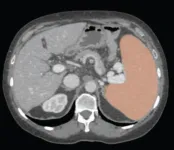
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, June 30, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), using an automated deep-learning AI tool, as well as weight-based volumetric thresholds, might afford large-scale evaluation for splenomegaly on CT examinations performed for any indication.
Noting that, historically, the standard linear splenic measurements used as a surrogate for splenic volume yielded suboptimal performance in detecting volume-based splenomegaly, “the weight-based volumetric thresholds indicated the presence of splenomegaly in most patients who underwent pre-liver transplant CT,” explained corresponding author Perry J. Pickhardt, MD, from the department of radiology at University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health.
Pickhardt and colleagues’ AJR accepted manuscript included a screening sample of 8,901 patients (4,235 men, 4,666 women; mean age, 56 years) who underwent CT colonoscopy (n = 7736) or renal-donor CT (n = 1165) from April 2004 to January 2017. A secondary cohort of 104 patients (62 men, 42 women; mean age, 56 years) with end-stage liver disease underwent pre-liver transplant CT from January 2011 to May 2013. Pickhardt et al.’s deep learning algorithm—previously developed, trained, and tested at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center—was used for spleen segmentation, to help determine splenic volumes, with two radiologists independently reviewing a subset of said segmentations.
Ultimately, this automated deep-learning AI tool was utilized to calculate splenic volumes from CT examinations in 8,853 patients from the primary outpatient population. Additionally, splenic volume was most strongly associated with weight, among a range of patient factors.
“To our knowledge,” the AJR authors concluded, “this study represents the largest reported sample of patients to undergo volumetric segmentation of the spleen.”
North America’s first radiological society, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) remains dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of medical imaging and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in radiology since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with the world’s longest continuously published radiology journal—American Journal of Roentgenology—the ARRS Annual Meeting, InPractice magazine, topical symposia, myriad multimedia educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
MEDIA CONTACT:
Logan K. Young, PIO
44211 Slatestone Court
Leesburg, VA 20176
lyoung@arrs.org
END
AI with volumetric thresholds facilitate opportunistic screening for splenomegaly
Using an automated deep-learning AI tool, as well as weight-based volumetric thresholds, might afford large-scale evaluation for splenomegaly on CT examinations performed for any indication
2023-06-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
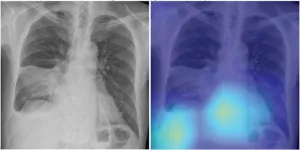
Deep-learning chest radiograph model predicts mortality for community-acquired pneumonia
2023-06-30
Leesburg, VA, June 30, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a deep learning-based model using initial chest radiographs predicted 30-day mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), improving upon the performance of an established risk prediction tool (i.e., CURB-65 score).
“The deep learning (DL) model may guide clinical decision-making in the management of patients with CAP by identifying high-risk patients who warrant hospitalization and intensive treatment,” concluded first author Eui Jin Hwang, MD, PhD, from the department of radiology at Seoul National ...
Astrophysicists propose a new way of measuring cosmic expansion: lensed gravitational waves
2023-06-30
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — The universe is expanding; we’ve had evidence of that for about a century. But just how quickly celestial objects are receding from each other is still up for debate.
It’s no small feat to measure the rate at which objects move away from each other across vast distances. Since the discovery of cosmic expansion, its rate has been measured and re-measured with increasing precision, with some of the latest values ranging from 67.4 up to 76.5 kilometers per second per megaparsec, which relates the recession velocity (in ...
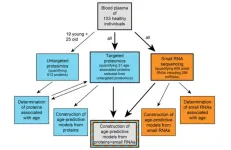
Age prediction from human blood plasma using proteomic and small RNA data: A comparative analysis
2023-06-30
“[...] we see our work as an indication that combining different molecular data types could be a general strategy to improve future aging clocks.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 30, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Age prediction from human blood plasma using proteomic and small RNA data: a comparative analysis.”
Aging clocks, built from comprehensive molecular data, have emerged as promising tools ...
