(Press-News.org) A team from Ames National Laboratory conducted an in-depth investigation of the magnetism of TbMn6Sn6, a Kagome layered topological magnet. They were surprised to find that the magnetic spin reorientation in TbMn6Sn6 occurs by generating increasing numbers of magnetically isotropic ions as the temperature increases.
Rob McQueeney, a scientist at Ames Lab and project lead, explained that TbMn6Sn6has two different magnetic ions in the material, terbium and manganese. The direction of the manganese moments controls the topological state, “But it’s the terbium moment that determines the direction that the manganese points,” he said. “The idea is, you have these two magnetic species and it is the combination of their interactions which controls the direction of the moment.”
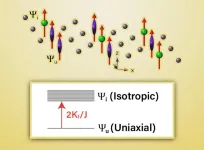
In this layered material, there is a magnetic phase transition that occurs as the temperature increases. During this phase transition, the magnetic moments switch from pointing perpendicular to the Kagome layer, or uniaxial, to pointing within the layer, or planar. This transition is called a spin reorientation.
McQueeney explained that in Kagome metals, the spin direction controls the properties of topological or Dirac electrons. Dirac electrons occur where the magnetic bands touch at one point. However, magnetic order causes gapping at the points where the bands are touching. This gapping stabilizes the topological Chern insulator state. “So you can go from a Dirac semimetal to a Chern insulator just by turning the direction of the moment,” he said.
As part of their TbMn6Sn6 investigation, the team performed inelastic neutron scattering experiments at the Spallation Neutron Source to understand how the magnetic interactions in the material drive the spin reorientation transition. McQueeney said that the terbium wants to be uniaxial at low temperatures, while the manganese is planar, so they are at odds.
According to McQueeney, the behavior at very low or very high temperatures is as expected. At low temperatures, the terbium is uniaxial (with electronic orbitals shaped like an ellipsoid). At high temperatures, the terbium is magnetically isotropic (with a spherical orbital shape), which allows the planar Mn to determine the overall moment direction. The team assumed that each terbium orbital would gradually deform from ellipsoidal to spherical. Instead, they found both types of terbium exist at intermediate temperatures, however the population of spherical terbium increases as the temperature increases.
“So, what we did was we determined how the magnetic excitations evolve from this uniaxial state into this easy plane state as a function of temperature. And the long-standing assumption of how it happens is correct,” said McQueeney. “But the nuance is that you can’t treat every terbium as being exactly the same on some timescale. Every terbium site can exist in two quantum states, uniaxial or isotropic, and if I look at a site, it’s either in one state or the other at some instant time. The probability that it's uniaxial or isotropic depends on temperature.” We call this an orbital binary quantum alloy.
This research is further discussed in “Orbital character of the spin-reorientation transition in TbMn6Sn6,” written by S.X.M. Riberolles, Tyler J. Slade, R.L. Dally, P.M. Sarte, Bing Li, Tianxiong Han, H. Lane, C. Stock, H. Bhandari, N.J. Ghimire, D.L. Abernathy, P.C. Canfield, J.W. Lynn, B.G. Ueland, and R.J. McQueeney, and published in nature communications.
Ames National Laboratory is a U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science National Laboratory operated by Iowa State University. Ames Laboratory creates innovative materials, technologies, and energy solutions. We use our expertise, unique capabilities, and interdisciplinary collaborations to solve global problems.
Ames Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit https://energy.gov/science.
END
Researchers make a surprising discovery about the magnetic interactions in a Kagome layered topological magnet
2023-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Deciphering progesterone’s mechanisms of action in breast cancer
2023-07-10
“The mechanisms underlying the observed effects of progesterone on breast cancer outcomes are unclear.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 10, 2023 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 1, 2023, entitled, “Deciphering the mechanisms of action of progesterone in breast cancer.”
A practice-changing, randomized, controlled clinical study established that preoperative hydroxyprogesterone administration improves disease-free and overall survival in patients with node-positive breast cancer. In this new perspective, researchers Gaurav Chakravorty, Suhail Ahmad, Mukul S. Godbole, Sudeep Gupta, Rajendra A. Badwe, ...
More data needed on lifestyle interventions for postpartum blood pressure control
2023-07-10
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy such as preeclampsia and gestational hypertension occur in up to 10% of pregnancies and are associated with a three-fold increased risk of chronic hypertension and up to two-fold increased risk of cardiovascular disease when compared with healthy pregnancies. While the year after pregnancy is a critical time to address hypertension risk with lifestyle changes (healthy diet and exercise), the effects of lifestyle interventions on postpartum blood pressures are not well documented.
