Those who are smarter live longer
Mouse lemurs that perform better in cognitive tests live longer
2023-07-12
(Press-News.org)
Cognitive abilities not only vary among different species but also among individuals within the same species. It is expected that smarter individuals live longer, as they are likely to make better decisions, regarding habitat and food selection, predator avoidance, and infant care. To investigate the factors influencing life expectancy of wild gray mouse lemurs, researchers from the German Primate Center conducted a long-term study in Madagascar. They administered four different cognitive tests and two personality tests to 198 animals, while also measuring their weight and tracking their survival over several years. The cognition tests assessed problem-solving (reaching food by manipulating a slider), spatial memory (remembering the location of hidden food), inhibitory control (taking a detour to access food), and causal understanding (retrieving food by pulling a string). The first personality test evaluated exploratory behavior, while the second measured curiosity through the animals’ reactions to unfamiliar objects.
Either being particularly smart or particularly explorative – both strategies can lead to longer life
In the study, individuals that performed better in the cognitive tests exhibited less exploratory behavior compared to poorer performing conspecifics. Conversely, more explorative individuals had higher weights, likely due to their ability to find food more easily. The study also found that animals with better cognitive performance, higher weight, and stronger exploratory behavior tended to have longer lifespans. “These results suggest that being either smart or exhibiting good physical condition and exploratory behavior are likely to be different strategies that can lead to a longer lifespan,” said Claudia Fichtel, first author of the study and a scientist at the German Primate Center. “In future studies, we aim to investigate how cognitive abilities translate into behavioral strategies to find food or mating partner.”
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-12
Within the scope of a vast research program undertaken in coordination with the Egyptian Ministry of Antiquities and the University of Liège, an international team—including scientists from the CNRS, Sorbonne University, and Université Grenoble Alpes—has revealed the artistic license exercised in two ancient Egyptian funerary paintings (dating to ~1,400 and ~1,200 BCE, respectively), as evident in newly discovered details invisible to the naked eye. Their findings are published in PLOS ONE (12 July).
The language of ancient ...
2023-07-12
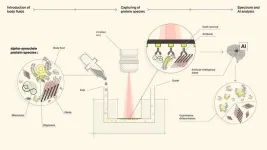
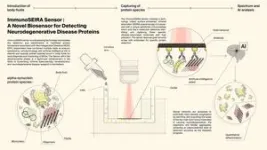
By combining multiple advanced technologies into a single system, EPFL researchers have made a significant step forward in diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) such as Parkinson's disease (PD) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). This novel device is known as the ImmunoSEIRA sensor, a biosensing technology that enables the detection and identification of misfolded protein biomarkers associated with NDDs. The research, published today in Science Advances, also harnesses the power of artificial intelligence (AI) by employing neural networks to quantify disease ...
2023-07-12
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic disease that causes organ damage and death, affected more than 250 million people worldwide in 2021, according to the World Health Organization.
One of the world’s most burdensome neglected tropical diseases, schistosomiasis occurs when worms are transmitted from freshwater snails to humans. The snails thrive in water with plants and algae that proliferate in areas of agricultural runoff containing fertilizer. People become infected during routine activities in infested water.
Researchers from the University of Notre Dame, in a study recently published in Nature, found that removing invasive vegetation at water access points in and around several ...
2023-07-12
Since the International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV) approved the use of ultrasound to promote the extraction of grape compounds back in 2019, its application for obtaining superior red wines has been studied extensively.
Now researchers are turning their attention to rosé – an expanding market which has seen strong growth over the past 15 years. A team from the University of Castilla-La Mancha and the University of Murcia in Spain used high-power ultrasound technology to treat Monastrell crushed grapes – a process known as sonication ...
2023-07-12
On July 12, 2023, a new research paper was published in Aging, titled, “Chemically induced reprogramming to reverse cellular aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 12, 2023 – In a groundbreaking study, researchers have unlocked a new frontier in the fight against aging and age-related diseases. The study, conducted by a team of scientists at Harvard Medical School, has published the first chemical approach to reprogram cells to a younger state. Previously, this was only achievable using a powerful gene ...
2023-07-12
The Naval Innovation Center (NIC) at the Naval Postgraduate School (NPS) in Monterey, Calif., is part of the Secretary of the Navy’s initiative to leverage the power of American innovation for national security. Integral to the function of the NIC is the Naval Innovation Exchange (NIX), a new program that organizes and empowers multidisciplinary teams of NPS students and faculty focused on developing prototype research solutions.
While in its early stages, the NIC at NPS will leverage and empower ...
2023-07-12
At a glance:
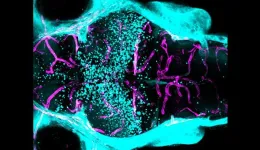
Working with mice and zebrafish, researchers identify a gene, expressed in neurons, that produces a signal needed for development and maintenance of the blood-brain barrier.
When mutated, the gene makes certain regions of the blood-brain barrier more permeable.
The findings could help scientists control the blood-brain barrier — important for delivering drugs into the central nervous system or countering damage from neurodegenerative disease
What makes the vital layer of protective cells around the brain and spinal cord — ...
2023-07-12
Psychedelic-based therapies are poised to change the treatments that psychiatrists can offer patients.
“I often talk about psychedelic treatments as catalysts for change, for both the individual and the field of psychiatry,” said Medical University of South Carolina psychiatrist Jennifer Jones, M.D., who conducts research on these treatments.
The highly anticipated approval of MDMA, or “ecstasy,” to treat post-traumatic stress disorder would be the first for a psychedelic drug, ushering in changes for patients, mental health providers and society. The Food and Drug Administration is expected to issue a decision on MDMA-assisted ...
2023-07-12
Cancer therapies that target specific genetic abnormalities in tumors have revolutionized treatment possibilities over the past two decades. While quality of life and survival are improved with targeted therapies, relapse is common due to the evolution of new tumor cells that are resistant to the targeted therapy. A new study by investigators from the Mass General Cancer Center, a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals how lung tumors may develop drug resistance over time, pointing to a protein, called APOBEC3A, that could be a promising target. Results, published in Nature, may help researchers develop new ...
2023-07-12
NEW YORK, NY-- A new study suggests that eye drops developed by Columbia University researchers could be a more effective–and comfortable–therapy for a common eye disease currently treated with injections into the eye.
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO), an eye disease that affects up to 2% of people over age 40, occurs when a vein in the eye’s retina becomes blocked, leading to swelling in the eye, inflammation, damage to the retina, and vision loss.
Standard therapy involves injecting into the eye a vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor (anti-VEGF) that reduces swelling. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Those who are smarter live longer
Mouse lemurs that perform better in cognitive tests live longer