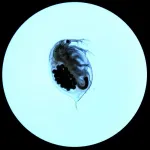
(Press-News.org) A new study on the coexistence of bacteria and fungi shows that a mutually beneficial, functioning symbiosis can be very fragile. Researchers at the Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology (Leibniz-HKI) in Jena found out that the bacterial species Mycetohabitans rhizoxinica lives happily in the hyphae of the fungus Rhizopus microsporus only when the bacteria produce a certain protein.
In a symbiosis, two organisms join together and benefit from each other; in endosymbiosis, one of the organisms takes this strategy further to live within the other. In some cases, they can't do without each other, like the fungus Rhizopus microsporus and the bacterium Mycetohabitans rhizoxinica (previously known as (Para)burkholderia rhizoxinica). The fungus can cause rice seedling blight, which leads to enormous crop losses in Asia every year. However, R. microsporus can only do this with M. rhizoxinica: the bacterium produces a plant toxin that is processed and released by the fungus. Without the bacterium, the fungus can no longer form spores and spread efficiently. In return, it supplies its endosymbiont with nutrients.
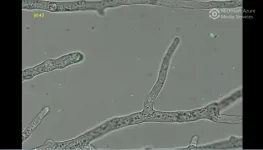
"In the wild, the two always live in symbiosis," explains Ingrid Richter, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Biomolecular Chemistry at Leibniz-HKI. In the laboratory, however, the researchers have succeeded in cultivating them separately. "As a result, we know that the bacteria are still able to infect the fungus," Richter said.
From parasitism to symbiosis?
The research team now found that a specific bacterial protein, or more precisely an effector protein, maintains the symbiosis. If the researchers deactivate the so-called TAL effector 1 (MTAL1), the bacteria multiply uncontrollably, and the fungus, as a result, closes off parts of its hyphae with new cell walls. The now-trapped bacteria subsequently die. "These TAL effectors are known from various plant-infecting bacteria," Richter said, where they allow the bacteria to invade plant cells.
In the case of R. microsporus and M. rhizoxinica, an initially parasitic relationship may have changed to a symbiotic one. Indeed, if the effector protein is not present, the bacteria can continue to infect the fungus - that is, they "melt" the cell wall and penetrate the fungal hyphae. However, they are then perceived as parasitic by the fungus. Only when the TAL effector is present is the symbiosis stable. "This shows the smooth transition between a symbiosis that benefits both partners and a possibly parasitic relationship that can be detrimental to one partner," Richter said.
Close microscopic observation
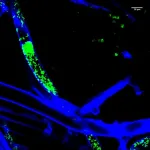
To be able to observe the infection process more closely, the researchers have developed a sophisticated system: they grow the fungus in microfluidic chips with very narrow channels. In one channel, there is only space for a single fungal hypha. Afterwards they add the bacteria and observe the infection process under a microscope for several hours. "Because of the design, the filamentous hyphae don't grow on top of each other, so we can see exactly what's happening," Richter explains. For example, she was able to show that the fungus builds up additional transverse walls in the hyphae when the TAL effector is switched off - and that there are particularly large numbers of bacteria in the areas separated in this way. "Using certain dyes, we can see that the trapped bacteria die after a few hours."
The researchers now want to further investigate the cellular processes that are triggered by the effector protein. "We suspect that the TAL effector binds in the fungal genome, because that is typical for these proteins - but we don't know where," Richter said. One reason is that the genome of R. microsporus has not yet been fully decoded.
The research results provide new insights into endosymbiotic partnerships that play a major role in evolution. For example, today's mitochondria, the energy providers in plant, animal, and fungal cells, were probably originally endosymbionts. They have their own DNA, but have long been unable to survive independently - unlike M. rhizoxinica. "In addition, through close microscopic observation, we have learned quite a bit about what tasks different types of hyphae have in the fungal mycelium, for example, the transport of nutrients," Richter explains.
The research work was supported by the EU under a Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant for Ingrid Richter, by the German Research Foundation under the Balance of the Microverse Cluster of Excellence, the ChemBioSys Collaborative Research Center, the Jena School for Microbial Communication, the Leibniz Prize for the study leader Christian Hertweck, and by the Swiss National Science Foundation.
END
A single molecule upsets symbiosis
Some bacteria live endosymbiotically in fungi - as long as they produce a certain protein
2023-07-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Potent greenhouse gas produced by industry could be readily abated with existing technologies
2023-07-05
CAMBRIDGE, MD (July 5, 2023)—Researchers have found that one method of reducing greenhouse gas emissions is available, affordable, and capable of being implemented right now. Nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas and ozone-depleting substance, could be readily abated with existing technology applied to industrial sources.
“The urgency of climate change requires that all greenhouse gas emissions be abated as quickly as is technologically and economically feasible,” said lead author Eric Davidson, a professor with the University of Maryland Center for Environmental ...
