Professor Tongming Yin 's team from State Key Laboratory for Tree Genetics and Breeding of Nanjing Forestry University proposed the role of MSL-lncRNAs in causing sex lability of female poplars
2023-07-06
(Press-News.org) Labile expression of sex was frequently reported by empirical observation in a variety of Populus species, but the underlying genetic mechanism remains largely unknown.
This article has been published on Horticulture Research with title: The proposed role of MSL-lncRNAs in causing sex lability of female poplars.
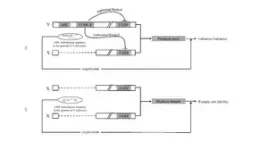
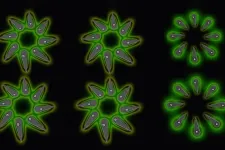
In this study, we carried out a systematic study on a maleness promoting gene, MSL, detected in Populus deltoides genome. Our results showed that both strands of MSL contained multiple cis-activating elements, which generated long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) promoting maleness. Although female P. deltoides did not have the male-specific MSL gene, a large number of partial sequences with high sequence similarity to this gene were detected in the genomes of a variety of sequenced poplars. Based on sequences alignment, the MSL sequence could be divided into three partial sequences, and heterologous expression of these partial sequences in Arabidopsis confirmed that they could promote maleness. In contrast to the tetradynamous stamens (four long and two short ones) of the wild-type flowers, we observed flowers with six long stamens, seven or eight or nine stamens, or stamens bearing two anthers, or branched stamens in the transformed lines (Fig. 3). Based on effect of MSL sequences on androecia development observed in this study, we proposed a molecular model triggering sex lability in female poplars (Fig. 4). In this model, activated transcription of MSL homologous sequences only leads to female lability, but does not cause male lability.
Our study Results in this study showed that activated transcription the MSL homologous sequences could promote maleness in heterologous expressed Arabidopsis. If these maleness promotors express in female poplars, they would lead to female lability. This study provided a unique perspective for better understanding the female sex lability in poplars.
###
References
Authors
Jinyan Mao1#, Suyun Wei1#, Yingnan Chen1, Yonghua Yang2, Tongming Yin1*
Affiliations
1 State Key Laboratory for Tree Genetics and Breeding, Co-Innovation Center for Sustainable Forestry in Southern China, Key Laboratory of Tree Genetics and Biotechnology of Educational Department of China, Key Laboratory of Tree Genetics and Breeding of Jiangsu Province, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037, China
2 Institute for Plant Molecular Biology, State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, School of Life Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
About Tongming Yin
Tongming Yin, a professor at Nanjing Forestry University, was born in February 1970. Research fields including Forest Tree Genetic Breeding, Molecular Genetics, Forest Genome and Bioinformatics. The articles have been published in international and domestic top journals such as Science, Nature, Nature Communications, New Phytologist, Plant Journal, Plant Physiology, Genome Research, Horticulture Research, etc.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-06
A new study, published in PeerJ Life and Environment, conducted by Dr. Martina Lazzaroni (University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna), Dr Joana Schar (University of Vienna) and colleagues, has shed light on the cognitive abilities of village dogs in understanding human communication. The research, which aimed to explore the impact of the domestication process on dogs' behavior and cognition, has yielded fascinating results, highlighting the importance of studying free-ranging dogs as representatives of the broader dog population.
Previous studies examining dogs' cognitive skills in understanding ...
2023-07-06
HOUSTON – (July 6, 2023) – Songtao Chen, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at Rice University, has won a prestigious National Science Foundation CAREER Award to advance the development of quantum networks by leveraging imperfections ⎯ known as point defects ⎯ in silicon material.
The grants are awarded each year to a selective cohort of about 500 early career faculty across all disciplines engaged in pathbreaking research and committed to growing their field through outreach and education.
Chen ...
2023-07-06
VANCOUVER, Wash. – The invasive Asian clam is more common in the lower Columbia River than its native habitat of southeast Asia, according to a study of the clam’s abundance in the river.
