(Press-News.org) Amazon river dolphins are under threat from fishing and proposed new dams and dredging, research shows.
Scientists used satellite tags to track eight dolphins in the Peruvian Amazon, to discover where they went in relation to fishing areas and proposed dams and dredging sites.
On average, 89% of the dolphins’ home “range” (the area they live in) was used for fishing.
Dolphins were found to be an average of 252km from the nearest proposed dam and 125km from the nearest proposed dredging site.
While these are significant distances, the dolphins’ ranges spanned over 50km on average, and dams and dredging can affect large stretches of river habitats.
Additionally, many Amazon river dolphins – already an endangered species – live closer to the proposed sites than the seven males and one female tagged in this study.
The research was carried out by the University of Exeter and Peruvian conservation organisation Pro Delphinus.
“It’s clear that the Amazon river dolphin is facing increasing threats from humans,” said Dr Elizabeth Campbell, of the Centre for Ecology and Conservation on Exeter’s Penryn Campus in Cornwall.
“Fishing can deplete populations of the dolphins’ prey, and dolphins are also at risk from intentional killing and bycatch (accidental catching).
“Bycatch has been known to be a threat to these dolphins for the last 30 years, but there’s no real data on how many dolphins are caught per year.”
The construction of dams, mainly in Brazil, is an expanding threat, with 175 dams operating or under construction in the Amazon basin, and at least 428 more planned over the next 30 years.
Additionally, the Amazon Waterway has been approved and is under contract for construction.
This will involve dredging sites across four main rivers of the Amazon basin, and the expansion of ports to facilitate ship navigation across the Amazon, Ucayali and Marañón rivers.
But the researchers say the Peruvian government has an opportunity to protect biodiversity.
“Peru has a chance to preserve its free-flowing rivers, keeping them a safe and healthy habitat for river dolphins and many other species,” Dr Campbell said.
“Given that many of these dams and dredging projects are still in the planning stage, we advise the government to consider the negative effects these activities have already had on river species elsewhere.”
Dr Campbell added: “River dolphin tracking programmes should now be expanded to span multiple seasons, to track more females at our study sites and to increase the numbers tracked in other areas to improve our knowledge of the movement patterns of this species.”
The Amazon River dolphin is found throughout the basins of the Amazon and Orinoco Rivers and is categorised as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
The study was funded by the South American River Dolphin Initiative and WWF Peru.
The paper, published in the journal Oryx, is entitled: “Satellite-monitored movements of the Amazon River dolphin and considerations for their conservation.”
END
Amazon dolphins at risk from fishing, dams and dredging
2023-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fewer teens now perceive themselves as overweight – international study of more than 745,000 adolescents
2023-07-03
A study involving more than 745,000 adolescents from 41 countries across Europe and North America identified an increase in the amount of teenagers who underestimate their body weight.
Tracking data from 2002 to 2018, the peer-reviewed findings, published today in Child and Adolescent Obesity, demonstrate a noticeable decrease in those who overestimate their weight too.
The team of international experts, who carried out the research, warn these shifting trends in body weight perception could reduce the effectiveness of public health interventions aimed at weight reduction in young people.
“During this impressionable age, body weight perception ...
Aston University appoints UK’s only Regius Professor of Pharmacy
2023-07-03
Professor Ian Wong has been appointed as Regius Professor of Pharmacy at Aston University
A Regius Professorship is a rare award bestowed on a university by the monarch - a mark of exceptionally high standards of research and teaching
Aston University’s Pharmacy School can trace its roots back to 1847.
Under embargo until 00:01 hrs BST 3 July 2023| Birmingham, UK
Aston University has appointed Professor Ian Wong as its new Regius Professor of Pharmacy.
Professor Wong is a pharmacoepidemiologist. His research focuses on the application ...
Why do we articulate more when speaking to babies and puppies?
