(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND—U.S. military veterans who lived in what were once known as “redlined” areas had a higher risk for heart attacks and other cardiovascular issues, according to a new study by researchers at Case Western Reserve University, University Hospitals and the Cleveland VA Medical Center.
In the 1930s, the federal government-sponsored Homeowners’ Loan Corp. (HOLC) established maps of U.S. neighborhoods that identified levels of mortgage risk. This practice led to disinvestments and segregation in “redlined” neighborhoods.
Judicial rulings--and, later, federal legislation--prohibited such government practices, but research has shown their impact has had lasting effects on educational and economic opportunities—as well as health outcomes. Nevertheless, few studies have targeted the association between redlining and cardiovascular disease.
The study was conducted primarily by Sadeer Al-Kindi, formerly an assistant professor at the Case Western Reserve School of Medicine and co-director of the Center for Integrated and Novel Approaches in Vascular Metabolic Disease at University Hospitals; Salil Deo, an associate professor of surgery at the School of Medicine and cardiac surgeon at the VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System; and Yakov Elgudin, director of lung transplantation at UH Cleveland Medical Center and an associate professor of surgery at the School of Medicine.
Their findings were published July 11 in JAMA Network Open.
“While we know these communities were historically disadvantaged,” Deo said, “limited information is available whether this decades-old practice still influences cardiovascular health today.”
The researchers used information from 80,000 U.S. veterans—some living, others deceased—with pre-existing cardiovascular disease who lived in census tracts color-coded by the HOLC and were enrolled in ongoing care at Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Centers nationwide.
They observed that, over a five-year study period, those who lived in redlined neighborhoods were 14% more likely to suffer from an adverse cardiac event like a stroke or heart attack. And this effect remained even after adjusting for known cardiovascular risk factors and other social determinants of health.
The researchers said their findings “underline the important fact that, despite improvements in public health, access to care—and citizen health in the United States overall—significant gaps exist between communities, and progress has not been uniform across all neighborhoods.”
They added that, “while thought-provoking and hypothesis-generating,” the data doesn’t explain what caused such higher rates of cardiovascular issues in redlined areas.
“Historical residential policies, such as redlining, may have a long-lasting effect on community health,” Al-Kindi said. “This study builds on emerging literature linking redlining with a host of present-day health issues.”
“Our nationwide study demonstrates that a century-old practice like redlining still affects our nation’s health today,” Deo said. “Future studies should aim to better define the reasons for the observed relationships between intergenerational inequities and cardiovascular health. These can then be targeted to improve the wellbeing for all individuals.”
###
Case Western Reserve University is one of the country's leading private research institutions. Located in Cleveland, we offer a unique combination of forward-thinking educational opportunities in an inspiring cultural setting. Our leading-edge faculty engage in teaching and research in a collaborative, hands-on environment. Our nationally recognized programs include arts and sciences, dental medicine, engineering, law, management, medicine, nursing and social work. About 6,000 undergraduate and 6,300 graduate students comprise our student body. Visit case.edu to see how Case Western Reserve thinks beyond the possible.
END
New study finds U.S. military veterans living in discriminatory ‘redlined’ areas suffered higher rates of cardiovascular disease
2023-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
$1.5 million donation supports research on effects of psychedelic DMT on the brain
2023-07-11
One of the most powerful psychedelics known, N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) has been described as causing imaginative visuals akin to the dream state. It is typically consumed on its own or in ayahuasca, a ceremonial brew that has been used for spiritual and visionary purposes by indigenous cultures for centuries. Some have expressed that DMT helped address psychological ailments such as depression and addiction, promoting emotional well-being. However, the way that DMT impacts the brain, body and health is largely unknown.
A ...
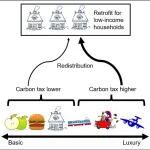
Carbon taxes that focus on luxury consumption are fairer than those that tax all emissions equally
2023-07-11
Not all carbon emissions are made for the same reason—they range from more essential purposes like heating a home to nonessential “luxury” activities like leisure travel. However, proposals for the implementations of carbon taxes tend to apply to all emissions at an equal rate. This can give rise to and exacerbate inequalities. A new analysis published on July 11 in the journal One Earth suggests taxing luxury carbon emissions at a higher rate instead; if all 88 countries analyzed in this study adopted the luxury-focused policy, this would achieve 75% of the emissions reduction needed to reach the Paris Agreement’s goal of limiting climate change ...
