(Press-News.org) From our cosmic backyard in the solar system to distant galaxies near the dawn of time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has delivered on its promise of revealing the universe like never before in its first year of science operations. To celebrate the completion of a successful first year, NASA has released Webb’s image of a small star-forming region in the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex.
“In just one year, the James Webb Space Telescope has transformed humanity’s view of the cosmos, peering into dust clouds and seeing light from faraway corners of the universe for the very first time. Every new image is a new discovery, empowering scientists around the globe to ask and answer questions they once could never dream of,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. “Webb is an investment in American innovation but also a scientific feat made possible with NASA’s international partners that share a can-do spirit to push the boundaries of what is known to be possible. Thousands of engineers, scientists, and leaders poured their life’s passion into this mission, and their efforts will continue to improve our understanding of the origins of the universe – and our place in it.”
The new Webb image released today features the nearest star-forming region to us. Its proximity at 390 light-years allows for a highly detailed close-up, with no foreground stars in the intervening space.
“On its first anniversary, the James Webb Space Telescope has already delivered upon its promise to unfold the universe, gifting humanity with a breathtaking treasure trove of images and science that will last for decades,” said Nicola Fox, associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. “An engineering marvel built by the world’s leading scientists and engineers, Webb has given us a more intricate understanding of galaxies, stars, and the atmospheres of planets outside of our solar system than ever before, laying the groundwork for NASA to lead the world in a new era of scientific discovery and the search for habitable worlds.”
Webb’s image shows a region containing approximately 50 young stars, all of them similar in mass to the Sun, or smaller. The darkest areas are the densest, where thick dust cocoons still-forming protostars. Huge bipolar jets of molecular hydrogen, represented in red, dominate the image, appearing horizontally across the upper third and vertically on the right. These occur when a star first bursts through its natal envelope of cosmic dust, shooting out a pair of opposing jets into space like a newborn first stretching her arms out into the world. In contrast, the star S1 has carved out a glowing cave of dust in the lower half of the image. It is the only star in the image that is significantly more massive than the Sun.
“Webb’s image of Rho Ophiuchi allows us to witness a very brief period in the stellar lifecycle with new clarity. Our own Sun experienced a phase like this, long ago, and now we have the technology to see the beginning of another’s star’s story,” said Klaus Pontoppidan, who served as Webb project scientist at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland, since before the telescope’s launch and through the first year of operations.
Some stars in the image display tell-tale shadows indicating protoplanetary disks – potential future planetary systems in the making.
A Full Year, Across the Full Sky
From its very first deep field image, unveiled by President Joe Biden, Vice President Kamala Harris, and Nelson live at the White House, Webb has delivered on its promise to show us more of the universe than ever before. However, Webb revealed much more than distant galaxies in the early universe.
“The breadth of science Webb is capable of exploring really becomes clear now, when we have a full year’s worth of data from targets across the sky,” said Eric Smith, associate director for research in the Astrophysics Division at NASA Headquarters and Webb program scientist. “Webb’s first year of science has not only taught us new things about our universe, but it has revealed the capabilities of the telescope to be greater than our expectations, meaning future discoveries will be even more amazing.” The global astronomy community has spent the past year excitedly poring over Webb’s initial public data and getting a feel for how to work with it.
Beyond the stunning infrared images, what really has scientists excited are Webb’s crisp spectra – the detailed information that can be gleaned from light by the telescope’s spectroscopic instruments. Webb’s spectra have confirmed the distances of some of the farthest galaxies ever observed, and have discovered the earliest, most distant supermassive black holes. They have identified the compositions of planet atmospheres (or lack thereof) with more detail than ever before, and have narrowed down what kinds of atmospheres may exist on rocky exoplanets for the first time. They also have revealed the chemical makeup of stellar nurseries and protoplanetary disks, detecting water, organic carbon-containing molecules, and more. Already, Webb observations have resulted in hundreds of scientific papers answering longstanding questions and raising new ones to address with Webb.
The breadth of Webb science is also apparent in its observations of the region of space we are most familiar with – our own solar system. Faint rings of gas giants appear out of the darkness, dotted by moons, while in the background Webb shows distant galaxies. By comparing detections of water and other molecules in our solar system with those found in the disks of other, much younger planetary systems, Webb is helping to build up clues about our own origins – how Earth became the ideal place for life as we know it.
"With a year of science under our belts, we know exactly how powerful this telescope is, and have delivered a year of spectacular data and discoveries,” said Webb Senior Project Scientist Jane Rigby of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. “We've selected an ambitious set of observations for year two — that builds on everything we've learned so far. Webb's science mission is just getting started — there's so much more to come."
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world's premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
END
Webb celebrates first year of science with close-up on birth of sun-like stars
2023-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lupus Research Alliance announces recipients of 2023 Diversity in Lupus Research Awards
2023-07-12
NEW YORK, NY, July 12. The Lupus Research Alliance is pleased to announce the 2023 recipients of the Career Development and Postdoctoral Awards to Promote Diversity in Lupus Research. The Diversity in Lupus Research Awards aim to foster the development of outstanding, underrepresented minority scientists and establish a diverse community of researchers and clinicians in the field of lupus.
