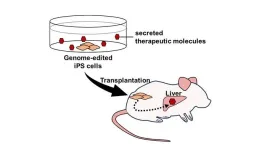
Therefore, we addressed this possibility by utilizing a Fabry disease mouse model, as a proof of concept. Fabry disease is caused by the genetical deficiency of α-Galactosidase A (GLA), leading to the accumulation of its substrates such as globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) and globotriaosylsphingosine (Lyso-Gb3). We previously developed an engineered enzyme, modified α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase (mNAGA), to cure Fabry disease by altering the substrate specificity of NAGA, which is a paralog of GLA, into that of GLA. Because mNAGA maintains the original antigenicity of NAGA, this modified enzyme has no immunological cross-reactivity with GLA, while having the GLA enzymatic activity. In this study, we tested whether transplantation of iPS cells secreting mNAGA by genome editing could supply the GLA activity in vivo.
First, we generated iPS cells secreting mNAGA by TALEN-mediated knock-in to the AAVS1 site, a safe harbor locus. In addition, to exclude the possible immunogenic reactions caused by the endogenous GLA of iPS cells in patients, we disrupted the GLA gene by CRISPR-Cas9. When the Fabry model cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts with no GLA activity were co-cultured with mNAGA-secreting iPS cells, the GLA activity was restored by mNAGA-expressing cells in vitro.
Next, we transplanted the iPS cells secreting mNAGA into the testes of Fabry disease model mice. After 7 or 8 weeks, the GLA activity in the liver was significantly improved, although no recovery of the activity was observed in the heart, kidney, or blood plasma. We also quantified the amounts of Gb3 and Lyso-Gb3 in the liver, but there was no detectable reduction of the substrates.
Due to the limited amount of mNAGA secreted from the transplanted iPS cells, the GLA activity in the liver was not high enough to reduce Gb3 or Lyso-Gb3. However, in the future, it may be possible to enhance the amount of secreted mNAGA through genome editing. There is also the possibility to directly deliver mNAGA to organs and tissues that need the GLA activity. For example, transplantation of a cardiomyocyte sheet derived from iPS cells secreting mNAGA directly delivers mNAGA to the heart. Furthermore, while this study focused on Fabry disease, the same strategy can be applied to other diseases.
This study demonstrated the potential of cell therapy using genome-edited iPS cells secreting therapeutic molecules. These genome-edited iPS cells could serve as not only a resource for cell transplantation but also a drug delivery system.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-03
Research Background
The era of Big Data features intelligence, ubiquity, and interconnection of all things. It comes with other advanced information technologies, such as the Internet, Cloud Computing (CC), Internet of Things (IoT), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) . Human society has also gradually entered the Ternary Space from the Binary Space. That is, from the Social Space (the sum of human behavior and social activities) to the Information Space (the computer, Internet, and data information built on physical space and social space) . The Ternary Space maps and digitally connect the urban physical and social ...
2023-07-03
Bluetongue virus, an incurable cattle and sheep-killing disease, is spread by tiny flies once thought to disappear in winter. New research demonstrates that though they are harder to find when it’s cold, they remain active.
Bluetongue virus is common in cattle throughout most of the United States, particularly in the southwestern U.S. with nearly 20% of some California cattle herds infected. Due to concerns about spread of this virus, exports of U.S. cattle and cattle products to parts of Europe and Asia have been restricted to prevent contamination.
However, not all infected animals die. The main symptoms are elevated temperatures, lethargy, ...
2023-07-03
Prof. Claudia Felser is a director at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids in Germany, Prof. B. Andrei Bernevig is a Professor of Physics at Princeton University in the United States and Visiting Ikerbasque Professor at Donostia International Physics Center in Spain.
The Prize will be presented on Wednesday 6th September 2023, during the Awards Session of the 30th General Conference of the EPS Condensed Matter Division (CMD30), to be held in Milan (joint organization with FisMat in Italy). This prize has been awarded since 1975 (this is the 40th edition) and is one ...
2023-07-03
The effort is led by Dr. David Talan, a professor of emergency medicine and infectious diseases in the UCLA Department of Emergency Medicine at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
Summer 2022 saw an outbreak of the disease that infected people in several countries across the globe. That outbreak receded by the following fall after widespread public attention and vaccination of high-risk individuals, prompting the World Health Organization on May 11, 2023 to declare an end to mpox as a global health emergency.
But a recent outbreak among 20 people in Chicago, including some vaccine breakthrough ...
2023-07-03
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society’s Journal of the Endocrine Society (JES) received its first Impact Factor score in 2022, while the Society’s other journals maintained high rankings on the prestigious measure of scholarly publishing.
The 2022 Impact Factors were released June 28 by Journal Citation Reports, an annual publication of Clarivate Analytics.
JES, which launched in 2017, is an open access journal providing rapid publication of clinical research, clinical practice information, and basic research in all areas of endocrinology. The publication also ...
2023-07-03
Resource managers and conservationists have been offered an innovative, new approach to selecting coral species for reef restoration. An international team of scientists worked together to develop this approach during a workshop organized by the University of Melbourne (U Melbourne) and the Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS). In a study published today in the Journal of Applied Ecology, this international team of scientists, led by a University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa researcher, revealed a strategy for choosing a set of key ...
2023-07-03
Brain damage caused by oxygen deficiency at birth is one of the main causes of death in newborns worldwide. Using a small animal model, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and DZNE tested treatment with 25 different active agents. Seven substances proved to be more effective than the standard therapy of artificial cooling: caffeine performed best. The results, published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports, could pave the way for new treatment options for newborns.
Children, who experience ...
2023-07-03
A new online platform to explore computationally calculated chemical reaction pathways has been released, allowing for in-depth understanding and design of chemical reactions.
Advances in computational chemistry have proven a great boon in the field of reaction design, leading to the discovery of new reaction pathways for the synthesis of high-value compounds. Computational chemistry generates much data, and the process of organizing and visualizing this data is vital to be able to utilize it for future research.
A team of researchers from Hokkaido University, led by Professor Keisuke Takahashi at the Faculty of Chemistry and Professor Satoshi ...
2023-07-03
Recurrent cystitis (RC) is a frequent infection of the urinary tract and bladder, which is highly prevalent among postmenopausal women. Under healthy circumstances, the human vagina is home to a host of beneficial intestinal bacteria, such as Lactobacilli. However, in the case of urinary tract infections (UTIs), there is a decrease in the abundance of Lactobacilli and an increase in pathogenic bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli).
Previous studies have shown that changes in vaginal microbiota are a key underlying reason for the development of UTIs. Further, a few clinical trials have demonstrated the utility of Lactobacillus-containing vaginal ...
2023-07-03
Amazon river dolphins are under threat from fishing and proposed new dams and dredging, research shows.
Scientists used satellite tags to track eight dolphins in the Peruvian Amazon, to discover where they went in relation to fishing areas and proposed dams and dredging sites.
On average, 89% of the dolphins’ home “range” (the area they live in) was used for fishing.
Dolphins were found to be an average of 252km from the nearest proposed dam and 125km from the nearest proposed dredging site.
While these are significant distances, the dolphins’ ranges ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Transplantation of genome-edited iPS cells delivers therapeutic molecules in vivo