A cell surface marker for identifying tumor-initiating cells in pancreatic cancer
2023-07-05
Tumor-initiating cells, or cancer stem cells, are gaining attention in cancer therapy, as they can travel through the body and cause cancerous tumors at other sites through metastasis. These cells also may cause resistance to chemotherapy. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a type of cancer that has a poor prognosis. The problem of metastasis is particularly prominent in this type of cancer. Though the tumor-initiating cells are implicated in the disease progression of some cancers, their specific role, unique traits, and the underlying signaling pathways of their action in pancreatic adenocarcinoma remain poorly understood. ...
New study aims to assess bleeding complications in patients undergoing high-risk PCI
2023-07-05
WASHINGTON (July 5, 2023) – A new multicenter, single-arm, open-label study is the first to exclusively assess bleeding complications in patients undergoing high-risk percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) with Impella with independent adjudication via a clinical events adjudication committee and will gather meaningful real-world data based on contemporary practice. The design and rationale of the study was published online today in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (JSCAI).
Nearly one in every five patients1 will experience a bleeding complication during a large-bore endovascular procedure. Periprocedural ...
First ultraviolet data collected by ESA’s JUICE mission
2023-07-05
SAN ANTONIO — July 5, 2023 —The Southwest Research Institute-led Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) aboard ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) spacecraft has successfully completed its initial commissioning following the April 14 launch. The UVS instrument is one of three instrument projects comprising NASA’s contribution to the JUICE mission. The mission’s science goals focus on Jupiter and its system, making multiple flybys of the planet’s large, ocean-bearing satellites with a particular emphasis on investigating Ganymede ...
Investigational three-month TB regimen is safe but ineffective, NIH study finds
2023-07-05
The first clinical trial of a three-month tuberculosis (TB) treatment regimen is closing enrollment because of a high rate of unfavorable outcomes with the investigational course of treatment. AIDS Clinical Trials Group 5362, also known as the CLO-FAST trial, sought to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a three-month clofazimine- and high-dose rifapentine-containing regimen. An interim data analysis showed that participants taking the investigational regimen experienced ongoing or recurring TB at rates above thresholds set in the study protocol. Based on these findings, ...
Public support for militarily defending NATO allies
2023-07-05
Voters in North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) member states are far more willing to militarily defend another country if the country joins NATO, versus if the same country does not join NATO, according to a study. To explore the possible consequences of expanding NATO membership, Michael Tomz and colleagues surveyed 14,000 voters in 13 NATO countries. Each survey participant was presented with a hypothetical Russian attack on one of four possible targets: Bosnia, Finland, Georgia, or Sweden—the four countries (other than Ukraine) furthest along in their bids for NATO accession at the time of ...
Mount Sinai launches Center for Ophthalmic Artificial Intelligence and Human Health
2023-07-05
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has launched the Center for Ophthalmic Artificial Intelligence and Human Health, the first of its kind in New York and one of the first in the United States. The Center is dedicated to advancing artificial intelligence (AI) in the field of ophthalmology, further positioning the Mount Sinai Health System as a leader in providing patient care through pioneering innovations and technologies.
In partnership with the Windreich Department of Artificial Intelligence and Human Health at Icahn Mount Sinai, the Center aims to ...
Sunscreen leaching poses minimal threat to aquatic wildlife
2023-07-05
New research reveals that sunscreen contamination may be less harmful to wildlife than previously thought. This study by Aaron Boyd, a PhD candidate at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada, demonstrates how exposure to sunscreen is actually a low risk for small aquatic animals compared to some of the suncream’s individual chemicals.
Sunscreens contain ultraviolet filters (UVFs) which have been found to be toxic to marine life such as corals, leading to the ban of some UVFs in Hawaii and Palau. If sunscreen is applied to the skin before swimming in lakes and rivers, these UVFs and other chemicals will leach into surrounding waters.
Mr ...
Exterminating greenhouse pests with bat-inspired drones
2023-07-05
Researchers have been testing real-life Batman-style gadgets to eradicate moth pests from greenhouses, including bat-inspired flying drones that hunt down and destroy moths – but new research reveals that the noise from drones can alter moth flight behaviour.
“The idea of using drones as an alternative solution to eliminating moths all started in the bedroom of one of the co-owners of the PATS startup company,” says Dayo Jansen, a PhD student from student from Wageningen University and Research in the Netherlands. ...
New telehealth certification available to health care professionals
2023-07-05
Embargoed until 8 a.m. ET/ 7 a.m. CT on Wednesday, July 5, 2023
DALLAS, July 5, 2023 — The COVID-19 pandemic radically changed the way health care professionals serve their patients. Over the past three years, a huge proportion of care has shifted to the virtual landscape as clinicians and patients search for a safe, reliable way to receive needed care.[1]
As part of its longstanding commitment to ensuring equitable access to high-quality health care, the American Heart Association has launched its first individual ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] A single molecule upsets symbiosisSome bacteria live endosymbiotically in fungi - as long as they produce a certain protein