Why do we articulate more when speaking to babies and puppies?
2023-07-01
(Press-News.org)
Babies and puppies have at least two things in common: aside from being newborns, they promote a positive emotional state in human mothers, leading them to articulate better when they speak. This finding is the result of research by an international team1 that included Alejandrina Cristia, a CNRS Researcher at the Laboratoire de sciences cognitives et psycholinguistique (LSCP) (CNRS/EHESS/ENS-PSL). Scientists studied the vocal behaviour of ten mothers to better understand why mothers articulate more when speaking to infants. Participants were asked to speak to a puppy, to their six-month-old baby, and to an adult for about ten minutes. Researchers extracted every voyel from the recordings, studied their acoustic characteristics, and measure the emotions expressed according to adults who were unaware of the context in which each vowel had been pronounced. Surprisingly, the team found that mothers articulated better and expressed more positive emotions when speaking to their babies or to puppies. In both situations, mothers displayed a range of positive emotions, which correlated with changes in their vocalisations. Other research shows that hyperarticulation leads to a clearer pronunciation of words and makes speech easier for infants to process. Published in the Journal of Child Language on 1 July, these findings demonstrate that future studies on maternal speech should consider the emotional state of individuals.
Notes
From Virginia Tech (Virginia, United States) and Pacific Lutheran University (Washington D.C., United States) END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-01
COVID-19 vaccination helped reduce disparities in disease incidence between low- and high-income communities, according to a new analysis led by Cedars-Sinai investigators.
While lower-income communities had lower vaccination rates than higher-income communities, the impact of vaccination on disease incidence was larger in lower-income communities. As a result, investigators say, vaccination led to reduced income-related disparities in COVID-19 incidence.
The findings were published today in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, a publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
“This study is a unique demonstration ...
2023-07-01
Scientists have successfully tested a novel way of boosting honey bees’ immune systems to help them fend off deadly viruses, which have contributed to the major losses of the critical pollinator globally.
In a new study, the research team, which includes entomologists with the University of Florida, the Agricultural Research Service-USDA, Louisiana State University and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, showed that prompting honey bees’ cells to produce free radicals helped the bees weather a host of viruses. In fact, the treatment greatly reduced, and in some cases, nearly eliminated virus ...
2023-07-01
ATLANTA — Dr. Jun Zou, a research assistant professor in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University, has received a five-year, $2.67 million federal grant to study the link between gut dysbiosis, an imbalance in the microbiota, and cardiac disease in diabetes.
The grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute will be used to explore the role of diabetes-induced alteration of gut microbiota ...
2023-06-30
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today released a plan to ensure the Department’s Federally funded research is more open and accessible to the public, researchers, and journalists as part of a broader effort by the Biden-Harris Administration to make government data more transparent. With 17 National Laboratories and scores of programs that fund university and private research, DOE directly supports thousands of research papers per year, and, when this plan goes into effect, those findings will be available ...
2023-06-30
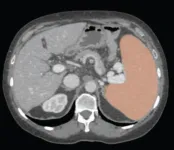
Leesburg, VA, June 30, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), using an automated deep-learning AI tool, as well as weight-based volumetric thresholds, might afford large-scale evaluation for splenomegaly on CT examinations performed for any indication.
Noting that, historically, the standard linear splenic measurements used as a surrogate for splenic volume yielded suboptimal performance in detecting volume-based splenomegaly, “the ...
2023-06-30
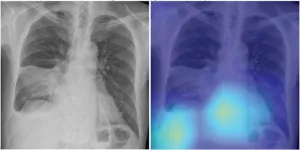
Leesburg, VA, June 30, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a deep learning-based model using initial chest radiographs predicted 30-day mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), improving upon the performance of an established risk prediction tool (i.e., CURB-65 score).
“The deep learning (DL) model may guide clinical decision-making in the management of patients with CAP by identifying high-risk patients who warrant hospitalization and intensive treatment,” concluded first author Eui Jin Hwang, MD, PhD, from the department of radiology at Seoul National ...
2023-06-30
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — The universe is expanding; we’ve had evidence of that for about a century. But just how quickly celestial objects are receding from each other is still up for debate.
It’s no small feat to measure the rate at which objects move away from each other across vast distances. Since the discovery of cosmic expansion, its rate has been measured and re-measured with increasing precision, with some of the latest values ranging from 67.4 up to 76.5 kilometers per second per megaparsec, which relates the recession velocity (in ...
2023-06-30
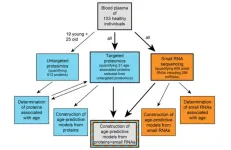
“[...] we see our work as an indication that combining different molecular data types could be a general strategy to improve future aging clocks.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 30, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Age prediction from human blood plasma using proteomic and small RNA data: a comparative analysis.”
Aging clocks, built from comprehensive molecular data, have emerged as promising tools ...
2023-06-30
How can you tell if a fruit fly is hungry? Ask a computer.
While that may sound like a bad dad joke, it’s reality at Tulane University, where researchers have developed a new A.I. tool that can tell you if a fruit fly is hungry, sleepy or singing (yes, fruit flies sing).
Dubbed MAFDA (for Novel Machine-learning-based Automatic Fly-behavioral Detection and Annotation) the system uses cameras and a newly developed software to track and identify complex interactive behaviors of individual flies within a larger group. This allows researchers to compare and contrast the behaviors of fruit flies with different genetic backgrounds.
For more than a century, ...
2023-06-30
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – June 30, 2023 – A study led by researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys has found that in young women, certain genetic mutations are associated with treatment-resistant breast cancer. These mutations are not linked to treatment-resistant breast cancer in older women. The findings, published in the journal Science Advances, could help improve precision medicine and suggest a brand-new way of classifying breast cancer.
“It’s well established that as you get older, you’re more likely to develop cancer. But we’re finding that this may not be true for all cancers depending on a person’s genetic makeup,” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Why do we articulate more when speaking to babies and puppies?