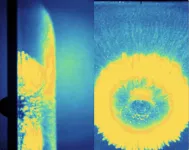
(Press-News.org) An experimental study explores the visible impact flash created by high velocity impacts. Impacts by debris and meteoroids pose a significant threat to satellites, space probes, and hypersonic craft. Such high-velocity impacts create a brief, intense burst of light, known as an impact flash, which contains information about both the target and the impactor. Gary Simpson, K.T. Ramesh, and colleagues explored the impact flash by shooting stainless steel spheres into an aluminum alloy plate, at a speed of three kilometers per second — about 6,700 miles per hour, or more than nine times the speed of sound. The resulting impact flashes were photographed using ultra-high-speed cameras and high-speed spectroscopy, which measures the color and brightness of the light. Immediately after impact, a luminous disc is seen expanding around the impacting sphere. Only a few millionths of a second later, the disc takes on an almost floral shape, as fragments ejected from the impact crater form an ejecta cone, with petal-like projections at the outer edge. The authors conclude that these impact flashes are created by the fragmentation of an ultra-fast jet of material ejected from the colliding bodies. Minuscule condensed fragments from the jet interact with the atmosphere to create an extremely bright radiating cloud of vapor, which expands at a speed of over ten kilometers per second (over 22,000 miles per hour). The material making up the target and the size of the jetted particles can be inferred from the flash, according to the authors.
END
Decoding the impact flash
2023-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SwRI delivers plasma spectrometer for Moon mission
2023-07-11
SAN ANTONIO — July 11, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute has delivered a plasma spectrometer for integration into a lunar lander as part of NASA’s Lunar Vertex investigation, scheduled to commence next year. The target site is the Reiner Gamma region on the Moon’s nearside, a mysterious area known to have a local magnetic field. The SwRI-developed Magnetic Anomaly Plasma Spectrometer (MAPS) will study the interaction of the solar wind with surface materials on the Moon, aiming to understand the origin of the sinuous patterns of ...
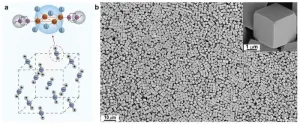
Efficient X-ray luminescence imaging with ultrastable and eco-friendly copper(I)-iodide cluster microcubes
2023-07-11
Scintillators are optical materials that emit low-energy ultraviolet and visible photons in response to ionizing radiation such as X-rays and gamma rays. This property makes scintillating materials useful for applications like non-destructive testing, X-ray astronomy, security inspection, and medical imaging.
In a recently published paper in Light Science & Applications, Professor Xiaowang Liu and Academician Wei Huang, along with their team from the Institute of Flexible Electronics at Northwestern Polytechnical University, ...
Ohio teen and Florida veteran named first national heart health program winners
2023-07-11
DALLAS, July 11, 2023 — Two dedicated volunteers have reached a prestigious milestone with the American Heart Association, the world’s leading nonprofit organization devoted to a world of healthier lives for all, for their personal passion and commitment to advance women’s heart health.
For the third year, changemakers across the country were nominated to join the American Heart Association’s Woman of Impact and Teen of Impact® campaigns. Aligning with the Go Red for Women® movement, the Association’s signature ...
Xerces Blue butterfly genome sequenced, an icon of anthropogenic extinction
2023-07-11
The Xerces Blue butterfly (Glaucopsyche xerces) was native to the coastal dunes of San Francisco, in the United States. As the city grew, much of the butterfly’s habitat was destroyed and its population was relegated to Golden Gate National Park. Its wings were a deep iridescent blue, with characteristic white spots on the ventral side. The last surviving specimens of the species were found in 1941, by entomologist W. Harry Lange. It is considered the first insect species to have become extinct in historical times. Its disappearance has made it a global icon of anthropogenic extinction, to ...
Bacteria in kitchen may not be as harmful as you think
2023-07-11
Washington, D.C. – Bacteria found in 74 kitchens spread among 5 European countries were mostly harmless according to new research published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“We have previously found considerable variations in kitchen standards, food preparation practices, and cleaning regimes between France, Norway, Portugal, Romania, and Hungary,” said Birgitte Moen, Ph.D., Scientist—Department of Food Safety and Quality, Nofima—Norwegian Institute of Food, Fisheries, and Aquaculture Research, Ås, Norway.
In ...
Allen Institute for Neural Dynamics launches first-ever crowdsourced neuroscience experiment
2023-07-11
The aim is to maximize impact by turning to the combined talent and insight of the broader international neuroscience community.
SEATTLE — July 11, 2023 — Today, scientists from the Allen Institute for Neural Dynamics, a division of the Allen Institute, launched the world’s first completely open- and crowd-sourced neuroscience experiment—inviting researchers from around the world to publicly design a shared experiment that will run on the Allen Brain Observatory, as part of the Institute’s OpenScope program. Experiments will probe ...
Marine fossils are a reliable benchmark for degrading and collapsing ecosystems
2023-07-11
Biologists attempting to conserve and restore denuded environments are limited by their scant knowledge of what those environments looked like before the arrival of humans. This is especially true of coastal ecosystems, many of which had already been drastically altered by pollution and overharvesting hundreds of years before scientists began monitoring them.
According to a new study published in the journal PeerJ, a faithful analogue of modern marine ecosystems lies just beneath the surface. Building on more than 20 years of conservation paleobiology, the results suggest that fossils of various marine groups — including worms, mollusks, crabs and sea urchins — are ...
Mount Sinai Queens opens new Cardiac Catheterization Lab to expedite care for heart attack patients
2023-07-11
Click here to watch a video on the new Cath Lab
Mount Sinai Queens today announced the opening of a new cardiac catheterization lab that will provide rapid and comprehensive care to hundreds of heart patients every year for life-threatening emergencies and scheduled cardiac procedures. The first cardiac catheterization lab in Astoria, it will transform treatment for patients in the growing communities of western Queens by vastly improving access to cardiac care in the borough and beyond.
Atul Kukar, DO, has been named the Director of the Mount Sinai Queens Catheterization Lab and leads a team of 14 specialists including interventional cardiologists, nurses, and technicians.
“Our ...
The ground is deforming, and buildings aren’t ready
2023-07-11
There is a “silent hazard” lurking underneath our major global cities, and our buildings were not designed to handle it.
A new Northwestern University study has, for the first time, linked underground climate change to the shifting ground beneath urban areas. As the ground heats up, it also deforms. This phenomenon causes building foundations and the surrounding ground to move excessively (due to expansions and contractions) and even crack, which ultimately affects structures’ long-term operational performance and durability. Researchers also report that past building damage ...
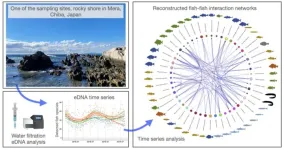
Deciphering fish species interactions for climate change insights
2023-07-11
A team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has developed a technique to study how different fish species interact with each other in a coastal region, a breakthrough that helps explain the complex relationships among marine species and how global warming impacts fish populations.
By analyzing minute traces of fish DNA from samples of seawater, the team combined the use of environmental DNA – known as eDNA – and advanced statistical analysis to not only detect ...