(Press-News.org) One of the most powerful psychedelics known, N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) has been described as causing imaginative visuals akin to the dream state. It is typically consumed on its own or in ayahuasca, a ceremonial brew that has been used for spiritual and visionary purposes by indigenous cultures for centuries. Some have expressed that DMT helped address psychological ailments such as depression and addiction, promoting emotional well-being. However, the way that DMT impacts the brain, body and health is largely unknown.
A gift of $1.5 million from Eugene Jhong will help launch a new research program within the UC San Diego Psychedelic and Health Research Initiative to learn more about the biological and psychological effects of DMT in humans.
The peak psychedelic effects of inhaled DMT dissipate within minutes. As part of the research supported by Jhong, the UC San Diego research team will implement continuous intravenous DMT infusion protocols to capture what is known as the “extended state” of visions long associated with DMT.
Led by principal investigators Fadel Zeidan, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Anesthesiology at UC San Diego School of Medicine, and Jon Dean, PhD, postdoctoral scholar in the UC San Diego Department of Anesthesiology and director of the Division of DMT Research at the UC San Diego Psychedelic Health and Research Initiative, the study will seek to map the phenomenological, neurological and physiological responses to DMT during the longer windows of time created with infusion protocols.
Interestingly, DMT is present naturally (endogenously) within human bodily fluids. In Dean’s previous research, he discovered that endogenous DMT also exists in the rat brain at levels comparable to serotonin, a neurotransmitter vital to brain function.
“Our goals are to employ multi-modal approaches to study extended state consciousness elucidated by DMT to further appreciate the nature of reality as well as the role of endogenous DMT in the human body. Reliable methods for measuring DMT directly in the human brain and bodily fluids do not exist, so the intriguing possibilities that endogenous DMT may play a role in consciousness, dreaming and protecting the brain from trauma are still scientific speculation,” said Dean.
“We are beyond grateful to Eugene Jhong for his visionary support of this novel research effort,” said Zeidan. “We will learn more about how the unique effects of DMT on consciousness interacts with human physiology to understand how these profound psychedelic effects evoked by DMT impact our well-being. Our long-term objective is to gain a better understanding of how DMT and other psychedelics could be used in a therapeutic manner to address pain, trauma and various medical conditions related to the brain.”
UC San Diego is currently the only university in the U.S. that has a dedicated division to conduct extended-state DMT research. The study is part of the UC San Diego Psychedelics and Health Research Initiative, which will soon be renamed the Center for Psychedelic Research, a newly approved academic center at UC San Diego School of Medicine.
Eugene Jhong stated, “I am pleased to support this innovative effort to explore extended DMT and am confident it will shed new and important insight into the question of our true nature.”
# # #
END
$1.5 million donation supports research on effects of psychedelic DMT on the brain
UC San Diego Psychedelics and Health Research Initiative received the gift from philanthropist Eugene Jhong to further our understanding of the unique states of consciousness induced by DMT and how it could benefit human health
2023-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Carbon taxes that focus on luxury consumption are fairer than those that tax all emissions equally
2023-07-11
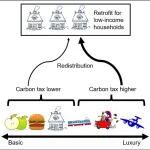
Not all carbon emissions are made for the same reason—they range from more essential purposes like heating a home to nonessential “luxury” activities like leisure travel. However, proposals for the implementations of carbon taxes tend to apply to all emissions at an equal rate. This can give rise to and exacerbate inequalities. A new analysis published on July 11 in the journal One Earth suggests taxing luxury carbon emissions at a higher rate instead; if all 88 countries analyzed in this study adopted the luxury-focused policy, this would achieve 75% of the emissions reduction needed to reach the Paris Agreement’s goal of limiting climate change ...
Thermal cloak passively keeps electric vehicles cool in the summer and warm in the winter
2023-07-11
When an electric vehicle is parked outside, its temperature can swing wildly from day to night and season to season, which can lead to deterioration of the battery. To dampen these fluctuations and extend the battery’s lifespan, researchers have designed an all-season thermal cloak that can cool an electric vehicle by 8°C on a hot day and warm it by 6.8°C at night. The cloak, made predominantly of silica and aluminum, can do so passively without outside energy input and operates without any modification between hot or cold weather. This prototype is described July 11 in the newly launched Device, an application-oriented sister journal ...