Lupus is a debilitating autoimmune disorder, and the prevalence, severity of symptoms, and mortality are higher among people of color. Yet a recent report by the National Science Foundation showed that while “Blacks or African Americans, Hispanics or Latinos, ...
A glimpse into the hexasome: 40 years on
2023-07-12
In 1983, scientists discovered hexasomes – a unique molecular structure that helps cells package their DNA. Now, a study conducted by the Eustermann group at EMBL Heidelberg has shed light on how DNA packaging into hexasomes can affect the function of enzymes involved in gene regulation.
DNA: a lot to unpack
DNA is a very long, thin thread containing our genetic instructions. Being much longer than the tiny space inside our cells, it needs a clever packaging system. That’s where nucleosomes come into play – tiny spool-like structures that help compact our genetic information. Multiple nucleosomes are then linked ...
Award for dementia researcher from New York City
2023-07-12
This year’s “Hartwig Piepenbrock-DZNE Prize”, endowed with 60,000 euros, goes to the British neuroscientist Alison Goate, DPhil. The award recognizes her outstanding contributions to research into Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Professor Goate researches and teaches at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, an international leader in biomedical education, research, and patient care located in New York City. The prize is presented jointly by the Piepenbrock Group and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE). The award ...
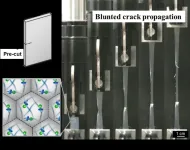
Towards crack-resistant nanoparticle-based latex films
2023-07-12
Synthetic polymer materials, such as plastics and rubbers, have become ubiquitous in our daily lives. It is, therefore, essential to ensure that they are safe, durable, and sustainable. This is especially true for synthetic latex films, which are widely used in packaging, biomedicine, and electronics.
But what exactly are synthetic latex films? Simply put, they are a type of nanoparticle-based films that are produced by drying out a mixture of polymer nanoparticles and water. As the solvent evaporates, the nanoparticles become more packed until finally the interactions between polymer chains at the boundaries of nanoparticles create a coherent film. Unfortunately, the latex films ...
Better and faster design of organic light-emitting materials with machine learning and quantum computing
2023-07-12
Over the past decade, organic luminescent materials have been recognized by academia and industry alike as promising components for light, flexible and versatile optoelectronic devices such as OLED displays. However, it is a challenge to find suitably efficient materials.
To address this challenge, a joint research team has developed a novel approach combining a machine learning model with quantum-classical computational molecular design to accelerate the discovery of efficient OLED emitters. This research was published May 17 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The ...
Understanding the intersection of Alzheimer’s Disease caregiving and the LGBT experience
2023-07-12
INDIANAPOLIS – A new study of caregivers of LGBT older adults living with Alzheimer’s disease provides rare insight into the intersection of caregiving and the LGBT experience.
Researchers from Regenstrief Institute and the medical schools of Indiana University and University of Colorado report that many common caregiver experiences -- such as feelings of social isolation and of being overwhelmed -- are similar for caregivers, whether an individual with Alzheimer’s disease is LGBT or not. However, because LGBT older adults often do not have adult children who can serve as caregivers or may be estranged ...
A step toward treating chemotherapy-resistant prostate cancer
2023-07-12
Prostate cancer is a leading cause of death among American men, and it’s resistant to one of the most powerful chemotherapy medications — cisplatin. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed the first therapy of its kind that disrupts prostate cancer cells’ metabolism and releases cisplatin into the weakened cells, causing them to die. In mouse models, an orally administered version shrunk tumors substantially.
Cisplatin attacks testicular, breast, bladder, lung and ovarian cancer cells, damages their DNA and effectively destroys tumors. However, it’s not effective against prostate cancer ...
A new tactic to take on leprosy
2023-07-12
Leprosy has existed since at least Biblical times, yet scientists still don’t know exactly how Mycobacterium leprae causes the disease’s symptoms. Though antibiotics can treat the illness, researchers are concerned about the increase in drug-resistant strains. Now, a team reporting in ACS Central Science has begun to understand the unique role certain immune receptors play in leprosy infections in mice, which could lead to new types of treatments for this disease and others in humans.
Thousands of people are currently affected by leprosy — also known as Hansen’s disease — according to the World Health Organization. The disease can cause skin ...
Ohio train derailment, clean-up resulted in high levels of some gases, study shows
2023-07-12
A freight train carrying industrial chemicals derailed near East Palestine, Ohio, in February 2023, and to avoid explosions, authorities conducted a controlled release and burned the cars’ contents. Residents were worried about their health and the environment, so researchers have been assessing the local air quality with stationary and mobile sampling methods. Now, in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, they report that some gases, including acrolein, reached levels that could be hazardous.
After the derailment, disaster response teams ...
EMBARGOED: In preclinical study, Sylvester researchers target treatment-resistant prostate cancer with oral chemotherapy that works 2 ways
2023-07-12
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL JULY 12, 2023, AT 8AM ET) – Researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have developed a first-of-its-kind, orally administered drug to disrupt prostate cancer cells’ metabolism and deliver the chemotherapy agent cisplatin directly into treatment-resistant prostate cancer cells.
They validated their targets in human prostate cancer biopsies, tested the new approach in human cancer cells and a mouse model ...