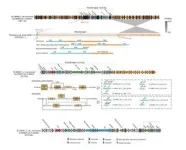
(Press-News.org) Viruses in man-made environments cause public health concerns, but they are generally less studied than bacteria. A recent study led by environmental scientists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) provided the first evidence of frequent interactions between viruses and bacteria in man-made environments. It found that viruses can potentially help host bacteria adapt and survive in nutrient-depleted man-made environments through a unique gene insertion.
By understanding these virus–bacteria interactions and identifying the possible spread of antibiotic resistance genes, the research team hopes its latest findings can help derive effective control strategies to minimize human exposure to harmful microorganisms.
Virus–host interactions are central to the ecology and evolution of microbial communities in diverse ecosystems. However, the immune mechanisms of infection and the virus–host interactions that occur in man-made environments, including buildings, public space, transportation and infrastructure, have been poorly understood.
“As more and more of the global population are living in urban areas, the importance of hygiene in man-made environments is growing, particularly indoor ones, as occupants inside are constantly exposed to diverse microorganisms, which have public health implications. However, most previous studies of man-made environments overlooked viruses,” said Professor Patrick Lee Kwan-Hon in the School of Energy and Environment (SEE) at CityU, who led the study.
“Therefore, in our study, we comprehensively investigated viruses in man-made environments, and we identified many novel molecular mechanisms in which viruses and bacteria interact with each other. These findings are important not only for basic microbial science, but also the management of man-made environments to protect residents’ health,” added Professor Lee.
In the study, researchers collected 738 samples from different types of man-made environments, including public facilities and residences, in Hong Kong. They collected the samples mainly from the surfaces of handrails, bollards, floors, poles, doorknobs and skin of residents. Then they used the metagenomic sequencing technique for analysis.
The analysis resulted in many interesting discoveries. First, the data showed that viruses are integral members of microbial communities in man-made environments. Among them, bacteriophages, a kind of virus that infects and replicates within bacteria, are all over various surfaces in man-made environments. The team also identified many viruses that are distinct from those in other ecosystems.
Second, the team found evidence of viruses inserting genes that control a specific step in a metabolic pathway and even the entire metabolic pathway into bacteria hosts. This suggests that viruses could help bacteria adapt and coevolve to survive in nutrient-depleted man-made environments.
The study also found diverse and novel immune systems against viruses in bacteria, and small proteins in viruses that can evade bacteria immune systems. These results suggest that viruses and bacteria hosts frequently interact with each other in man-made environments and that they each have mechanisms to defend against each other.
They also detected antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in viruses on human skin and frequently touched indoor surfaces. These ARG-carrying viruses might infect bacterial hosts, and ARGs might be horizontally transferred between bacterial species. Therefore, the role played by viruses in man-made environments in the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria is crucial and warrants further investigation.
“Our study shows that the diversity, composition, metabolic functions and lifestyle of viruses vary, depending on the conditions of each man-made environment,” said Professor Lee. “Therefore, it is important to develop customized control strategies to minimize human exposure to harmful microorganisms and to better protect residents’ health. Our findings can contribute to this goal by enhancing the fundamental understanding of complex virus–bacteria interactions in man-made environments.”
The findings were published in the scientific journal Nature Communications under the title “Highly host-linked viromes in the built environment possess habitat-dependent diversity and functions for potential virus-host coevolution”.
The first author is Miss Du Shicong, PhD student in SEE, and the corresponding author is Professor Lee. Other team members include Professor Alvin Lai Chi-Keung, Professor Chan Chak-Keung and Dr Tong Xinzhao, from SEE, and Professor Christopher E. Mason, from Weill Cornell Medicine.
The research is supported by the Research Grants Council’s Research Impact Fund and the General Research Fund in Hong Kong.
https://www.cityu.edu.hk/research/stories/2023/07/06/unveiling-secret-viruses-bacteria-interactions-man-made-environments
END
Unveiling the secret of viruses-bacteria interactions in man-made environments
2023-07-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ASBMB weighs in on changes to NIH fellowship review
2023-07-06
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent feedback in June to the National Institutes of Health about its proposed changes to the Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award fellowship application and review process.
The proposed changes indicate that the NIH adopted nearly all of the ASBMB’s earlier recommendations (here and here) to reduce institutional and investigator bias and refocus the evaluation on an applicant’s potential and the impact of the ...
Wastewater monitoring could act as pandemic early warning system
2023-07-06
Wastewater monitoring could act as an early warning system to help countries better prepare for future pandemics, according to a new study.