The findings don’t bode well for potential future invasions by the even more destructive quagga and zebra mussels. So far, the Columbia is one of the only major U.S. rivers to remain free of these notorious ecology-destroying, equipment-clogging bivalves.
To understand how new invaders might spread, a Washington State University-led ...
2023-07-06
Karma Nanglu says his favorite animal is whichever one he’s working on. But his latest subject may hold first place status for a while: a 500-million-year-old fossil from the wonderfully weird group of marine invertebrates, the tunicates.
“This animal is as exciting a discovery as some of the stuff I found when hanging off a cliffside of a mountain, or jumping out of a helicopter. It’s just as cool,” said Nanglu, postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology at Harvard University.
In a new study in Nature Communications, Nanglu and coauthors describe the new fossil, ...
2023-07-06
Halide perovskites are a family of materials that have attracted attention for their superior optoelectronic properties and potential applications in devices such as high-performance solar cells, light-emitting diodes, and lasers.
These materials have largely been implemented into thin-film or micron-sized device applications. Precisely integrating these materials at the nanoscale could open up even more remarkable applications, like on-chip light sources, photodetectors, and memristors. However, achieving this integration has remained challenging because this delicate material can be damaged by conventional fabrication and patterning ...
2023-07-06
EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) has launched the Pathogens Portal – an online platform that enables researchers, clinicians, and policymakers to access the most comprehensive collection of biomolecular data about pathogens. The portal features data spanning over 200,000 pathogen species and strains and is set to become a key tool for infection biology and pathogen surveillance.
The list of pathogens featured in the portal was collated using the UK’s Health and Safety Executive’s ...
2023-07-06
When animals suffer from acute or chronic stress, they produce more hormones causing shifts in the nervous system, immune response, and behavior. Some animals, if they are in the presence of a conspecific, can modulate their response to buffer stress. This is known as social buffering.
There is some research suggesting that snakes can exhibit complex social behavior. Nevertheless, social buffering in reptiles, as well as in other asocial organisms and solitary foragers, hasn’t been studied extensively. Now, researchers in the US have examined if rattlesnakes inhabiting Southern California use social buffering to alleviate acute stress.
“We showed that when ...
2023-07-06
Every year in Belgium, 1,600 people wait for a transplant. Of these, in 2021, only 939 received an organ. Thus more than 40% of patients often have to wait more than a year before hoping to receive a transplant. When a transplant is possible, it is essential to ensure its success so as not to “waste” an organ. One of the keys to successful transplants is an anti-rejection drug, tacrolimus, which patients must take for life. But it is extremely difficult to dose this drug correctly, which can lead to significant risks of transplant failure in the event of underdosing and significant side effects in the event of overdosing (diabetes, hirsutism, hair loss, neuropathy or nephrotoxic ...
2023-07-06
UCL press release
Under embargo until Thursday, 6 July 2023, 00:01 London time
Giant stone artefacts found on rare Ice Age site in Kent
Researchers at the UCL Institute of Archaeology have discovered some of the largest early prehistoric stone tools in Britain.
The excavations, which took place in Kent and were commissioned in advance of development of the Maritime Academy School in Frindsbury, revealed prehistoric artefacts in deep Ice Age sediments preserved on a hillside above the Medway Valley.
The researchers, from UCL Archaeology South-East, discovered 800 stone artefacts thought to be over 300,000 years old, buried in sediments which filled a sinkhole and ...
2023-07-06
UNVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A new type of ferroelectric polymer that is exceptionally good at converting electrical energy into mechanical strain holds promise as a high-performance motion controller or “actuator” with great potential for applications in medical devices, advanced robotics, and precision positioning systems, according to a team of international researchers led by Penn State.
Mechanical strain, how a material changes shape when force is applied, is an important property for an actuator, which is any material that will change or deform when an external force such as electrical energy is applied. Traditionally, these actuator ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Professor Tongming Yin 's team from State Key Laboratory for Tree Genetics and Breeding of Nanjing Forestry University proposed the role of MSL-lncRNAs in causing sex lability of female poplars