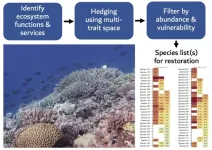
(Press-News.org) Resource managers and conservationists have been offered an innovative, new approach to selecting coral species for reef restoration. An international team of scientists worked together to develop this approach during a workshop organized by the University of Melbourne (U Melbourne) and the Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS). In a study published today in the Journal of Applied Ecology, this international team of scientists, led by a University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa researcher, revealed a strategy for choosing a set of key coral species that will best maintain ecosystem functions critical for reef health.
Coral reefs worldwide are rapidly disappearing due to a number of anthropogenic disturbances, with global warming being the biggest threat. In response, coral reef restoration is a growing research field and industry. Most coral reefs comprise tens to hundreds of stony coral species, yet resources for coral reef restoration are insufficient to restore them all. Methods for selecting species that will best maintain species diversity and ecosystem function are currently unavailable.
“The ecosystem services that coral reefs provide for people, such as coastal protection and fisheries, depend upon coral species with a broad range of what are called life history strategies, for example slow to fast growing, mounding to branching shapes, and under to upper storey,” said Joshua Madin, study lead author and research professor at the Hawai‘i Institute of Marine Biology in the UH Mānoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST). “Therefore, restoration practitioners need to consider this range of local species when restoring coral reefs—much like forest restoration requires more than just fast-growing plants.”
The research team combined databases of coral species traits with their ecological characteristics, including their resistance to thermal bleaching, to see how best to select sets of species for restoration using a hedging approach, much like that used for investment portfolios.
“Selection based on ecological characteristics is important for hedging against future species loss, whereas trait diversity is important for hedging against the loss of certain ecosystem services, reef-building groups, life history categories, and evolutionary variety,” said Madin.
This hedging approach provides a simple framework for aiding restoration practitioners in selecting target species for their projects, depending on spatial scale and resources.
“For example, if a program only has funds to focus on 20 coral species, they would want to focus on the sets of species to get the most ecosystem bang for their buck,” said Professor Madeleine van Oppen from U Melbourne and AIMS, who is the senior author on the paper. “Current coral restoration programs tend to focus on easy to collect, “weedy" coral species, which have similar characteristics and cannot support ecosystem services on their own.”
The study also found that, if species data are limited, selecting species at random is much better than selecting species that are easy to collect. The extra effort required will pay off in terms of preserving ecosystem services that communities rely on. The method can be applied to any coral reef for which coral trait data are available.
As coral reefs face greater risks, including in Hawai’i and Australia, where people depend on reefs for tourism, recreation, coastal protection, and sustenance, coral restoration is the focus of much research and development. The new approach to selecting coral species is already being applied to a hybrid reef program in Hawai’i funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. The goal of that ground-breaking project is to create an engineered structure that provides habitat for corals and other reef life while protecting coastlines from flooding, erosion and storm damage.
END
Hedging strategy for coral restoration balances diversity, ecosystem benefits
2023-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New approaches against the consequences of birth asphyxia
2023-07-03
Brain damage caused by oxygen deficiency at birth is one of the main causes of death in newborns worldwide. Using a small animal model, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and DZNE tested treatment with 25 different active agents. Seven substances proved to be more effective than the standard therapy of artificial cooling: caffeine performed best. The results, published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports, could pave the way for new treatment options for newborns.
Children, who experience ...
Virtual exploration of chemical reactions
2023-07-03
A new online platform to explore computationally calculated chemical reaction pathways has been released, allowing for in-depth understanding and design of chemical reactions.
Advances in computational chemistry have proven a great boon in the field of reaction design, leading to the discovery of new reaction pathways for the synthesis of high-value compounds. Computational chemistry generates much data, and the process of organizing and visualizing this data is vital to be able to utilize it for future research.
A team of researchers from Hokkaido University, led by Professor Keisuke Takahashi at the Faculty of Chemistry and Professor Satoshi ...
Vaginal suppository containing lactobacilli can prevent recurrent cystitis in women
2023-07-03
Recurrent cystitis (RC) is a frequent infection of the urinary tract and bladder, which is highly prevalent among postmenopausal women. Under healthy circumstances, the human vagina is home to a host of beneficial intestinal bacteria, such as Lactobacilli. However, in the case of urinary tract infections (UTIs), there is a decrease in the abundance of Lactobacilli and an increase in pathogenic bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli).