Breaking into tears with microrheology to design custom eye drops
2023-07-11
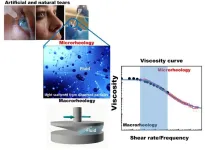
WASHINGTON, July 11, 2023 – Compared to artificial tears, or eye drops, human tears are significantly more complex liquids, with a wide range of components including lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, water, and salt. It is this complex mixture that gives tears the perfect thickness and ability to moisturize the eye, a design that is hard to replicate with fewer ingredients.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, Vega et al. researched human tears at the micron level to reveal new ways of customizing artificial tears to address individual symptoms of dry eye disease. The detailed insights they gained about the composition and behavior ...
Unborn babies use ‘greedy’ gene from dads to ‘remote-control’ mums into feeding them extra food
2023-07-11
Unborn babies use ‘greedy’ gene from dads to ‘remote-control’ mums into feeding them extra food
Fetuses use a copy of a gene inherited from their dad to force their mum to release as much nutrients as possible during pregnancy, Cambridge scientists have discovered.
The unborn baby ‘remote controls’ its mother’s metabolism so the two are in a nutritional tug of war. The mother’s body wants the baby to survive but needs to keep enough glucose and fats circulating in her system for her own health, to be able to deliver ...
The science behind skipping stones
2023-07-11
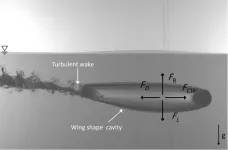
WASHINGTON, July 11, 2023 – Inspired by the need to safeguard marine animals and promote sustainable solutions within marine environments, an interdisciplinary team of researchers from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi Arabia and Sofia University in Bulgaria are delving into the hydrodynamics of buoyant objects at the air-water interface.
By studying these dynamics, their goal is to expand the understanding of fluid hydrodynamics and complex surface interactions – and advance fields such as the design and performance of marine engineering systems, buoy systems, and ...
Association of racial discrimination with obesity in children and adolescents
2023-07-11
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that personally mediated racial discrimination may be a risk factor for developing obesity in children and adolescents, above and beyond socioeconomic status. The results highlight the need for a multifaceted approach to address racial discrimination and its impact on the health of children and adolescents.
Authors: Adolfo G. Cuevas, Ph.D., of the New York University School of Global Public Health in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.22839)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Association between historical neighborhood redlining and cardiovascular outcomes among veterans
2023-07-11
About The Study: In this cohort study of U.S. veterans, the findings suggest that those with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who reside in historically redlined neighborhoods continue to have a higher prevalence of traditional cardiovascular risk factors and higher cardiovascular risk. Even close to a century after this practice was discontinued, redlining appears to still be adversely associated with adverse cardiovascular events.
Authors: Sadeer Al-Kindi, M.D., of University Hospitals in Cleveland, and Salil V. Deo, ...
Genome sequencing nearly twice as effective as a targeted gene-sequencing test at diagnosing genetic disorders in newborns and infants
2023-07-11
July 11, 2023 (BOSTON) – A new national study, led by researchers at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, has found whole genome sequencing (WGS) to be nearly twice as effective as a targeted gene sequencing test at identifying abnormalities responsible for genetic disorders in newborns and infants. The study, “A Comparative Analysis of Rapid Whole Genomic Sequencing and a Targeted Neonatal Gene Panel in Infants with a Suspected Genetic Disorder: The Genomic Medicine for Ill Neonates and Infants ...
Racial discrimination increases risk for childhood obesity
2023-07-11
Children who experience racial discrimination are more likely to later have a higher body mass index (BMI) and larger waistline, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open. The findings illustrate that racial discrimination may be a risk factor for young people developing obesity—above and beyond other socioeconomic factors such as family income.
“Exposure to racial discrimination must be acknowledged as both a social determinant of obesity and a significant contributor to obesity disparities among children and adolescents,” said Adolfo Cuevas, assistant professor of social and behavioral sciences at the NYU School of Global Public Health and the study’s ...
First large US clinical trial of cytisinicline finds the smoking cessation medication effective and well tolerated
2023-07-11
BOSTON – The first large-scale U.S. clinical trial of cytisinicline, led by a Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigator, found the smoking cessation medication to be effective and well tolerated in adults who wished to break their nicotine dependence. In the Phase 3 study published in JAMA, researchers reported that cytisinicline could offer adults who smoke a potential new treatment option.
“Cigarette smoking remains the leading preventable cause of death worldwide, yet no new smoking cessation medication has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for nearly two decades,” says Nancy Rigotti, MD, director of MGH’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] $1.5 million donation supports research on effects of psychedelic DMT on the brainUC San Diego Psychedelics and Health Research Initiative received the gift from philanthropist Eugene Jhong to further our understanding of the unique states of consciousness induced by DMT and how it could benefit human health