Thermal cloak passively keeps electric vehicles cool in the summer and warm in the winter
2023-07-11
When an electric vehicle is parked outside, its temperature can swing wildly from day to night and season to season, which can lead to deterioration of the battery. To dampen these fluctuations and extend the battery’s lifespan, researchers have designed an all-season thermal cloak that can cool an electric vehicle by 8°C on a hot day and warm it by 6.8°C at night. The cloak, made predominantly of silica and aluminum, can do so passively without outside energy input and operates without any modification between hot or cold weather. This prototype is described July 11 in the newly launched Device, an application-oriented sister journal ...
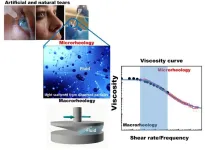
Breaking into tears with microrheology to design custom eye drops
2023-07-11
WASHINGTON, July 11, 2023 – Compared to artificial tears, or eye drops, human tears are significantly more complex liquids, with a wide range of components including lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, water, and salt. It is this complex mixture that gives tears the perfect thickness and ability to moisturize the eye, a design that is hard to replicate with fewer ingredients.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, Vega et al. researched human tears at the micron level to reveal new ways of customizing artificial tears to address individual symptoms of dry eye disease. The detailed insights they gained about the composition and behavior ...
Unborn babies use ‘greedy’ gene from dads to ‘remote-control’ mums into feeding them extra food
2023-07-11
Unborn babies use ‘greedy’ gene from dads to ‘remote-control’ mums into feeding them extra food
Fetuses use a copy of a gene inherited from their dad to force their mum to release as much nutrients as possible during pregnancy, Cambridge scientists have discovered.
The unborn baby ‘remote controls’ its mother’s metabolism so the two are in a nutritional tug of war. The mother’s body wants the baby to survive but needs to keep enough glucose and fats circulating in her system for her own health, to be able to deliver ...
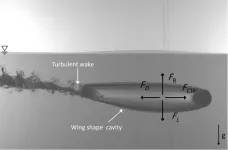
The science behind skipping stones
2023-07-11
WASHINGTON, July 11, 2023 – Inspired by the need to safeguard marine animals and promote sustainable solutions within marine environments, an interdisciplinary team of researchers from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi Arabia and Sofia University in Bulgaria are delving into the hydrodynamics of buoyant objects at the air-water interface.
By studying these dynamics, their goal is to expand the understanding of fluid hydrodynamics and complex surface interactions – and advance fields such as the design and performance of marine engineering systems, buoy systems, and ...
Association of racial discrimination with obesity in children and adolescents
2023-07-11
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that personally mediated racial discrimination may be a risk factor for developing obesity in children and adolescents, above and beyond socioeconomic status. The results highlight the need for a multifaceted approach to address racial discrimination and its impact on the health of children and adolescents.
Authors: Adolfo G. Cuevas, Ph.D., of the New York University School of Global Public Health in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.22839)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Association between historical neighborhood redlining and cardiovascular outcomes among veterans
2023-07-11
About The Study: In this cohort study of U.S. veterans, the findings suggest that those with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who reside in historically redlined neighborhoods continue to have a higher prevalence of traditional cardiovascular risk factors and higher cardiovascular risk. Even close to a century after this practice was discontinued, redlining appears to still be adversely associated with adverse cardiovascular events.
Authors: Sadeer Al-Kindi, M.D., of University Hospitals in Cleveland, and Salil V. Deo, ...
Genome sequencing nearly twice as effective as a targeted gene-sequencing test at diagnosing genetic disorders in newborns and infants
2023-07-11
July 11, 2023 (BOSTON) – A new national study, led by researchers at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, has found whole genome sequencing (WGS) to be nearly twice as effective as a targeted gene sequencing test at identifying abnormalities responsible for genetic disorders in newborns and infants. The study, “A Comparative Analysis of Rapid Whole Genomic Sequencing and a Targeted Neonatal Gene Panel in Infants with a Suspected Genetic Disorder: The Genomic Medicine for Ill Neonates and Infants ...
Racial discrimination increases risk for childhood obesity
2023-07-11
Children who experience racial discrimination are more likely to later have a higher body mass index (BMI) and larger waistline, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open. The findings illustrate that racial discrimination may be a risk factor for young people developing obesity—above and beyond other socioeconomic factors such as family income.
“Exposure to racial discrimination must be acknowledged as both a social determinant of obesity and a significant contributor to obesity disparities among children and adolescents,” said Adolfo Cuevas, assistant professor of social and behavioral sciences at the NYU School of Global Public Health and the study’s ...