(Press-News.org) A study involving more than 745,000 adolescents from 41 countries across Europe and North America identified an increase in the amount of teenagers who underestimate their body weight.
Tracking data from 2002 to 2018, the peer-reviewed findings, published today in Child and Adolescent Obesity, demonstrate a noticeable decrease in those who overestimate their weight too.
The team of international experts, who carried out the research, warn these shifting trends in body weight perception could reduce the effectiveness of public health interventions aimed at weight reduction in young people.
“During this impressionable age, body weight perception may influence a young person’s lifestyle choices, such as the amount and types of food they eat and their exercise habits,” says lead author Doctor Anouk Geraets, from the Department of Social Sciences, at the University of Luxembourg.
“So it’s concerning that we’re seeing a trend where fewer adolescents perceive themselves as being overweight – as this could undermine ongoing efforts to tackle increasing levels of obesity in this age group. Young people who underestimate their weight and therefore do not consider themselves to be overweight may not feel they need to lose excess weight and, as a result, they may make unhealthy lifestyle choices.”
A person’s perception of their body weight may not accurately reflect their actual weight. A discrepancy in body weight perception (BWP) may either be an underestimation (where actual weight is higher than perceived weight) or an overestimation (where actual weight is lower than perceived weight).
In the present study, the researchers examined survey data from 746,121 11-, 13- and 15-year-olds from 41 countries collected at four-yearly intervals between 2002 and 2018 in the International Health Behavior in School-Aged Children (HBSC), a WHO collaborative study.
The team modeled trends in BWP among adolescents across different countries over time, making adjustments for age, gender, and family socioeconomic status. They found:
Underestimation of weight status increased, and overestimation of weight status decreased over time among both sexes, with stronger trends for girls.
Correct weight perception increased over time among girls, while it decreased among boys.
Changes in correct weight perception, underestimation and overestimation of weight status differed across different countries – but these changes could not be explained by an increase in country-level overweight/obesity prevalence.
The authors speculated that the observed differences between girls and boys in BWP may support the idea there are sex differences in body ideals – and that these body ideals have changed over time. Notably, the increased underestimation and decreased overestimation of weight status over time for girls may be explained by the emergence of an athletic and strong body, as a new contemporary body ideal for both sexes.
“This study has clinical and public health implications. The increase in correct weight perception and the decrease in overestimation may have a positive effect on unnecessary and unhealthy weight loss behaviors among adolescents, while the increase in underestimation might indicate the need for interventions to strengthen correct weight perception,” says lead author Doctor Anouk Geraets.
“More research is now needed to understand the factors underlying these time trends and to develop effective public health interventions.”
While the large number of participating countries is a strength of the present study – but as these only included countries in Europe, the USA and Canada, the results can’t be generalized to other regions. In addition, although steps were taken to adjust the models for certain potential confounding factors, several other factors – such as body image, dieting, changing eating patterns, or migration – may also have played a role in the observed trends over time.
END
Fewer teens now perceive themselves as overweight – international study of more than 745,000 adolescents
Changes in body weight perception could undermine public health interventions to tackle obesity
2023-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Aston University appoints UK’s only Regius Professor of Pharmacy
2023-07-03
Professor Ian Wong has been appointed as Regius Professor of Pharmacy at Aston University
A Regius Professorship is a rare award bestowed on a university by the monarch - a mark of exceptionally high standards of research and teaching
Aston University’s Pharmacy School can trace its roots back to 1847.
Under embargo until 00:01 hrs BST 3 July 2023| Birmingham, UK
Aston University has appointed Professor Ian Wong as its new Regius Professor of Pharmacy.
Professor Wong is a pharmacoepidemiologist. His research focuses on the application ...
Why do we articulate more when speaking to babies and puppies?
2023-07-01
Babies and puppies have at least two things in common: aside from being newborns, they promote a positive emotional state in human mothers, leading them to articulate better when they speak. This finding is the result of research by an international team1 that included Alejandrina Cristia, a CNRS Researcher at the Laboratoire de sciences cognitives et psycholinguistique (LSCP) (CNRS/EHESS/ENS-PSL). Scientists studied the vocal behaviour of ten mothers to better understand why mothers articulate more when speaking to infants. Participants were asked to ...
COVID-19 vaccination reduced disease disparities between low- and high-income communities
2023-07-01
COVID-19 vaccination helped reduce disparities in disease incidence between low- and high-income communities, according to a new analysis led by Cedars-Sinai investigators.
While lower-income communities had lower vaccination rates than higher-income communities, the impact of vaccination on disease incidence was larger in lower-income communities. As a result, investigators say, vaccination led to reduced income-related disparities in COVID-19 incidence.
The findings were published today in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, a publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
“This study is a unique demonstration ...
Immune-boosting therapy helps honey bees resist deadly viruses
2023-07-01
Scientists have successfully tested a novel way of boosting honey bees’ immune systems to help them fend off deadly viruses, which have contributed to the major losses of the critical pollinator globally.
In a new study, the research team, which includes entomologists with the University of Florida, the Agricultural Research Service-USDA, Louisiana State University and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, showed that prompting honey bees’ cells to produce free radicals helped the bees weather a host of viruses. In fact, the treatment greatly reduced, and in some cases, nearly eliminated virus ...