A new Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine study has found that there are few relevant studies on the ...
New biodegradable plastics are compostable in your backyard
2023-07-10
We use plastics in almost every aspect of our lives. These materials are cheap to make and incredibly stable. The problem comes when we're done using something plastic — it can persist in the environment for years. Over time, plastic will break down into smaller fragments, called microplastics, that can pose significant environmental and health concerns.
The best-case solution would be to use bio-based plastics that biodegrade instead, but many of those bioplastics are not designed to degrade in backyard composting conditions. They must be processed in commercial composting facilities, which are not accessible in all regions of the ...
Canned, frozen corn industry struggling across US growing regions
2023-07-10
URBANA, Ill. — For those whose primary experience with corn is the butter-drenched cob variety, it might come as a surprise that other forms of sweet corn are in trouble. A new University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign analysis shows sweet corn production for frozen and canned products has been steadily shrinking in the U.S. over the past 27 years, particularly in rainfed portions of the Midwest.
“The processing sweet corn industry [corn grown for canned and frozen products] was thriving in the U.S. throughout the 20th century. This type of production, ...
Ethics & Human Research, July-August 2023
2023-07-10
Antiracist Structural Intervention at the Emory University Institutional Review Board
Francois Rollin, Vanessa Van Doren, Jessica Alvarez, Rebecca Rousselle, Jada Bussey-Jones
Although racial and ethnic categories are social constructs without inherent biologic or genetic meaning, race and ethnicity impact health outcomes through racism. The use of racial categories in biomedical research often misattributes the cause of health inequities to genetic and inherent biological differences rather than to racism. Improving research ...
Unhealthy beverage consumption highest among economically-vulnerable households that rely on multiple food assistance programs
2023-07-10
Philadelphia, July 10, 2023 – A long-standing and contentiously debated question is the extent to which US federal food assistance programs contribute to or deter healthy beverage intake. Findings of a new study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, show that while beverage intake patterns rarely differed between mothers and young children who participated only in the Supplementation Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), only the Supplemental ...
Tumor monocyte content predicts immunochemotherapy outcomes for esophageal cancer
2023-07-10
JULY 10, 2023, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has discovered that the presence of relatively high numbers of immune cells known as monocytes in tumors is linked to better outcomes in esophageal cancer patients treated with a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy, or immunochemotherapy. Esophageal cancer is the sixth leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, and the incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma has been climbing at a relatively swift clip over the past 40 years. Survival times for inoperable or metastatic forms of the cancer range from 6 to 12 months.
Led by Ludwig Oxford Director Xin Lu and ...
Game-playing automaton acts like an ‘irrational’ human
2023-07-10
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Humans make lots of irrational decisions in predictable ways, but what if we’re all just doing our best within the limits of our abilities?
Researchers were able to simulate human behaviors using a probabilistic finite automaton, a well-known model of limited computational power. They programmed the automatons to compete against each other in a wildlife poaching game, as either a rhino poacher or a ranger trying to stop the poaching.
When the automatons could remember everything, they settled into an optimal game strategy. But when researchers limited their memories, they took some decision-making shortcuts – the same ...
Nearly two thirds of youth would stop vaping without added sweet flavors, menthol, synthetic cooling agents
2023-07-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Major progress could be made in fighting the youth vaping epidemic with a complete restriction on sweet flavorings and cooling agents in both cartridge and disposable e-cigarette devices, according to a new study from the Center for Tobacco Research at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center. The current U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) flavor ban only applies to cartridge electronic cigarette devices.
A new study published in the Journal of Studies on Addiction and Drugs by researchers ...
Girls Deliver: building an integrated, feminist ecosystem to support adolescent girls at the Women Deliver 2023 Conference
2023-07-10
July 10, 2023 — The Population Council’s GIRL Center, and co-hosts AFIDEP, AMPLIFY Girls, Baobab Research Programme Consortium, Children’s Investment Fund Foundation, Coalition for Adolescent Girls, Exemplars in Global Health, FP2030, Girl Effect, Girls First Fund, Conrad N. Hilton Foundation, the National Democratic Institute (NDI), Plan International, PMNCH, Purposeful, Together for Girls, UNICEF, Women Deliver, and The World Bank Africa Gender Innovation Lab, are proud to host the “Girls Deliver: Pre-Conference on Adolescent Girls,” on July 16. This one-day global convening ...