(Press-News.org) An estimated 50 million individuals in the United States struggle with the challenges of cocaine or alcohol use disorders, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Beyond the well-documented health risks, addiction to these substances detrimentally affects our cognitive flexibility, which is the ability to adapt and switch between different tasks or strategies. Although previous research has hinted at this connection, the underlying reasons for this cognitive impairment remain elusive.
Cognitive flexibility is a crucial element in various domains of our life, including academic achievement, employment success and transitioning into adulthood. As we age, this flexibility plays an important role in mitigating cognitive decline. A deficiency in cognitive flexibility, however, is linked to academic deficits and a lower quality of life.
A groundbreaking study led by Dr. Jun Wang, associate professor in the Department of Neuroscience and Experimental Therapeutics at the Texas A&M University School of Medicine, provides new insight into the damaging impact that chronic cocaine or alcohol use has on cognitive flexibility. The research, published in the journal of Nature Communication, emphasizes the role of the local inhibitory brain circuit in mediating the negative effects of substance use on cognitive flexibility.
Substance use influences a specific group of neurons called striatal direct-pathway medium spiny neurons (dMSNs), with projections to a part of the brain known as the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr). Conversely, cognitive flexibility is facilitated by striatal cholinergic interneurons (CINs), which receive potent inhibitory signals from the striatum.
“Our hypothesis was that increased dMSN activity from substance use inhibits CINs, leading to a reduction in cognitive flexibility,” Wang said. “Our research confirms that substance use induces long-lasting changes in the inhibitory communication between dMSNs and CINs, consequently dampening cognitive flexibility. Furthermore, the dMSN-to-SNr brain circuit reinforces drug and alcohol use, while the associated collateral dMSN-to-CIN pathway hinders cognitive flexibility. Thus, our study provides new insights into the brain circuitry involved in the impairment of cognitive flexibility due to substance use.”
Wang and his team are optimistic about the potential therapeutic applications of their findings and anticipate that they could inform new treatment strategies for substance-induced cognitive decline. The research receives support from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) and an X-grant from the Presidential Excellence Fund at Texas A&M University.
END
Substance use linked to long-lasting brain changes, cognitive decline
New Texas A&M research underlines the relationship between substance use and significant modifications to an inhibitory brain circuit, resulting in decreased cognitive flexibility.
2023-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CU Anschutz study shows CBD use in pregnancy could impact the fetal brain
2023-07-12
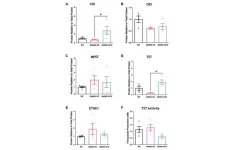
AURORA, Colo. (July 11, 2023) – Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have found that cannabidiol (CBD), often used to treat anxiety and nausea, can potentially harm a developing fetus.
The paper was published in Molecular Psychiatry today.
People consume cannabis or a non-psychoactive component cannabidiol (CBD) to help with nausea and anxiety during pregnancy because they think it is safe and healthy. But CBD crosses the placenta and accumulates in the fetal brain.
Until now, no one knew how fetal exposure to CBD affected brain development, said Emily ...
Paths for reducing harmful air pollution in South Asia identified
2023-07-11
Fine particulate matter comes from wood burning, power generation, motor vehicles and other combustion sources that emit tiny particles into the air. At only 2.5 micrometers or smaller, these particles are small enough to be inhaled and cause lasting damage to the heart and lungs. Known as PM2.5, exposure to these particles is a leading mortality risk factor in India and the surrounding region of South Asia.
A new study by researchers in Randall Martin’s lab in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis evaluated the contribution of various emission sectors and fuels to PM2.5 mass for 29 states in India ...
Zoonotic researcher receives ORAU Ralph E. Powe Junior Faculty Enhancement Award
2023-07-11
Daniel Becker, Ph.D., an assistant professor of Biology in the Dodge Family College of Arts and Sciences, has received an Oak Ridge Associated Universities Ralph E. Powe Junior Faculty Enhancement Award for his continued research on bat migration in western Oklahoma.