An international collaboration involving Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, The Rockefeller Foundation, Mathematica and the United Kingdom’s Health Security Agency has shed light on how different countries monitor wastewater during infectious diseases outbreaks and where improvements could be made.
For the study, samples from treatment plants, rivers, wetlands and open drains were reported ...
T cells require healthy “power plants”
2023-07-06
All cells have their own power plants, called mitochondria. There are often more than 100 mitochondria per cell and each possesses their own genome, which in turn contains genes responsible for energy production. If errors creep into these genes, this can cause problems in the cell and result in diseases. Scientists from the Berlin Institute of Health at Charité (BIH) and the Max Delbrück Center have now discovered that the T cells of the immune system are especially sensitive to genetic disturbances within their mitochondrial power plants. They have published their findings ...
Sweat it out: Novel wearable biosensor for monitoring sweat electrolytes for use in healthcare and sports
2023-07-06
The remarkable level of miniaturization possible in modern electronics has paved the way for realizing healthcare devices previously confined to the realm of science fiction. Wearable sensors are a prominent example of this. As the name suggests, these devices are worn on the body, usually directly on the skin. They can monitor important bodily parameters, including heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle activity.
Some wearable sensors can also detect chemicals in bodily fluids. For instance, sweat biosensors ...
New teaching method can even out children's reading skills
2023-07-06
How well do children know letters and their corresponding sounds? In Norway, the gender difference on these tasks when children start school is significant. The girls have a clear head start.
“We see these differences in all categories – for upper case and lower case letters, for the names of the letters and for their corresponding sounds,” says Hermundur Sigmundsson, a professor at Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Department of Psychology.
Girls’ letter-sound knowledge is clearly better than that of boys,’ and girls remain far better readers than boys at age 15. Since reading is key for so many ...
Scientists synthesize isotopic atropisomers based on carbon isotope discrimination
2023-07-06
In chemistry, a molecule or ion is said to be chiral if it cannot be superposed on to its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, or conformational changes. A chiral molecule or ion exists in two forms, called enantiomers, that are mirror images of each other; they are often distinguished as either ‘right-handed’ or ‘left-handed’ by their absolute configuration. Enantiomers exhibit similar physical and chemical properties, except when interacting with polarized light and reacting with other chiral compounds, ...
New study shows robust pandemic preparedness strongly linked to lower COVID-19 mortality rates
2023-07-06
New Study Shows Robust Pandemic Preparedness
Strongly Linked to Lower COVID-19 Mortality Rates
Preparedness matters: Accounting for age and national capabilities to diagnose COVID-19 deaths reveals that pre-pandemic investments in capacity saved lives—though U.S. remains an outlier.
The vast majority of countries that entered the COVID-19 pandemic with strong capacity to prevent, detect, and respond to disease threats achieved lower pandemic mortality rates than less prepared nations, ...
Species lump for the Western Flycatcher; species status for the goshawk of North America; and species splits in several Caribbean birds among 2023 Check-list changes
2023-07-06
The 64th Supplement to the American Ornithological Society’s (AOS) Check-list of North American Birds, published today in Ornithology, includes numerous updates to the classification of North American bird species.
A few highlights from this year’s supplement, detailed below, include a species lump for the Western Flycatcher, species status for the goshawk of North America, and species splits in several Caribbean birds leading to five additional species.
The Check-list, published since 1886, is updated annually by the AOS’s North American Classification Committee (NACC), the official authority on the names and classification of the ...
Study explores incarceration, employment and re-offense during COVID-19 pandemic
2023-07-06
There are more than 2 million people incarcerated in the United States. In 2019, more than 608,000 individuals were released from prison. It is estimated that up to 55 percent of people released from prison will be re-incarcerated within five years. The cause of high recidivism or re-offense rates in the U.S. is multi-dimensional. Moreover, the relationship between employment and crime is complex.
To combat an unstable work history and lack of interpersonal skills, some communities have implemented transitional employment programs, ...
How hot is too ‘too hot’ for humans?
2023-07-06
Ongoing research by Prof. Lewis Halsey and his team at the University of Roehampton, UK has identified that an upper critical temperature (UCT) exists for humans and is likely to be between 40°C and 50°C. Further research is now underway to explain this rise in metabolic energy costs at high temperatures.
Prof. Halsey and his team have found that resting metabolic rate, a measure of how much energy the human body consumes to keep ticking over, can be higher when people are exposed to hot and humid conditions. ...