New A.I. system can decode fruit fly behaviors. Why that’s ‘pivotal’ for future human genetics research
2023-06-30
How can you tell if a fruit fly is hungry? Ask a computer.
While that may sound like a bad dad joke, it’s reality at Tulane University, where researchers have developed a new A.I. tool that can tell you if a fruit fly is hungry, sleepy or singing (yes, fruit flies sing).
Dubbed MAFDA (for Novel Machine-learning-based Automatic Fly-behavioral Detection and Annotation) the system uses cameras and a newly developed software to track and identify complex interactive behaviors of individual flies within a larger group. This allows researchers to compare and contrast the behaviors of fruit flies with different genetic backgrounds.
For more than a century, ...
Breast cancer by age: Study reveals early mutations that predict patient outcomes
2023-06-30
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – June 30, 2023 – A study led by researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys has found that in young women, certain genetic mutations are associated with treatment-resistant breast cancer. These mutations are not linked to treatment-resistant breast cancer in older women. The findings, published in the journal Science Advances, could help improve precision medicine and suggest a brand-new way of classifying breast cancer.
“It’s well established that as you get older, you’re more likely to develop cancer. But we’re finding that this may not be true for all cancers depending on a person’s genetic makeup,” ...
Displays controlled by flexible fins and liquid droplets more versatile, efficient than LED screens
2023-06-30
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Flexible displays that can change color, convey information and even send veiled messages via infrared radiation are now possible, thanks to new research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. Engineers inspired by the morphing skins of animals like chameleons and octopuses have developed capillary-controlled robotic flapping fins to create switchable optical and infrared light multipixel displays that are 1,000 times more energy efficient than light-emitting devices.
The new study led by mechanical science and engineering professor Sameh Tawfick demonstrates ...
CU Anschutz researchers identify unique cell receptor, potential for new therapies
2023-06-30
AURORA, Colo. (June 30, 2023) – Researchers from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have identified a potential new immune checkpoint receptor that could lead to treatments for diseases such as lung and bowel cancer and autoimmune conditions including IBD.
The study, published today in Science Immunology, examines a family of 13 receptors, or proteins that transmit signals for cells to follow, called killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR). Of the 13 receptors, one is unique in that it has not readily been observed on immune cells of ...
A new bacterial blueprint to aid in the war on antibiotic resistance
2023-06-30
A team of scientists from around the globe, including those from Trinity College Dublin, has gained high-res structural insights into a key bacterial enzyme, which may help chemists design new drugs to inhibit it and thus suppress disease-causing bacteria. Their work is important as fears continue to grow around rising rates of antibiotic resistance.
The scientists, led by Martin Caffrey, Fellow Emeritus in Trinity’s School of Medicine and School of Biochemistry and Immunology, used next-gen X-ray crystallography and single particle cryo-electron microscopy ...
Climate disasters, traumatic events have long-term impacts on youths' academics
2023-06-30
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Experiencing traumatic events such as natural disasters may have long-term consequences for the academic progress and future food security of youth — a problem researchers said could worsen with the increased frequency of extreme weather events due to climate change.
In a study using data from Peru, researchers from Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences found that being exposed to a greater number of traumatic events or “shocks,” such as a natural disaster or loss of family income, in early ...
Researchers demonstrate single-molecule electronic "switch" using ladder-like molecules
2023-06-30
Researchers have demonstrated a new material for single-molecule electronic switches, which can effectively vary current at the nanoscale in response to external stimuli. The material for this molecular switch has a unique structure created by locking a linear molecular backbone into a ladder-type structure. A new study finds that the ladder-type molecular structure greatly enhances the stability of the material, making it highly promising for use in single-molecule electronics applications.
Reported in the journal Chem, the study shows that the ladder-type molecule serves as a robust and reversible molecular switch over a wide range of conductivity levels and different molecular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
[Press-News.org] AI with volumetric thresholds facilitate opportunistic screening for splenomegalyUsing an automated deep-learning AI tool, as well as weight-based volumetric thresholds, might afford large-scale evaluation for splenomegaly on CT examinations performed for any indication