“We’re studying migratory Mexican free-tailed bats and the pathogens they might carry that are possible threats to human or wildlife health,” Becker said. “This award allows us to purchase the microchips we implant in the bats and ...
Cancer disparities: Sylvester researchers, collaborators seek answers to prostate, breast cancer among people of African ancestry
2023-07-11
MIAMI, FLORIDA (July 11, 2023) – “Please, please do it (cancer screening), if not for yourself, then for the next generation. We need to see the day when we end cancer.”
Those are the impassioned words of Charinus Johnson-Davis, who was diagnosed with breast cancer a dozen years ago but is now cancer-free after a double-mastectomy and 28 rounds of chemotherapy plus radiation. She is on a mission to help address cancer disparities affecting Black women and men, and is one of the first to enroll in the African Cancer Genome Registry, a new study at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer ...
AGS supports CMS decision to require real-world data for monoclonal antibodies
2023-07-11
New York (July 11, 2023) — The American Geriatrics Society (AGS) supports the recently announced decision from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to require the collection of real-world information via a registry to study monoclonal antibodies directed against amyloid for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. This decision applies to monoclonal antibodies that receive traditional approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Currently, lecanemab (trade name ...
GSA Connects 2023: A premier international scientific meeting
2023-07-11
11 July 2023
The Geological Society of America
Release no. 23-25
Contact: Justin Samuel
+1-303-357-1026
jsamuel@geosociety.org
For immediate release
GSA Connects 2023: A Premier International Scientific Meeting
The Geological Society of America visits Pittsburgh
Boulder, Colo., USA: Media registration is open now for The
Geological Society of America’s Connects 2023
meeting, to be held 15–18 October 2023 at the David L Lawrence Convention
Center (1000 Fort Duquesne Blvd) in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA. The
organizing committee is pleased to be planning a dynamic meeting centered
around ...
Generative AI ‘fools’ scientists with artificial data, bringing automated data analysis closer
2023-07-11
The same AI technology used to mimic human art can now synthesize artificial scientific data, advancing efforts toward fully automated data analysis.
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed an AI that generates artificial data from microscopy experiments commonly used to characterize atomic-level material structures. Drawing from the technology underlying art generators, the AI allows the researchers to incorporate background noise and experimental imperfections into the generated ...
Satisfaction with online dating app depends on what you’re looking for
2023-07-11
With an estimated 75 million active users each month, Tinder is the most popular dating app in the world. But a new study by Stanford Medicine researchers and collaborators has found, surprisingly - though perhaps not to users of the app - that many users are not swiping for dates.
In a survey of more than a thousand Tinder users, half said they were not interested in meeting offline, and nearly two-thirds were already married or "in a relationship."
In fact, the psychological motivations behind people's use of the app varied widely and had a strong influence on their satisfaction with the app and the dates it led to, according to the study published June 23 ...
University of Illinois study finds turning food waste into bioenergy can become a profitable industry
2023-07-11
URBANA, Ill. — Food waste is a major problem around the world. In the United States, an estimated 30 to 40% of edible food is lost or wasted, costing billions of dollars each year. One potential solution is to divert food waste from landfills to renewable energy production, but this isn’t done on a large scale anywhere. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign investigates the feasibility of implementing energy production from food waste in the state of Illinois.
“We have a large amount of organic waste in the U.S., which eventually enters landfills and emits greenhouse gasses. However, this material ...
Hepatic hydrogen sulfide levels are reduced in mouse model of progeria
2023-07-11
“To date, no studies have directly measured [hydrogen sulfide] production in Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 11, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Hepatic hydrogen sulfide levels are reduced in mouse model of Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome.”
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) is a rare ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Substance use linked to long-lasting brain changes, cognitive declineNew Texas A&M research underlines the relationship between substance use and significant modifications to an inhibitory brain circuit, resulting in decreased cognitive flexibility.