2023-07-01
Babies and puppies have at least two things in common: aside from being newborns, they promote a positive emotional state in human mothers, leading them to articulate better when they speak. This finding is the result of research by an international team1 that included Alejandrina Cristia, a CNRS Researcher at the Laboratoire de sciences cognitives et psycholinguistique (LSCP) (CNRS/EHESS/ENS-PSL). Scientists studied the vocal behaviour of ten mothers to better understand why mothers articulate more when speaking to infants. Participants were asked to ...
COVID-19 vaccination reduced disease disparities between low- and high-income communities
2023-07-01
COVID-19 vaccination helped reduce disparities in disease incidence between low- and high-income communities, according to a new analysis led by Cedars-Sinai investigators.
While lower-income communities had lower vaccination rates than higher-income communities, the impact of vaccination on disease incidence was larger in lower-income communities. As a result, investigators say, vaccination led to reduced income-related disparities in COVID-19 incidence.
The findings were published today in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, a publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
“This study is a unique demonstration ...
Immune-boosting therapy helps honey bees resist deadly viruses
2023-07-01
Scientists have successfully tested a novel way of boosting honey bees’ immune systems to help them fend off deadly viruses, which have contributed to the major losses of the critical pollinator globally.
In a new study, the research team, which includes entomologists with the University of Florida, the Agricultural Research Service-USDA, Louisiana State University and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, showed that prompting honey bees’ cells to produce free radicals helped the bees weather a host of viruses. In fact, the treatment greatly reduced, and in some cases, nearly eliminated virus ...
Biomedical Sciences researcher gets $2.67 million grant to study cardiac disease in diabetes
2023-07-01
ATLANTA — Dr. Jun Zou, a research assistant professor in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University, has received a five-year, $2.67 million federal grant to study the link between gut dysbiosis, an imbalance in the microbiota, and cardiac disease in diabetes.
The grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute will be used to explore the role of diabetes-induced alteration of gut microbiota ...
US Department of Energy releases plan to ensure free, immediate, and equitable access to federally funded research
2023-06-30
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today released a plan to ensure the Department’s Federally funded research is more open and accessible to the public, researchers, and journalists as part of a broader effort by the Biden-Harris Administration to make government data more transparent. With 17 National Laboratories and scores of programs that fund university and private research, DOE directly supports thousands of research papers per year, and, when this plan goes into effect, those findings will be available ...
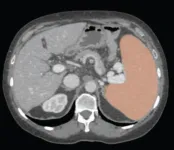
AI with volumetric thresholds facilitate opportunistic screening for splenomegaly
2023-06-30
Leesburg, VA, June 30, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), using an automated deep-learning AI tool, as well as weight-based volumetric thresholds, might afford large-scale evaluation for splenomegaly on CT examinations performed for any indication.
Noting that, historically, the standard linear splenic measurements used as a surrogate for splenic volume yielded suboptimal performance in detecting volume-based splenomegaly, “the ...
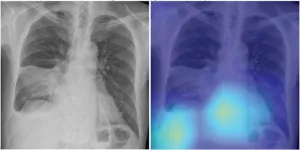
Deep-learning chest radiograph model predicts mortality for community-acquired pneumonia
2023-06-30
Leesburg, VA, June 30, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a deep learning-based model using initial chest radiographs predicted 30-day mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), improving upon the performance of an established risk prediction tool (i.e., CURB-65 score).
“The deep learning (DL) model may guide clinical decision-making in the management of patients with CAP by identifying high-risk patients who warrant hospitalization and intensive treatment,” concluded first author Eui Jin Hwang, MD, PhD, from the department of radiology at Seoul National ...
Astrophysicists propose a new way of measuring cosmic expansion: lensed gravitational waves
2023-06-30
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — The universe is expanding; we’ve had evidence of that for about a century. But just how quickly celestial objects are receding from each other is still up for debate.
It’s no small feat to measure the rate at which objects move away from each other across vast distances. Since the discovery of cosmic expansion, its rate has been measured and re-measured with increasing precision, with some of the latest values ranging from 67.4 up to 76.5 kilometers per second per megaparsec, which relates the recession velocity (in ...