Previous studies have shown that changes in vaginal microbiota are a key underlying reason for the development of UTIs. Further, a few clinical trials have demonstrated the utility of Lactobacillus-containing vaginal ...
Amazon dolphins at risk from fishing, dams and dredging
2023-07-03
Amazon river dolphins are under threat from fishing and proposed new dams and dredging, research shows.
Scientists used satellite tags to track eight dolphins in the Peruvian Amazon, to discover where they went in relation to fishing areas and proposed dams and dredging sites.
On average, 89% of the dolphins’ home “range” (the area they live in) was used for fishing.
Dolphins were found to be an average of 252km from the nearest proposed dam and 125km from the nearest proposed dredging site.
While these are significant distances, the dolphins’ ranges ...
Fewer teens now perceive themselves as overweight – international study of more than 745,000 adolescents
2023-07-03
A study involving more than 745,000 adolescents from 41 countries across Europe and North America identified an increase in the amount of teenagers who underestimate their body weight.
Tracking data from 2002 to 2018, the peer-reviewed findings, published today in Child and Adolescent Obesity, demonstrate a noticeable decrease in those who overestimate their weight too.
The team of international experts, who carried out the research, warn these shifting trends in body weight perception could reduce the effectiveness of public health interventions aimed at weight reduction in young people.
“During this impressionable age, body weight perception ...
Aston University appoints UK’s only Regius Professor of Pharmacy
2023-07-03
Professor Ian Wong has been appointed as Regius Professor of Pharmacy at Aston University
A Regius Professorship is a rare award bestowed on a university by the monarch - a mark of exceptionally high standards of research and teaching
Aston University’s Pharmacy School can trace its roots back to 1847.
Under embargo until 00:01 hrs BST 3 July 2023| Birmingham, UK
Aston University has appointed Professor Ian Wong as its new Regius Professor of Pharmacy.
Professor Wong is a pharmacoepidemiologist. His research focuses on the application ...
Why do we articulate more when speaking to babies and puppies?
2023-07-01
Babies and puppies have at least two things in common: aside from being newborns, they promote a positive emotional state in human mothers, leading them to articulate better when they speak. This finding is the result of research by an international team1 that included Alejandrina Cristia, a CNRS Researcher at the Laboratoire de sciences cognitives et psycholinguistique (LSCP) (CNRS/EHESS/ENS-PSL). Scientists studied the vocal behaviour of ten mothers to better understand why mothers articulate more when speaking to infants. Participants were asked to ...
COVID-19 vaccination reduced disease disparities between low- and high-income communities
2023-07-01
COVID-19 vaccination helped reduce disparities in disease incidence between low- and high-income communities, according to a new analysis led by Cedars-Sinai investigators.
While lower-income communities had lower vaccination rates than higher-income communities, the impact of vaccination on disease incidence was larger in lower-income communities. As a result, investigators say, vaccination led to reduced income-related disparities in COVID-19 incidence.
The findings were published today in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, a publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
“This study is a unique demonstration ...
Immune-boosting therapy helps honey bees resist deadly viruses
2023-07-01
Scientists have successfully tested a novel way of boosting honey bees’ immune systems to help them fend off deadly viruses, which have contributed to the major losses of the critical pollinator globally.
In a new study, the research team, which includes entomologists with the University of Florida, the Agricultural Research Service-USDA, Louisiana State University and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, showed that prompting honey bees’ cells to produce free radicals helped the bees weather a host of viruses. In fact, the treatment greatly reduced, and in some cases, nearly eliminated virus ...
Biomedical Sciences researcher gets $2.67 million grant to study cardiac disease in diabetes
2023-07-01
ATLANTA — Dr. Jun Zou, a research assistant professor in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University, has received a five-year, $2.67 million federal grant to study the link between gut dysbiosis, an imbalance in the microbiota, and cardiac disease in diabetes.
The grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute will be used to explore the role of diabetes-induced alteration of gut microbiota ...