Biomedical Sciences researcher gets $2.67 million grant to study cardiac disease in diabetes
2023-07-01
ATLANTA — Dr. Jun Zou, a research assistant professor in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University, has received a five-year, $2.67 million federal grant to study the link between gut dysbiosis, an imbalance in the microbiota, and cardiac disease in diabetes.
The grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute will be used to explore the role of diabetes-induced alteration of gut microbiota ...
US Department of Energy releases plan to ensure free, immediate, and equitable access to federally funded research
2023-06-30
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today released a plan to ensure the Department’s Federally funded research is more open and accessible to the public, researchers, and journalists as part of a broader effort by the Biden-Harris Administration to make government data more transparent. With 17 National Laboratories and scores of programs that fund university and private research, DOE directly supports thousands of research papers per year, and, when this plan goes into effect, those findings will be available ...
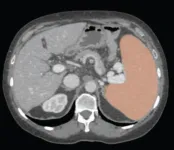
AI with volumetric thresholds facilitate opportunistic screening for splenomegaly
2023-06-30
Leesburg, VA, June 30, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), using an automated deep-learning AI tool, as well as weight-based volumetric thresholds, might afford large-scale evaluation for splenomegaly on CT examinations performed for any indication.
Noting that, historically, the standard linear splenic measurements used as a surrogate for splenic volume yielded suboptimal performance in detecting volume-based splenomegaly, “the ...
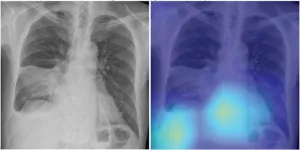
Deep-learning chest radiograph model predicts mortality for community-acquired pneumonia
2023-06-30
Leesburg, VA, June 30, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a deep learning-based model using initial chest radiographs predicted 30-day mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), improving upon the performance of an established risk prediction tool (i.e., CURB-65 score).
“The deep learning (DL) model may guide clinical decision-making in the management of patients with CAP by identifying high-risk patients who warrant hospitalization and intensive treatment,” concluded first author Eui Jin Hwang, MD, PhD, from the department of radiology at Seoul National ...
Astrophysicists propose a new way of measuring cosmic expansion: lensed gravitational waves
2023-06-30
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — The universe is expanding; we’ve had evidence of that for about a century. But just how quickly celestial objects are receding from each other is still up for debate.
It’s no small feat to measure the rate at which objects move away from each other across vast distances. Since the discovery of cosmic expansion, its rate has been measured and re-measured with increasing precision, with some of the latest values ranging from 67.4 up to 76.5 kilometers per second per megaparsec, which relates the recession velocity (in ...
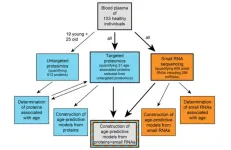
Age prediction from human blood plasma using proteomic and small RNA data: A comparative analysis
2023-06-30
“[...] we see our work as an indication that combining different molecular data types could be a general strategy to improve future aging clocks.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 30, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Age prediction from human blood plasma using proteomic and small RNA data: a comparative analysis.”
Aging clocks, built from comprehensive molecular data, have emerged as promising tools ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Korea University, Stanford University, and IESGA launch Water Sustainability Index to combat ESG greenwashing
Molecular glue discovery: large scale instead of lucky strike
Insulin resistance predictor highlights cancer connection
Explaining next-generation solar cells
Slippery ions create a smoother path to blue energy
Magnetic resonance imaging opens the door to better treatments for underdiagnosed atypical Parkinsonisms
National poll finds gaps in community preparedness for teen cardiac emergencies
One strategy to block both drug-resistant bacteria and influenza: new broad-spectrum infection prevention approach validated
Survey: 3 in 4 skip physical therapy homework, stunting progress
College students who spend hours on social media are more likely to be lonely – national US study
Evidence behind intermittent fasting for weight loss fails to match hype
How AI tools like DeepSeek are transforming emotional and mental health care of Chinese youth
Study finds link between sugary drinks and anxiety in young people
Scientists show how to predict world’s deadly scorpion hotspots
ASU researchers to lead AAAS panel on water insecurity in the United States
ASU professor Anne Stone to present at AAAS Conference in Phoenix on ancient origins of modern disease
Proposals for exploring viruses and skin as the next experimental quantum frontiers share US$30,000 science award
ASU researchers showcase scalable tech solutions for older adults living alone with cognitive decline at AAAS 2026
Scientists identify smooth regional trends in fruit fly survival strategies
Antipathy toward snakes? Your parents likely talked you into that at an early age
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for Feb. 2026
Online exposure to medical misinformation concentrated among older adults
Telehealth improves access to genetic services for adult survivors of childhood cancers
Outdated mortality benchmarks risk missing early signs of famine and delay recognizing mass starvation
Newly discovered bacterium converts carbon dioxide into chemicals using electricity
Flipping and reversing mini-proteins could improve disease treatment
Scientists reveal major hidden source of atmospheric nitrogen pollution in fragile lake basin
Biochar emerges as a powerful tool for soil carbon neutrality and climate mitigation
Tiny cell messengers show big promise for safer protein and gene delivery
AMS releases statement regarding the decision to rescind EPA’s 2009 Endangerment Finding
[Press-News.org] Fewer teens now perceive themselves as overweight – international study of more than 745,000 adolescentsChanges in body weight perception could undermine public health interventions to tackle obesity